緩存可以說是加速服務響應速度的一種非常有效并且簡單的方式。在緩存領域,有很多知名的框架,如ehcache 、guava、hazelcast等。redis作為key-value型數(shù)據(jù)庫,由于他的這一特性,redis也成為一種流行的數(shù)據(jù)緩存工具。
在傳統(tǒng)方式下對于緩存的處理代碼是非常臃腫的。
例如:我們要把一個查詢函數(shù)加入緩存功能,大致需要三步。
一、在函數(shù)執(zhí)行前,我們需要先檢查緩存中是否存在數(shù)據(jù),如果存在則返回緩存數(shù)據(jù)
二、如果不存在,就需要在數(shù)據(jù)庫的數(shù)據(jù)查詢出來。
三、最后把數(shù)據(jù)存放在緩存中,當下次調(diào)用此函數(shù)時,就可以直接使用緩存數(shù)據(jù),減輕了數(shù)據(jù)庫壓力。
那么實現(xiàn)上面的三步需要多少代碼呢?下面是一個示例:
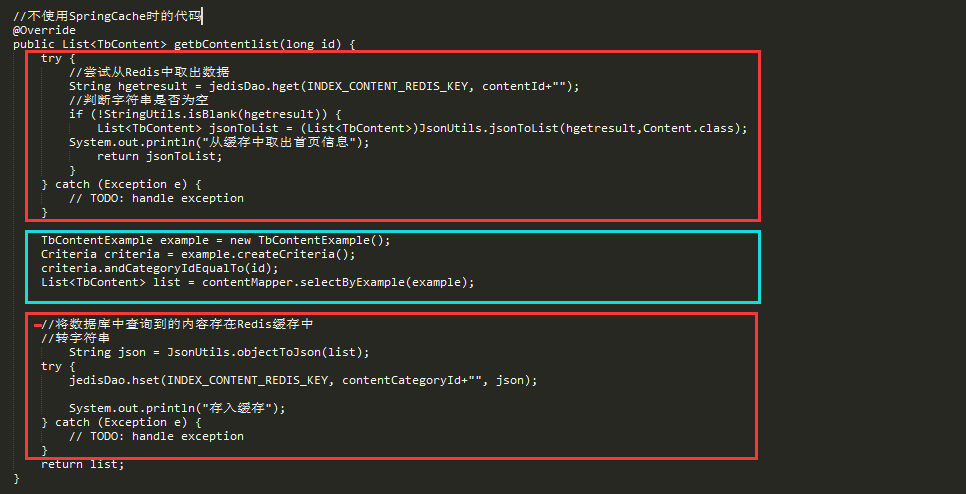
上圖中的紅色部分都是模板代碼,真正與這個函數(shù)有關的代碼卻只占了1/5,對于所有需要實現(xiàn)緩存功能的函數(shù),都需要加上臃腫的模板代碼。可謂是一種極不優(yōu)雅的解決方案。
那么如何讓臃腫的代碼重回清新的當初呢?
aop不就是專門解決這種模板式代碼的最佳方案嗎,幸運的是我們不需要再自己實現(xiàn)切面了,springcache已經(jīng)為我們提供好了切面,我們只需要進行簡單的配置,就可以重回當初了,像下面這樣:
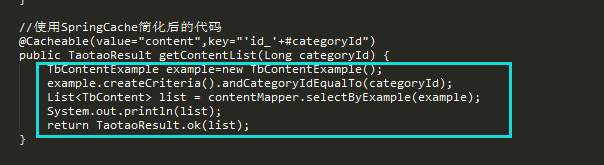
只需要加一個注解就可以了,對于原來的代碼連改都不需要改,是不是已經(jīng)躍躍欲試了?
對于配置springcache只需要三步:
第一步:加入相關依賴:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
<dependency> <groupid>redis.clients</groupid> <artifactid>jedis</artifactid> <version>2.9.0</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupid>org.springframework.data</groupid> <artifactid>spring-data-redis</artifactid> <version>1.6.0.release</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupid>org.apache.commons</groupid> <artifactid>commons-lang3</artifactid> <version>3.3.2</version></dependency> |
第二步:配置springcache,redis連接等信息
applicationcontext-redis.xml
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
|
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?><beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/xmlschema-instance" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc" xmlns:cache="http://www.springframework.org/schema/cache" xsi:schemalocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.2.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.2.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc-4.2.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/cache http://www.springframework.org/schema/cache/spring-cache-4.2.xsd"> <!-- 配置文件加載 --> <context:property-placeholder location="classpath:*.properties"/><cache:annotation-driven cache-manager="cachemanager"/> <!-- redis連接池 --> <bean id="poolconfig" class="redis.clients.jedis.jedispoolconfig"> <property name="maxidle" value="${redis.maxidle}" /> <property name="maxwaitmillis" value="${redis.maxwait}" /> <property name="testonborrow" value="${redis.testonborrow}" /> </bean> <!-- 連接工廠 --> <bean id="jedisconnectionfactory" class="org.springframework.data.redis.connection.jedis.jedisconnectionfactory" p:host-name="${redis.host}" p:port="${redis.port}" p:password="${redis.pass}" p:pool-config-ref="poolconfig"/> <!-- redis模板 --> <bean id="redistemplate" class="org.springframework.data.redis.core.redistemplate"> <property name="connectionfactory" ref="jedisconnectionfactory" /> </bean> <bean id="cachemanager" class="org.springframework.cache.support.simplecachemanager"> <property name="caches"> <set> <!-- 這里可以配置多個redis --> <bean class="com.cky.rest.utils.rediscache"> <property name="redistemplate" ref="redistemplate" /> <property name="name" value="content"/> <!-- name對應的名稱要在類或方法的注解中使用 --> </bean> </set> </property> </bean> </beans> |
redis.properties文件:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
# redis settings # server ip redis.host=192.168.100.55# server port redis.port=6379# server pass redis.pass=# use dbindex redis.database=0#max idel instance of jedisredis.maxidle=300#if wait too long ,throw jedisconnectionexceptionredis.maxwait=3000#if true,it will validate before borrow jedis instance,what you get instance is all usefullredis.testonborrow=true |
第三步,編寫cache接口實現(xiàn)類
spring對于緩存只是提供了抽象的接口,并且通過接口來調(diào)用功能,沒有具體的實現(xiàn)類,所以需要我們自己實現(xiàn)具體的操作。
在上面配置中可知,每個實現(xiàn)類都會注入一個redistemplate實例,我們就可以通過redistemplate來操作redis
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
|
package com.cky.rest.utils;import java.io.serializable;import org.apache.commons.lang3.serializationutils;import org.springframework.cache.cache;import org.springframework.cache.support.simplevaluewrapper;import org.springframework.dao.dataaccessexception;import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.redisconnection;import org.springframework.data.redis.core.rediscallback;import org.springframework.data.redis.core.redistemplate;public class rediscache implements cache { private redistemplate<string, object> redistemplate; private string name; @override public void clear() { system.out.println("-------緩存清理------"); redistemplate.execute(new rediscallback<string>() { @override public string doinredis(redisconnection connection) throws dataaccessexception { connection.flushdb(); return "ok"; } }); } @override public void evict(object key) { system.out.println("-------緩存刪除------"); final string keyf=key.tostring(); redistemplate.execute(new rediscallback<long>() { @override public long doinredis(redisconnection connection) throws dataaccessexception { return connection.del(keyf.getbytes()); } }); } @override public valuewrapper get(object key) { system.out.println("------緩存獲取-------"+key.tostring()); final string keyf = key.tostring(); object object = null; object = redistemplate.execute(new rediscallback<object>() { @override public object doinredis(redisconnection connection) throws dataaccessexception { byte[] key = keyf.getbytes(); byte[] value = connection.get(key); if (value == null) { system.out.println("------緩存不存在-------"); return null; } return serializationutils.deserialize(value); } }); valuewrapper obj=(object != null ? new simplevaluewrapper(object) : null); system.out.println("------獲取到內(nèi)容-------"+obj); return obj; } @override public void put(object key, object value) { system.out.println("-------加入緩存------"); system.out.println("key----:"+key); system.out.println("key----:"+value); final string keystring = key.tostring(); final object valuef = value; final long livetime = 86400; redistemplate.execute(new rediscallback<long>() { @override public long doinredis(redisconnection connection) throws dataaccessexception { byte[] keyb = keystring.getbytes(); byte[] valueb = serializationutils.serialize((serializable) valuef); connection.set(keyb, valueb); if (livetime > 0) { connection.expire(keyb, livetime); } return 1l; } }); } @override public <t> t get(object arg0, class<t> arg1) { // todo auto-generated method stub return null; } @override public string getname() { return this.name; } @override public object getnativecache() { return this.redistemplate; } @override public valuewrapper putifabsent(object arg0, object arg1) { // todo auto-generated method stub return null; } public redistemplate<string, object> getredistemplate() { return redistemplate; } public void setredistemplate(redistemplate<string, object> redistemplate) { this.redistemplate = redistemplate; } public void setname(string name) { this.name = name; }} |
在配置過程中曾經(jīng)出現(xiàn)過兩次錯誤:
1.xxxx.classnotfoundexception 最后發(fā)現(xiàn)是jar下載不完整,把maven本地倉庫的對應jar包文件夾刪除完從新下載就好了
2.xxxx.methodnotfoundexception 這種情況是版本不對,換成第一步中的版本就可以了
springcache中常見注解的使用:
@cacheable注解
最常用的注解,會把被注解方法的返回值緩存。工作原理是:首先在緩存中查找,如果沒有執(zhí)行方法并緩存結(jié)果,然后返回數(shù)據(jù)。此注解的緩存名必須指定,和cachemanager中的caches中的某一個cache的name值相對應。可以使用value或cachenames指定。
如果沒有指定key屬性,spring會使用默認的主鍵生成器產(chǎn)生主鍵。也可以自定義主鍵,在key中可以使用spel表達式。如下:
|
1
2
3
4
|
@cacheable(cachenames=”content”,key=”#user.userid”)public user getuser(user user){ xxxxx} |
可以使用condition屬性,來給緩存添加條件,如下:
|
1
2
|
@cacheable(cachenames=”content”,key=”#user.userid”,condition=”#user.age<40”)public user getuser(user user){xxxxx} |
@cacheput注解
先執(zhí)行方法,然后將返回值放回緩存。可以用作緩存的更新。
@cacheevict注解
該注解負責從緩存中顯式移除數(shù)據(jù),通常緩存數(shù)據(jù)都有有效期,當過期時數(shù)據(jù)也會被移除。
此注解多了兩個屬性:
allentries是否移除所有緩存條目。
beforeinvocation:在方法調(diào)用前還是調(diào)用后完成移除操作。true/false
以上就是本文的全部內(nèi)容,希望對大家的學習有所幫助,也希望大家多多支持服務器之家。
原文鏈接:http://www.cnblogs.com/chenkeyu/p/8028781.html















