flask框架是python開發的一個基于werkzeug和jinja 2的web開發微框架,它的優勢就是極其簡潔, 但又非常靈活,而且容易學習和應用。因此flask框架是python新手快速開始web開發最好的選擇,此外, 使用flask框架的另一個好處在于你可以非常輕松地將基于python的機器學習算法或數據分析算法集成到 web應用中。

1、可以用flask框架做什么
從博客應用到克隆一個facebook或者twitter,理論上你可以用flask做任何事情。有很多庫 可以直接使用,例如flask-sockets,flask-google-maps等,而且flask框架支持mysql、postgresql、 mongodb等諸多數據庫。
我能想到的一些可以用flask框架實現的web應用類型:博客應用、聊天應用、儀表盤應用、rest api、管理頁面、郵件服務等。
如果希望深入學習flask web開發,推薦這個教程:深入淺出flask 安裝flask
使用pip安裝flask:
|
1
|
$ pip install flask |
2、hello,world
創建一個文件app.py,然后只需要幾個簡單的步驟,就可以寫出flask版本的hello world
引入flask類
|
1
|
from flask import flask |
創建flask對象,我們將使用該對象進行應用的配置和運行:
|
1
|
app = flask(__name__) |
name 是python中的特殊變量,如果文件作為主程序執行,那么 __name__ 變量的值就是 __main__ ,如果是被其他模塊引入,那么 __name__ 的值就是模塊名稱。
編寫主程序
在主程序中,執行 run() 來啟動應用:
|
1
2
|
if __name__ =="__main__": app.run(debug=true, port=8080) |
改名啟動一個本地服務器,默認情況下其地址是 localhost:5000 ,在上面的代碼中,我們使用關鍵字 參數 port 將監聽端口修改為8080。
路由
使用app變量的 route() 裝飾器來告訴flask框架url如何觸發我們的視圖函數:
|
1
2
3
|
@app.route('/')def hello_world(): return 'hello, world!' |
上面的標識,對路徑'/‘的請求,將轉為對 hello_world() 函數的調用。很直白,對吧?
運行
現在,讓我們完整地看一下app.py的整個代碼:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
from flask import flaskapp = flask(__name__)@app.route('/')def hello_world(): return 'hello, world!'if __name__ =="__main__": app.run(debug=true,port=8080) |
然后運行起來:
|
1
|
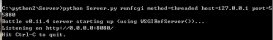
$ python app.py |
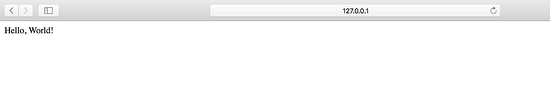
你應該會看到如下輸入:
現在就可以打開瀏覽器訪問 http://127.0.0.1:8080/ 了:
* serving flask app "app" (lazy loading)
* environment: production
* debug mode: on
* running on http://127.0.0.1:8080/ (press ctrl+c to quit)
* restarting with stat
* debugger is active!
* debugger pin: 770-937-705
3、使用html模板
首先我們看看如何原始的html代碼插入flask應用:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
from flask import flaskapp = flask(__name__)@app.route('/greet')def greet(): user = {'username': 'john', 'age': "20"} return '''<html> <head> <title>templating</title> </head> <body> <h1>hello, ''' + user['username'] + '''!, you're ''' + user['age'] + ''' years old.</h1> </body></html>'''if __name__ == '__main__':app.run(debug = true,port=8080) |
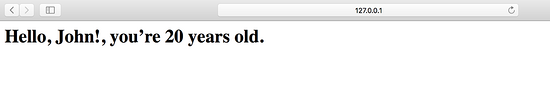
在上面的代碼中,我們使用拼接的html字符串來展示user字典的數據。現在訪問 http://127.0.0.1:8080/greet :
拼接html字符串非常容易出錯,因此flask使用jinja 2模板引擎來分離數據邏輯和展示層。
我們將模板文件按如下路徑放置:
|
1
2
3
4
|
apps folder/app.pytemplates |-/index.html |
使用模板時,視圖函數應當返回 render_template() 的調用結果。例如下面的代碼片段 渲染模板 index.html ,并將渲染結果作為視圖函數的返回值:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
from flask import flask, render_templateapp = flask(__name__)@app.route('/hello')def hello(): return render_template('index.html', name="alex")if __name__ == '__main__': app.run(debug = true) |
在上面的代碼中,模板文件 index.html 依賴于變量 name ,其內容如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
<html><body> {% if name %} <h2>hello {{ name }}.</h2> {% else %} <h2>hello.</h2> {% endif %} </body></html> |
模板文件的語法擴充了html,因此可以使用變量和邏輯。
在瀏覽器中訪問 http://127.0.0.1:8080/hello/alex :

4、使用表單
每個web應用都需要使用表單來采集用戶數據。現在讓我們使用flask框架創建一個 簡單的表單來收集用戶的基本信息,例如名稱、年齡、郵件、興趣愛好等,我們將 這個模板文件命名為 bio_form.html
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
<!doctype html><html><head> <title></title></head><body> <h1>bio data form</h1> <form action="showbio"> <label>username</label> <input type="name" name="username"><br> <label>email</label> <input type="email" name="email"><br> <label>hobbies</label> <input type="name" name="hobbies"><br> <input type="submit" name=""> </form></body></html> |
視圖函數 bio_data_form 同時支持post和get請求。get請求將渲染 bio_form.html 模板,而post請求將重定向到 showbio :
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
@app.route('/form', methods=['post', 'get'])def bio_data_form(): if request.method == "post": username = request.form['username'] age = request.form['age'] email = request.form['email'] hobbies = request.form['hobbies'] return redirect(url_for('showbio', username=username, age=age, email=email, hobbies=hobbies)) return render_template("bio_form.html") |
下面是showbio的實現:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
@app.route('/showbio', methods=['get'])def showbio(): username = request.args.get('username') age = request.args.get('age') email = request.args.get('email') hobbies = request.args.get('hobbies') return render_template("show_bio.html", username=username, age=age, email=email, hobbies=hobbies) |
以及show_bio.html的內容:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
<!doctype html><html><head> <title>bio-data details</title></head><body> <h1>bio-data details</h1> <hr> <h1>username: {{ username }}</h1> <h1>email: {{ email }}</h1> <h1>hobbies: {{ hobbies }}</h1></body></html> |
5、數據庫集成:使用sqlalchemy
flask不能直接連接數據庫,需要借助于orm(object relational mapper)。 在這一部分,我們將借助于sqlalchemy使用postgres數據庫。
安裝flask-sqlalchemy和postgres
首先安裝flask-sqlalchemy:
|
1
|
$ pip install flask-sqlalchemy |
然后從官方下載并安裝postgres:https://postgresapp.com/
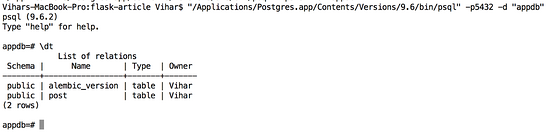
創建數據庫
在終端中使用下面的命令創建一個appdb數據庫:
|
1
|
$ createdb appdb |
更新應用配置
修改app.config,添加數據庫相關的配置信息:
|
1
2
3
4
|
app.config['debug'] = trueapp.config['sqlalchemy_database_uri']='postgresql://localhost/appdb'sqlalchemy_track_modifications = truedb = sqlalchemy(app) |
然后在代碼中就可以使用這些配置數據了:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
from flask import flask, request, render_templatefrom flask_sqlalchemy import sqlalchemy# settingsapp = flask(__name__)app.config['debug'] = trueapp.config['sqlalchemy_database_uri'] = 'postgresql://localhost/appdb'db = sqlalchemy(app)@app.route('/')def hello_world(): return 'hello, world!'if __name__ == '__main__': app.run() |
現在,讓我們創建第一個模型(model)。所有模型的基類是db.model,使用column來定義 數據列:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
class post(db.model): id = db.column(db.integer(), primary_key=true) title = db.column(db.string(80), unique=true) post_text = db.column(db.string(255)) def __init__(self, title, post_text): self.title = title self.post_text = post_text |
在代碼中使用模型:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
|
from flask import flaskfrom flask_sqlalchemy import sqlalchemyapp = flask(__name__)app.config['sqlalchemy_database_uri'] = 'postgresql://localhost/testdb'db = sqlalchemy(app)class post(db.model): id = db.column(db.integer(), primary_key=true) title = db.column(db.string(80), unique=true) post_text = db.column(db.string(255)) def __init__(self, title, post_text): self.title = title self.post_text = post_text@app.route('/')def index(): return "hello world"app = flask(__name__)if __name__ == "__main__": app.run() |
6、模型-數據同步
使用orm時,需要執行遷移操作以便在模型和持久化數據之間保持同步。我們使用 flask-migrate這個擴展來完成該任務。
首先安裝:
|
1
2
|
$ pip install flask-migrate$ pip install flask_script |
然后在代碼中引入:
|
1
2
|
from flask_script import managerfrom flask_migrate import migrate, migratecommand |
進行必要的配置:
|
1
2
3
|
migrate = migrate(app, db)manager = manager(app)manager.add_command('db', migratecommand) |
運行管理器:
|
1
2
|
if __name__ == '__main__': manager.run() |
完整的代碼如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
|
from flask import flaskfrom flask_sqlalchemy import sqlalchemyfrom flask_script import managerfrom flask_migrate import migrate, migratecommandapp = flask(__name__)app.config['sqlalchemy_database_uri'] = 'postgresql://localhost/appdb'db = sqlalchemy(app)migrate = migrate(app, db)manager = manager(app)manager.add_command('db', migratecommand)class post(db.model): id = db.column(db.integer(), primary_key=true) title = db.column(db.string(80), unique=true) post_text = db.column(db.string(255)) def __init__(self, title, post_text): self.title = title self.post_text = post_text@app.route('/')def index(): return "hello world"if __name__ == "__main__": manager.run() |
使用如下的命令初始化alembic:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
$ python app.py db initcreating directory /users/vihar/desktop/flask-databases/migrations ... done.........generating /users/vihar/desktop/flask-databases/migrations/alembic.ini ... done |
執行第一個遷移任務:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
$ python app.py db migrateinfo [alembic.runtime.migration] context impl postgresqlimpl.info [alembic.runtime.migration] will assume transactional ddl.info [alembic.autogenerate.compare] detected added table 'post'generating /users/vihar/desktop/flask-databases/migrations/versions/ed3b3a028447_.py ... done |
一旦上述命令執行完畢,我們的數據表就會創建成功。現在更新數據庫:
|
1
|
$ python app.py db upgrade |
以上就是本文的全部內容,希望對大家的學習有所幫助,也希望大家多多支持服務器之家。
原文鏈接:http://blog.hubwiz.com/2018/12/10/flask-framework-web-development/