Spring中的注解大概可以分為兩大類:
1)spring的bean容器相關的注解,或者說bean工廠相關的注解;
2)springmvc相關的注解。
spring的bean容器相關的注解,先后有:@Required, @Autowired, @PostConstruct, @PreDestory,還有Spring3.0開始支持的JSR-330標準javax.inject.*中的注解(@Inject, @Named, @Qualifier, @Provider, @Scope, @Singleton).
springmvc相關的注解有:@Controller, @RequestMapping, @RequestParam, @ResponseBody等等。
要理解Spring中的注解,先要理解Java中的注解。
1. Java中的注解
Java中1.5中開始引入注解,我們最熟悉的應該是:@Override, 它的定義如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
/** * Indicates that a method declaration is intended to override a * method declaration in a supertype. If a method is annotated with * this annotation type compilers are required to generate an error * message unless at least one of the following conditions hold: * The method does override or implement a method declared in a * supertype. * The method has a signature that is override-equivalent to that of * any public method declared in Object. * * @author Peter von der Ahé * @author Joshua Bloch * @jls 9.6.1.4 @Override * @since 1.5 */@Target(ElementType.METHOD)@Retention(RetentionPolicy.SOURCE)public @interface Override {} |
從注釋,我們可以看出,@Override的作用是,提示編譯器,使用了@Override注解的方法必須override父類或者java.lang.Object中的一個同名方法。我們看到@Override的定義中使用到了 @Target, @Retention,它們就是所謂的“元注解”——就是定義注解的注解,或者說注解注解的注解(暈了...)。我們看下@Retention
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
/** * Indicates how long annotations with the annotated type are to * be retained. If no Retention annotation is present on * an annotation type declaration, the retention policy defaults to * RetentionPolicy.CLASS. */@Documented@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)@Target(ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE)public @interface Retention { /** * Returns the retention policy. * @return the retention policy */ RetentionPolicy value();} |
@Retention用于提示注解被保留多長時間,有三種取值:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
public enum RetentionPolicy { /** * Annotations are to be discarded by the compiler. */ SOURCE, /** * Annotations are to be recorded in the class file by the compiler * but need not be retained by the VM at run time. This is the default * behavior. */ CLASS, /** * Annotations are to be recorded in the class file by the compiler and * retained by the VM at run time, so they may be read reflectively. * * @see java.lang.reflect.AnnotatedElement */ RUNTIME} |
RetentionPolicy.SOURCE 保留在源碼級別,被編譯器拋棄(@Override就是此類); RetentionPolicy.CLASS被編譯器保留在編譯后的類文件級別,但是被虛擬機丟棄;
RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME保留至運行時,可以被反射讀取。
再看 @Target:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
package java.lang.annotation;/** * Indicates the contexts in which an annotation type is applicable. The * declaration contexts and type contexts in which an annotation type may be * applicable are specified in JLS 9.6.4.1, and denoted in source code by enum * constants of java.lang.annotation.ElementType * @since 1.5 * @jls 9.6.4.1 @Target * @jls 9.7.4 Where Annotations May Appear */@Documented@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)@Target(ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE)public @interface Target { /** * Returns an array of the kinds of elements an annotation type * can be applied to. * @return an array of the kinds of elements an annotation type * can be applied to */ ElementType[] value();} |
@Target用于提示該注解使用的地方,取值有:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
|
public enum ElementType { /** Class, interface (including annotation type), or enum declaration */ TYPE, /** Field declaration (includes enum constants) */ FIELD, /** Method declaration */ METHOD, /** Formal parameter declaration */ PARAMETER, /** Constructor declaration */ CONSTRUCTOR, /** Local variable declaration */ LOCAL_VARIABLE, /** Annotation type declaration */ ANNOTATION_TYPE, /** Package declaration */ PACKAGE, /** * Type parameter declaration * @since 1.8 */ TYPE_PARAMETER, /** * Use of a type * @since 1.8 */ TYPE_USE} |
分別表示該注解可以被使用的地方:1)類,接口,注解,enum; 2)屬性域;3)方法;4)參數;5)構造函數;6)局部變量;7)注解類型;8)包
所以:
|
1
2
3
4
|
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)@Retention(RetentionPolicy.SOURCE)public @interface Override {} |
表示 @Override 只能使用在方法上,保留在源碼級別,被編譯器處理,然后拋棄掉。
還有一個經常使用的元注解 @Documented :
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
/** * Indicates that annotations with a type are to be documented by javadoc * and similar tools by default. This type should be used to annotate the * declarations of types whose annotations affect the use of annotated * elements by their clients. If a type declaration is annotated with * Documented, its annotations become part of the public API * of the annotated elements. */@Documented@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)@Target(ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE)public @interface Documented {} |
表示注解是否能被 javadoc 處理并保留在文檔中。
2. 使用 元注解 來自定義注解 和 處理自定義注解
有了元注解,那么我就可以使用它來自定義我們需要的注解。結合自定義注解和AOP或者過濾器,是一種十分強大的武器。比如可以使用注解來實現權限的細粒度的控制——在類或者方法上使用權限注解,然后在AOP或者過濾器中進行攔截處理。下面是一個關于登錄的權限的注解的實現:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
/** * 不需要登錄注解 */@Target({ ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE })@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)@Documentedpublic @interface NoLogin {} |
我們自定義了一個注解 @NoLogin, 可以被用于 方法 和 類 上,注解一直保留到運行期,可以被反射讀取到。該注解的含義是:被 @NoLogin 注解的類或者方法,即使用戶沒有登錄,也是可以訪問的。下面就是對注解進行處理了:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
|
/** * 檢查登錄攔截器 * 如不需要檢查登錄可在方法或者controller上加上@NoLogin */public class CheckLoginInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor { private static final Logger logger = Logger.getLogger(CheckLoginInterceptor.class); @Override public Boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception { if (!(handler instanceof HandlerMethod)) { logger.warn("當前操作handler不為HandlerMethod=" + handler.getClass().getName() + ",req=" + request.getQueryString()); return true; } HandlerMethod handlerMethod = (HandlerMethod) handler; String methodName = handlerMethod.getMethod().getName(); // 判斷是否需要檢查登錄 NoLogin noLogin = handlerMethod.getMethod().getAnnotation(NoLogin.class); if (null != noLogin) { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("當前操作methodName=" + methodName + "不需要檢查登錄情況"); } return true; } noLogin = handlerMethod.getMethod().getDeclaringClass().getAnnotation(NoLogin.class); if (null != noLogin) { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("當前操作methodName=" + methodName + "不需要檢查登錄情況"); } return true; } if (null == request.getSession().getAttribute(CommonConstants.SESSION_KEY_USER)) { logger.warn("當前操作" + methodName + "用戶未登錄,ip=" + request.getRemoteAddr()); response.getWriter().write(JsonConvertor.convertFailResult(ErrorCodeEnum.NOT_LOGIN).toString()); // 返回錯誤信息 return false; } return true; } @Override public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception { } @Override public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception { }} |
上面我們定義了一個登錄攔截器,首先使用反射來判斷方法上是否被 @NoLogin 注解:
NoLogin noLogin = handlerMethod.getMethod().getAnnotation(NoLogin.class);
然后判斷類是否被 @NoLogin 注解:
noLogin = handlerMethod.getMethod().getDeclaringClass().getAnnotation(NoLogin.class);
如果被注解了,就返回 true,如果沒有被注解,就判斷是否已經登錄,沒有登錄則返回錯誤信息給前臺和false. 這是一個簡單的使用 注解 和 過濾器 來進行權限處理的例子。擴展開來,那么我們就可以使用注解,來表示某方法或者類,只能被具有某種角色,或者具有某種權限的用戶所訪問,然后在過濾器中進行判斷處理。
3. spring的bean容器相關的注解
1)@Autowired 是我們使用得最多的注解,其實就是 autowire=byType 就是根據類型的自動注入依賴(基于注解的依賴注入),可以被使用再屬性域,方法,構造函數上。
2)@Qualifier 就是 autowire=byName, @Autowired注解判斷多個bean類型相同時,就需要使用 @Qualifier("xxBean") 來指定依賴的bean的id:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
@Controller@RequestMapping("/user")public class HelloController { @Autowired @Qualifier("userService") private UserService userService; |
3)@Resource 屬于JSR250標準,用于屬性域額和方法上。也是 byName 類型的依賴注入。使用方式:@Resource(name="xxBean"). 不帶參數的 @Resource 默認值類名首字母小寫。
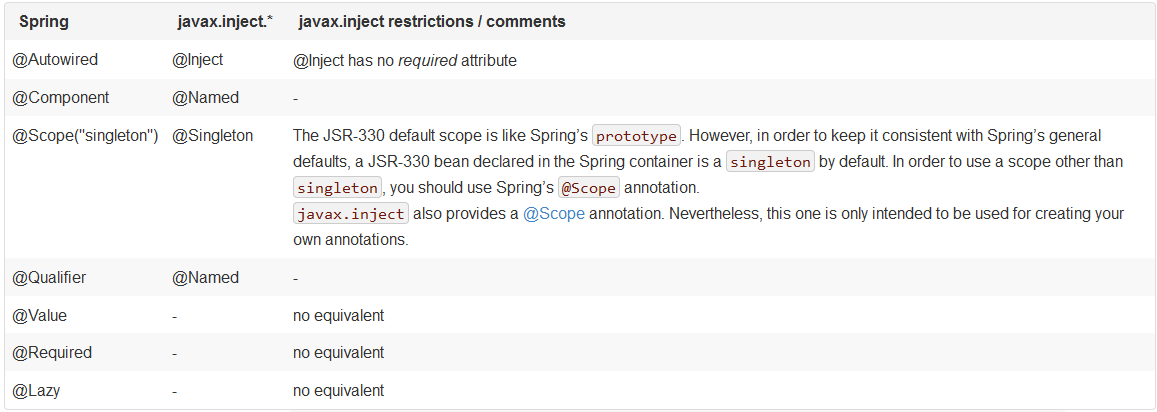
4)JSR-330標準javax.inject.*中的注解(@Inject, @Named, @Qualifier, @Provider, @Scope, @Singleton)。@Inject就相當于@Autowired, @Named 就相當于 @Qualifier, 另外 @Named 用在類上還有 @Component的功能。
5)@Component, @Controller, @Service, @Repository, 這幾個注解不同于上面的注解,上面的注解都是將被依賴的bean注入進入,而這幾個注解的作用都是生產bean, 這些注解都是注解在類上,將類注解成spring的bean工廠中一個一個的bean。@Controller, @Service, @Repository基本就是語義更加細化的@Component。
6)@PostConstruct 和 @PreDestroy 不是用于依賴注入,而是bean 的生命周期。類似于 init-method(InitializeingBean) destory-method(DisposableBean)
4. spring中注解的處理
spring中注解的處理基本都是通過實現接口 BeanPostProcessor 來進行的:
|
1
2
3
4
|
public interface BeanPostProcessor { Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException; Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException;} |
相關的處理類有: AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor,CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor,PersistenceAnnotationBeanPostProcessor, RequiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
這些處理類,可以通過 <context:annotation-config/> 配置隱式的配置進spring容器。這些都是依賴注入的處理,還有生產bean的注解(@Component, @Controller, @Service, @Repository)的處理:
<context:component-scan base-package="net.aazj.service,net.aazj.aop" />
這些都是通過指定掃描的基包路徑來進行的,將他們掃描進spring的bean容器。注意 context:component-scan 也會默認將 AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor,CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor 配置進來。所以<context:annotation-config/>是可以省略的。另外context:component-scan也可以掃描@Aspect風格的AOP注解,但是需要在配置文件中加入 <aop:aspectj-autoproxy/> 進行配合。
5. Spring注解和JSR-330標準注解的區別:
總結
以上就是本文關于快速理解spring中的各種注解的全部內容,希望對大家有所幫助。感興趣的朋友可以繼續參閱本站其他相關專題,如有不足之處,歡迎留言指出。感謝朋友們對本站的支持!
原文鏈接:http://www.cnblogs.com/softidea/p/4527657.html















