本文實例講述了Python快速排序算法。分享給大家供大家參考,具體如下:
快速排序的時間復雜度是O(NlogN)
算法描述:
① 先從序列中取出一個數作為基準數
② 分區過程, 將比這個數大的數全部放到它的右邊, 小于或等于它的數全部放到它的左邊
③ 再對左右區間重復第二步, 直到各區間只有一個數
假設對 6, 1, 2, 7, 9, 3, 4, 5, 10, 8 進行排序, 首先在這個序列中隨便找一個基準數(用來參照), 比如選擇 6 為基準數, 接下來把所有比基準數大的數放在6的右邊, 比6小的數放在左邊
原理分析:
① 選擇最左邊的數為基準數key
② 設立兩個游標 low 和 high , 分別指向數組的最低位和最高位
③ 然后high先動, 如果high位上的數比key大, 則向前走, 如果high-1位上的數比key大, 繼續向前走, 直到該位上的數<=key
④ 此時比較low位, 如果<=key, low向后走, 變為low+1, 依次類推, 直到該位上的數比key大
⑤ 交換high和low位上的數
⑥ 重復以上步驟, 直到low=high , 交換 key 和 high 位上的值
⑦ 最后進行遞歸操作
示例代碼:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
|
#!/usr/bin/env python# coding:utf-8# 設置最低位和最高位def quickSort(nums, low, high): # 設置一個比較基準key key = nums[low] while low<high: # 如果最高位的數 大于等于 key則向前走 while low<high and nums[high] >= key: high -= 1 # 如果最低位的數 小于等于 key則向后走 while low<high and nums[low] <= key: low += 1 # 交換值 nums[low], nums[high] = nums[high], nums[low] #最后low=high, 此時交換key和high位上的值, 使小于key的值在key左邊, 大的在key右邊 nums[nums.index(key)], nums[low] = nums[low], nums[nums.index(key)] # 返回最低位的位置 return low# 進行重復操作def interval(nums, low, high): if low<high: # 進行排序并得到最低位位置以循環操作 key_index = quickSort(nums, low, high) interval(nums, low, key_index) interval(nums, key_index+1, high)nums = [64,3,9,2,4,7,0,12,45,]interval(nums, 0, len(nums)-1)print "服務器之家測試結果:"print nums"""[0, 2, 3, 4, 7, 9, 12, 45, 64]""" |
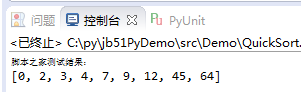
運行結果:
希望本文所述對大家Python程序設計有所幫助。
原文鏈接:http://www.cnblogs.com/qlshine/p/6032111.html