1.背景
sysbench是一款壓力測試工具,可以測試系統(tǒng)的硬件性能,也可以用來對數(shù)據(jù)庫進行基準測試。sysbench 支持的測試有cpu運算性能測試、內(nèi)存分配及傳輸速度測試、磁盤io性能測試、posix線程性能測試、互斥性測試測試、數(shù)據(jù)庫性能測試(oltp基準測試)。目前支持的數(shù)據(jù)庫主要是mysql數(shù)據(jù)庫和pg數(shù)據(jù)庫。
在新服務(wù)器上線時,建議對服務(wù)器的性能做一次測試,最好與既往的同類型的服務(wù)器的性能測試報表做一個橫線比較,發(fā)現(xiàn)潛在問題。及新機器上線前,對服務(wù)器做一次體檢。
對數(shù)據(jù)庫而言,我們可以通過sysbench工具實現(xiàn)對數(shù)據(jù)庫的基準測試。在現(xiàn)在的系統(tǒng)架構(gòu)中,前端都比較容易彈性水平拓展,數(shù)據(jù)庫相對較難,因此,基準測試對數(shù)據(jù)庫具有很重要的作用。而對數(shù)據(jù)庫的基準測試的作用,就是分析在當前的配置下(包括硬件配置、os、數(shù)據(jù)庫設(shè)置等),數(shù)據(jù)庫的性能表現(xiàn),從而找出mysql的性能閾值,并根據(jù)實際系統(tǒng)的要求調(diào)整配置。
2.sysbench的安裝
1)安裝命令
yum -y install sysbench
2)查看安裝的版本
sysbench --version

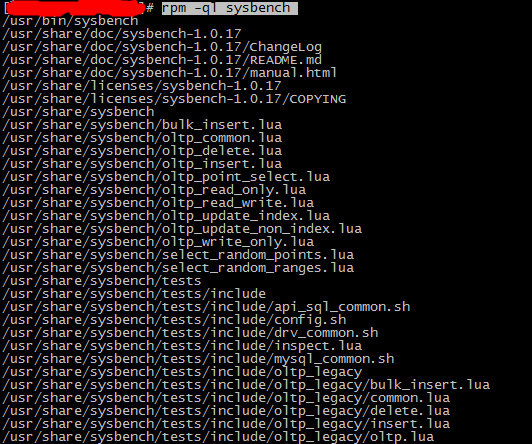
3)查看已安裝軟件的信息(主要是通 rpm 命令)。
查詢sysbench的安裝信息,主要是測試mysql時,需要使用sysbench自帶的lua腳本進行測試。如果使用快速安裝的方式,默認的腳本路徑為:/usr/share/sysbench。
如果不在這個命令,我們我們執(zhí)行以下命令查看,查找已安裝在本機linux系統(tǒng)上面的所有的sysbench軟件的程序:
rpm -qa sysbench
列出該軟件所有的文件與目錄所在完整文件名(list):
rpm -ql sysbench
3.sysbench 語法
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
|
sysbench --helpusage: sysbench [options]... [testname] [command]commands implemented by most tests: prepare run cleanup helpgeneral options: --threads=n number of threads to use [1] --events=n limit for total number of events [0] --time=n limit for total execution time in seconds [10] --forced-shutdown=string number of seconds to wait after the --time limit before forcing shutdown, or 'off' to disable [off] --thread-stack-size=size size of stack per thread [64k] --rate=n average transactions rate. 0 for unlimited rate [0] --report-interval=n periodically report intermediate statistics with a specified interval in seconds. 0 disables intermediate reports [0] --report-checkpoints=[list,...] dump full statistics and reset all counters at specified points in time. the argument is a list of comma-separated values representing the amount of time in seconds elapsed from start of test when report checkpoint(s) must be performed. report checkpoints are off by default. [] --debug[=on|off] print more debugging info [off] --validate[=on|off] perform validation checks where possible [off] --help[=on|off] print help and exit [off] --version[=on|off] print version and exit [off] --config-file=filename file containing command line options --tx-rate=n deprecated alias for --rate [0] --max-requests=n deprecated alias for --events [0] --max-time=n deprecated alias for --time [0] --num-threads=n deprecated alias for --threads [1]pseudo-random numbers generator options: --rand-type=string random numbers distribution {uniform,gaussian,special,pareto} [special] --rand-spec-iter=n number of iterations used for numbers generation [12] --rand-spec-pct=n percentage of values to be treated as 'special' (for special distribution) [1] --rand-spec-res=n percentage of 'special' values to use (for special distribution) [75] --rand-seed=n seed for random number generator. when 0, the current time is used as a rng seed. [0] --rand-pareto-h=n parameter h for pareto distribution [0.2]log options: --verbosity=n verbosity level {5 - debug, 0 - only critical messages} [3] --percentile=n percentile to calculate in latency statistics (1-100). use the special value of 0 to disable percentile calculations [95] --histogram[=on|off] print latency histogram in report [off]general database options: --db-driver=string specifies database driver to use ('help' to get list of available drivers) [mysql] --db-ps-mode=string prepared statements usage mode {auto, disable} [auto] --db-debug[=on|off] print database-specific debug information [off]compiled-in database drivers: mysql - mysql driver pgsql - postgresql drivermysql options: --mysql-host=[list,...] mysql server host [localhost] --mysql-port=[list,...] mysql server port [3306] --mysql-socket=[list,...] mysql socket --mysql-user=string mysql user [sbtest] --mysql-password=string mysql password [] --mysql-db=string mysql database name [sbtest] --mysql-ssl[=on|off] use ssl connections, if available in the client library [off] --mysql-ssl-cipher=string use specific cipher for ssl connections [] --mysql-compression[=on|off] use compression, if available in the client library [off] --mysql-debug[=on|off] trace all client library calls [off] --mysql-ignore-errors=[list,...] list of errors to ignore, or "all" [1213,1020,1205] --mysql-dry-run[=on|off] dry run, pretend that all mysql client api calls are successful without executing them [off]pgsql options: --pgsql-host=string postgresql server host [localhost] --pgsql-port=n postgresql server port [5432] --pgsql-user=string postgresql user [sbtest] --pgsql-password=string postgresql password [] --pgsql-db=string postgresql database name [sbtest]compiled-in tests: fileio - file i/o test cpu - cpu performance test memory - memory functions speed test threads - threads subsystem performance test mutex - mutex performance test |
基本語法如下:
sysbench [options]... [testname] [command]
command 是sysbench要執(zhí)行的命令,包括prepare、run和cleanup。prepare是為測試提前準備數(shù)據(jù),run是執(zhí)行正式的測試,cleanup是在測試完成后對數(shù)據(jù)庫進行清理
testname 指定了要進行的測試,在老版本的sysbench中,可以通過--test參數(shù)指定測試的腳本;而在新版本中,--test參數(shù)已經(jīng)聲明為廢棄,可以不使用--test,而是直接指定腳本。測試時使用的腳本為lua腳本,可以使用sysbench自帶腳本,也可以自己開發(fā)。
options 關(guān)于mysql的主要包括mysql 連接信息參數(shù) 和 mysql 執(zhí)行相關(guān)的參數(shù)。
4 測試
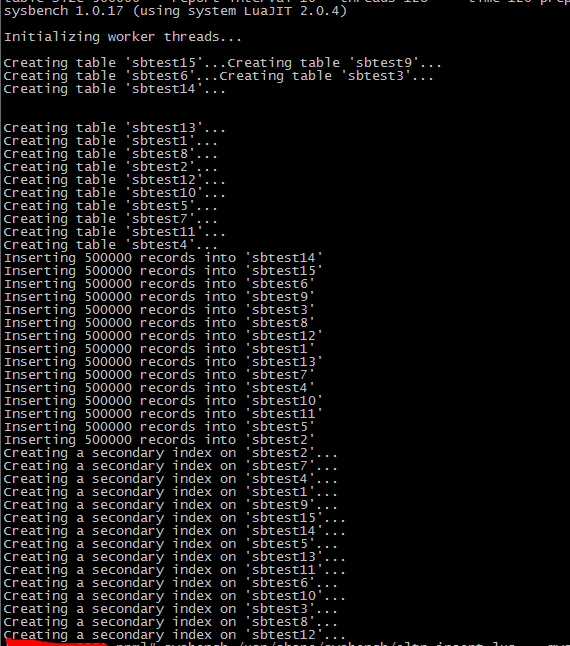
step 1 準備壓測數(shù)據(jù)
|
1
|
sysbench /usr/share/sysbench/oltp_insert.lua --mysql-host=xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx --mysql-port=3306 --mysql-user=testsbuser --mysql-password='textpwd' --mysql-db=tssysbench --db-driver=mysql --tables=15 --table-size=500000 --report-interval=10 --threads=128 --time=120 prepare |
step 2 壓測
|
1
|
sysbench /usr/share/sysbench/oltp_insert.lua --mysql-host=xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx --mysql-port=3306 --mysql-user=testsbuser --mysql-password='textpwd' --mysql-db=tssysbench --db-driver=mysql --tables=15 --table-size=500000 --report-interval=10 --threads=128 --time=120 run |
也可以將測試結(jié)果導(dǎo)出到文件中,便于后續(xù)分析。
|
1
|
sysbench /usr/share/sysbench/oltp_insert.lua --mysql-host=xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx --mysql-port=3306 --mysql-user=testsbuser --mysql-password='testpwd' --mysql-db=tssysbench --db-driver=mysql --tables=15 --table-size=500000 --report-interval=10 --threads=128 --time=120 run >> ./mysysbench.log |

step 3 清理壓測數(shù)據(jù)
|
1
|
sysbench /usr/share/sysbench/oltp_insert.lua --mysql-host=xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx --mysql-port=3306 --mysql-user=testsbuser --mysql-password='testpwd' --mysql-db=tssysbench --db-driver=mysql --tables=15 --table-size=500000 --report-interval=10 --threads=128 --time=120 cleanup |

5.注意事項
(1) 測試數(shù)據(jù)庫需要提前創(chuàng)建,及時測試賬號擁有創(chuàng)建數(shù)據(jù)庫的權(quán)限。
--mysql-db 參數(shù)指定了測試的數(shù)據(jù),默認是sbtest。
不提前創(chuàng)建,報錯信息如下;
fatal: `sysbench.cmdline.call_command' function failed: /usr/share/sysbench/oltp_common.lua:83: connection creation failed
(last message repeated 3 times)
fatal: error 1049: unknown database 'sysbench_db'
fatal: `sysbench.cmdline.call_command' function failed: /usr/share/sysbench/oltp_common.lua:83: connection creation failed
fatal: unable to connect to mysql server on host 'xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx', port 3306, aborting...
(last message repeated 1 times)
fatal: error 1049: unknown database 'sysbench_db'
(last message repeated 1 times)
或是(不指定數(shù)據(jù)庫)
fatal: `sysbench.cmdline.call_command' function failed: /usr/share/sysbench/oltp_common.lua:83: connection creation failed
fatal: error 1049: unknown database 'sbtest'
fatal: unable to connect to mysql server on host 'xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx', port 3306, aborting...
(2)不要在mysql服務(wù)器運行的機器上進行測試,一方面可能無法體現(xiàn)網(wǎng)絡(luò)(哪怕是局域網(wǎng))的影響,另一方面,sysbench的運行(尤其是設(shè)置的并發(fā)數(shù)較高時)會影響mysql服務(wù)器的表現(xiàn).
(3)逐步增加客戶端的并發(fā)連接數(shù)(--thread參數(shù)),觀察在連接數(shù)不同情況下,mysql服務(wù)器的表現(xiàn)。
(4)如果連續(xù)進行多次測試,注意確保之前測試的數(shù)據(jù)已經(jīng)被清理干凈。
(5)如果生成的報告,圖形化分析,可以通過gnuplot工具進行分析。
總結(jié)
以上所述是小編給大家介紹的通過sysbench工具實現(xiàn)mysql數(shù)據(jù)庫的性能測試的方法,希望對大家有所幫助,如果大家有任何疑問請給我留言,小編會及時回復(fù)大家的。在此也非常感謝大家對服務(wù)器之家網(wǎng)站的支持!
如果你覺得本文對你有幫助,歡迎轉(zhuǎn)載,煩請注明出處,謝謝!原文鏈接:https://www.cnblogs.com/xuliuzai/p/11243376.html