前言
Spring 的 JDBC Templet 是 Spring 對 JDBC 使用的一個基本的封裝。他主要是幫助程序員實現了數據庫連接的管理,其余的使用方式和直接使用 JDBC 沒有什么大的區別。
業務需求
JDBC 的使用大家都比較熟悉了。這里主要為了演示在 SpringBoot 中使用 Spring JDBC Templet 的步驟,所以我們就設計一個簡單的需求。一個用戶對象的 CURD 的操作。對象有兩個屬性,一個屬性是id,一個屬性是名稱。存儲在 MySQL 的 auth_user 表里面。
新建項目和增加依賴
在 Intellij IDEA 里面新建一個空的 SpringBoot 項目。具體步驟參考
Intellij IDEA創建spring-boot項目的圖文教程。根據本樣例的需求,我們要添加下面三個依賴
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId></dependency><dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jdbc</artifactId></dependency><dependency> <groupId>mysql</groupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> <version>6.0.6</version></dependency> |
因為要發布 Http Rest 的服務,所以添加 spring-boot-starter-web 依賴,這里我們要使用 JDBC Tempet 方法來訪問數據庫,所以添加了 spring-boot-starter-jdbc 依賴,要訪問 MySQL 數據庫,所以添加了 MySQL 最新版本的 JDBC 驅動程序。
準備數據庫環境
假定在 Linux 操作系統上已經安裝了 MySQL 5.7。以下操作都是在操作系統的命令行中,通過 root 用戶登錄到 MySQL 的命令行客戶端中執行的。
建庫建表
|
1
2
|
create database springboot_jdbc;create table auth_user (uuid bigint not null,name varchar(32), primary key (uuid)) default charset=utf8mb4; |
設定用戶權限
|
1
2
|
grant all privileges on springboot_jdbc.* to 'springboot'@'%' identified by 'springboot';flush privileges; |
配置數據源(連接池)
SpringBoot 的數據源是自動配置的。在 SpringBoot 2.0 中,有幾種數據源配置可選,他們按照 HikariCP -> Tomcat pooling -> Commons DBCP2 優先順序來選擇最后實際使用哪個數據源。
在項目加入 spring-boot-starter-jdbc 依賴的時候,就已經包括了 HikariCP 數據源的依賴,所以這里自動配置 HikariCP 連接池數據源。
在 appplications.properties 中增加如下的配置
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
#通用數據源配置spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driverspring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://10.110.2.5:3306/spring-boot-jdbc?charset=utf8mb4&useSSL=falsespring.datasource.username=springbootspring.datasource.password=springboot# Hikari 數據源專用配置spring.datasource.hikari.maximum-pool-size=20spring.datasource.hikari.minimum-idle=5 |
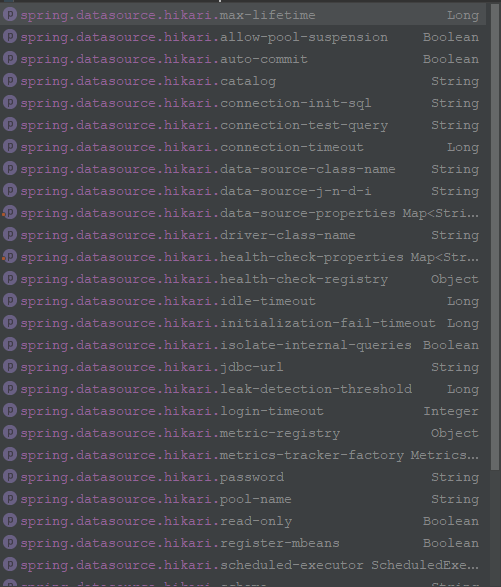
其中 Hikari 數據源的大部分配置如下圖。每個配置代表的含義可以自行查詢一下
程序開發
用戶數據庫實體
根據需求,對應的用戶數據實體有兩個屬性,一個是 id ,一個是 name 。這是一個純 POJO 對象。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
|
package com.yanggaochao.springboot.learn.springbootjdbclearn.domain.dao;/** * 用戶實體對象 * * @author 楊高超 * @since 2018-03-09 */public class UserDO { private Long id; private String name; public Long getId() { return id; } public void setId(Long id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; }} |
通用的 Http Rest 返回對象
通常在 Http Rest 接口中,我們不僅想直接返回業務對象的內容,還要返回一些通用的信息,例如接口調用的結果,調用失敗的時候返回的自定義文本消息等。那么我們就需要建立兩個通用的 rest 返回對象,除了返回通用的接口調用結果和文本消息,一個包括一個單獨的業務內容,一個包含一個持有多個業務內容的集合。具體定義如下
單獨業務內容返回對象
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
|
package com.yanggaochao.springboot.learn.springbootjdbclearn.domain.bo;/** * 單個對象返回結果 * * @author 楊高超 * @since 2018-03-09 */public class RestItemResult<T> { private String result; private String message; private T item; public String getResult() { return result; } public void setResult(String result) { this.result = result; } public String getMessage() { return message; } public void setMessage(String message) { this.message = message; } public T getItem() { return item; } public void setItem(T item) { this.item = item; }} |
集合業務內容返回對象
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
|
package com.yanggaochao.springboot.learn.springbootjdbclearn.domain.bo;import java.util.Collection;/** * 集合對象返回結果 * * @author 楊高超 * @since 2018-03-09 */public class RestCollectionResult<T> { private String result; private String message; private Collection<T> items; public String getResult() { return result; } public void setResult(String result) { this.result = result; } public String getMessage() { return message; } public void setMessage(String message) { this.message = message; } public Collection<T> getItems() { return items; } public void setItems(Collection<T> items) { this.items = items; }} |
數據持久層開發
用戶數據持久層接口定義
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
|
package com.yanggaochao.springboot.learn.springbootjdbclearn.dao;import com.yanggaochao.springboot.learn.springbootjdbclearn.domain.dao.UserDO;import java.util.List;/** * 用戶數據層接口 * * @author 楊高超 * @since 2018-03-09 */public interface UserDao { /** * 向數據庫中保存一個新用戶 * * @param user 要保存的用戶對象 * @return 是否增肌成功 */ Boolean add(UserDO user); /** * 更新數據庫中的一個用戶 * * @param user 要更新的用戶對象 * @return 是否更新成功 */ Boolean update(UserDO user); /** * 刪除一個指定的用戶 * * @param id 要刪除的用戶的標識 * @return 是否刪除成功 */ boolean delete(Long id); /** * 精確查詢一個指定的用戶 * * @param id 要查詢的用戶的標識 * @return 如果能夠查詢到,返回用戶信息,否則返回 null */ UserDO locate(Long id); /** * 通過名稱模糊查詢用戶 * * @param name 要模糊查詢的名稱 * @return 查詢到的用戶列表 */ List<UserDO> matchName(String name);} |
用戶數據持久層實現
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
|
package com.yanggaochao.springboot.learn.springbootjdbclearn.dao.impl;import com.yanggaochao.springboot.learn.springbootjdbclearn.dao.UserDao;import com.yanggaochao.springboot.learn.springbootjdbclearn.domain.dao.UserDO;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;import org.springframework.jdbc.support.rowset.SqlRowSet;import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.List;/** * 用戶對象數據庫訪問實現類 * * @author 楊高超 * @since 2018-03-09 */@Repositorypublic class UserDaoJDBCTempletImpl implements UserDao { private final JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate; @Autowired public UserDaoJDBCTempletImpl(JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate) { this.jdbcTemplate = jdbcTemplate; } @Override public Boolean add(UserDO user) { String sql = "INSERT INTO AUTH_USER(UUID,NAME) VALUES(?,?)"; return jdbcTemplate.update(sql, user.getId(), user.getName()) > 0; } @Override public Boolean update(UserDO user) { String sql = "UPDATE AUTH_USER SET NAME = ? WHERE UUID = ?"; return jdbcTemplate.update(sql, user.getName(), user.getId()) > 0; } @Override public boolean delete(Long id) { String sql = "DELETE FROM AUTH_USER WHERE UUID = ?"; return jdbcTemplate.update(sql, id) > 0; } @Override public UserDO locate(Long id) { String sql = "SELECT * FROM AUTH_USER WHERE UUID=?"; SqlRowSet rs = jdbcTemplate.queryForRowSet(sql, id); if (rs.next()) { return generateEntity(rs); } return null; } @Override public List<UserDO> matchName(String name) { String sql = "SELECT * FROM AUTH_USER WHERE NAME LIKE ?"; SqlRowSet rs = jdbcTemplate.queryForRowSet(sql, "%" + name + "%"); List<UserDO> users = new ArrayList<>(); while (rs.next()) { users.add(generateEntity(rs)); } return users; } private UserDO generateEntity(SqlRowSet rs) { UserDO weChatPay = new UserDO(); weChatPay.setId(rs.getLong("UUID")); weChatPay.setName(rs.getString("NAME")); return weChatPay; }} |
這里首先用一個注解 @Repository 表示這是一個數據持久層的類,SpringBoot 將自動將這個類實例化。然后在構造函數上增加一個 @Autowired ,SpringBoot 在實例化這個類的時候,會自動將 JDBCTemplet 實例注入到這個類里面。這里 JDBCTemplet 實例是 SpringBoot 根據 applications.properties 中數據源相關的配置自動配置出來的。按照 SpringBoot 自動配置數據源的算法,這里將會配置的數據源是 HikariCP。
剩下的則和普通的 Spring JDBCTemplet 開發一樣,通過程序員手動在對象和數據庫 SQL 之間進行轉換,實現了用戶的增加、修改、刪除、模糊匹配、精確查詢等功能。
數據業務層開發
數據業務層接口定義
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
package com.yanggaochao.springboot.learn.springbootjdbclearn.service;import com.yanggaochao.springboot.learn.springbootjdbclearn.domain.dao.UserDO;import java.util.List;/** * 用戶服務層接口 * * @author 楊高超 * @since 2018-03-09 */public interface UserService { UserDO add(UserDO user); UserDO update(UserDO user); boolean delete(Long id); UserDO locate(Long id); List<UserDO> matchName(String name);} |
數據業務層實現
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
|
package com.yanggaochao.springboot.learn.springbootjdbclearn.service.impl;import com.yanggaochao.springboot.learn.springbootjdbclearn.dao.UserDao;import com.yanggaochao.springboot.learn.springbootjdbclearn.domain.dao.UserDO;import com.yanggaochao.springboot.learn.springbootjdbclearn.service.UserService;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;import java.util.Date;import java.util.List;/** * 用戶業務層實現類 * * @author 楊高超 * @since 2018-03-09 */@Servicepublic class UserServiceImpl implements UserService { private final UserDao userDao; @Autowired public UserServiceImpl(UserDao userDao) { this.userDao = userDao; } @Override public UserDO add(UserDO user) { user.setId(new Date().getTime()); if (userDao.add(user)) { return user; } return null; } @Override public UserDO update(UserDO user) { if (userDao.update(user)) { return locate(user.getId()); } return null; } @Override public boolean delete(Long id) { return userDao.delete(id); } @Override public UserDO locate(Long id) { return userDao.locate(id); } @Override public List<UserDO> matchName(String name) { return userDao.matchName(name); }} |
這里通過一個 @Service 注解聲明這個實現類是一個業務層的類。持久層的 UserDao 通過 @Autowired 讓 SpringBoot 實例化這個業務層類的時候,自動將對應的持久層類注入到這個業務類中。
這里在增加用戶對象的時候,給用戶設定標識的時候,簡單的用了一個當前時間的毫秒數作為標識。實際開發的過程中,這個地方需要用一個保證全局唯一的機制來保證這個標識不能重復。
對外服務層開發
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
|
package com.yanggaochao.springboot.learn.springbootjdbclearn.web;import com.yanggaochao.springboot.learn.springbootjdbclearn.domain.bo.RestCollectionResult;import com.yanggaochao.springboot.learn.springbootjdbclearn.domain.bo.RestItemResult;import com.yanggaochao.springboot.learn.springbootjdbclearn.domain.dao.UserDO;import com.yanggaochao.springboot.learn.springbootjdbclearn.service.UserService;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;import java.util.List;/** * 用戶 Http Rest 接口 * * @author 楊高超 * @since 2018-03-09 */@RestController@RequestMapping("api/v1/user")public class UserApi { @Autowired private UserService userService; @RequestMapping(value = "/add", method = RequestMethod.POST) public RestItemResult<UserDO> add(@RequestBody UserDO user) { RestItemResult<UserDO> result = new RestItemResult<>(); user = userService.add(user); if (user != null) { result.setItem(user); result.setResult("success"); } else { result.setMessage("新增用戶失敗"); result.setResult("failure"); } return result; } @RequestMapping(value = "/update", method = RequestMethod.POST) public RestItemResult<UserDO> update(@RequestBody UserDO user) { RestItemResult<UserDO> result = new RestItemResult<>(); user = userService.update(user); if (user != null) { result.setItem(user); result.setResult("success"); } else { result.setMessage("修改用戶失敗"); result.setResult("failure"); } return result; } @RequestMapping(value = "/delete/{uuid}", method = RequestMethod.GET) public RestItemResult<UserDO> delete(@PathVariable Long uuid) { RestItemResult<UserDO> result = new RestItemResult<>(); if (userService.delete(uuid)) { result.setResult("success"); } else { result.setMessage("刪除用戶失敗"); result.setResult("failure"); } return result; } @RequestMapping(value = "/locate/{uuid}", method = RequestMethod.GET) public RestItemResult<UserDO> locate(@PathVariable Long uuid) { RestItemResult<UserDO> result = new RestItemResult<>(); UserDO user = userService.locate(uuid); if (user != null) { result.setItem(user); result.setResult("success"); } else { result.setMessage("查詢用戶失敗"); result.setResult("failure"); } return result; } @RequestMapping(value = "/match/{name}", method = RequestMethod.GET) public RestCollectionResult<UserDO> match(@PathVariable String name) { RestCollectionResult<UserDO> result = new RestCollectionResult<>(); List<UserDO> users = userService.matchName(name); result.setItems(users); result.setResult("success"); return result; }} |
這里 @RestController 用來聲明這是一個 Http Rest 接口類。通過類上的 @RequestMapping 和方法上的 @RequestMapping組合形成每個接口的調用路由。方法上的 @RequestMapping 中的 method 屬性聲明了 http 調用的方法。 @RequestBody 注解自動將 post 數據中的 json 對象轉成 POJO 對象。@PathVariable 將 http url 路徑中的數據自動轉換成為服務方法的參數。
Http Rest 接口測試
測試通過 Apache commons的 HttpClient 來調用 Http Rest 服務。
Http Resst 調用輔助類
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
|
package com.yanggaochao.springboot.learn.springbootjdbclearn;import org.apache.commons.httpclient.DefaultHttpMethodRetryHandler;import org.apache.commons.httpclient.HttpClient;import org.apache.commons.httpclient.methods.GetMethod;import org.apache.commons.httpclient.methods.PostMethod;import org.apache.commons.httpclient.methods.StringRequestEntity;import org.apache.commons.httpclient.params.HttpMethodParams;import java.io.BufferedReader;import java.io.InputStream;import java.io.InputStreamReader;import java.io.Reader;import java.util.Map;/** * @author 楊高超 * @since 2018-03-09 */public class HttpClientHelper { /** * 用 get 方法發起一個http請求 * * @param url 要訪問的 http 的 url * @return 訪問 http 后得到的回應文本 */ public String httpGetRequest(String url, Map<String, String> headers) { try { HttpClient httpclient = new HttpClient(); GetMethod method = new GetMethod(url); method.setRequestHeader("Content-Type", "application/json; charset=utf-8"); method.getParams().setParameter(HttpMethodParams.RETRY_HANDLER, new DefaultHttpMethodRetryHandler(3, false)); if (headers != null) { for (String key : headers.keySet()) { method.setRequestHeader(key, headers.get(key)); } } int statusCode = httpclient.executeMethod(method); if (statusCode == 200) { return parseInputStream(method.getResponseBodyAsStream()); } else { System.out.println(url + " status = " + statusCode); } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return null; } /** * 用 post 方法發起一個 http 請求 * * @param url 要訪問的 http 的 url * @param data post 請求中的 data 數據 * @return 訪問 http 后得到的回應文本 */ public String httpPostRequest(String url, String data, Map<String, String> headers) { try { HttpClient httpclient = new HttpClient(); PostMethod method = new PostMethod(url); method.setRequestHeader("Content-Type", "application/json;charset=UTF-8"); method.setRequestHeader("User-Agent", "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; WOW64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/34.0.1847.131 Safari/537.36"); if (headers != null) { for (String key : headers.keySet()) { method.setRequestHeader(key, headers.get(key)); } } method.setRequestEntity(new StringRequestEntity(data, "json", "utf-8")); int statusCode = httpclient.executeMethod(method); if (statusCode == 200) { return parseInputStream(method.getResponseBodyAsStream()); } else { System.out.println(url + " status = " + statusCode + parseInputStream(method.getResponseBodyAsStream())); } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return null; } /** * 從 java.io.Reader 中解析文本數據 * * @param rd java.io.Reader 對象 * @throws Exception 發生錯誤時拋出異常 */ private String parseReader(Reader rd) throws Exception { BufferedReader brd = new BufferedReader(rd); String line; StringBuilder respongseContext = new StringBuilder(); while ((line = brd.readLine()) != null) { respongseContext.append(line).append("\n"); } //rd.close(); if (respongseContext.length() > 0) { respongseContext.deleteCharAt(respongseContext.length() - 1); } return respongseContext.toString(); } /** * 從輸入流中解析文本數據 * * @param is 輸入流 * @throws Exception 發生錯誤時拋出異常 */ private String parseInputStream(InputStream is) throws Exception { return parseReader(new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(is))); }} |
這里主要是實現了用 GET 和 POST 方法調用 Http Rest 服務的方法。
測試用例
采用 JUnit 來執行測試用例。為了實現測試,我們額外增加了下面的 maven 依賴
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
<dependency> <groupId>commons-httpclient</groupId> <artifactId>commons-httpclient</artifactId> <version>3.1</version> <scope>test</scope></dependency><dependency> <groupId>org.codehaus.jettison</groupId> <artifactId>jettison</artifactId> <version>1.3.3</version> <scope>test</scope></dependency> |
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
|
package com.yanggaochao.springboot.learn.springbootjdbclearn;import org.codehaus.jettison.json.JSONObject;import org.junit.After;import org.junit.Before;import org.junit.Test;import java.net.URLEncoder;import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.List;/** * Description: * * @author 楊高超 * @since 2018-03-09 */public class UserApiTest { private String userAddUrl = "http://localhost:3030/security/api/v1/user/add"; private String userLocateUrl = "http://localhost:3030/security/api/v1/user/locate/"; private String userDeleteUrl = "http://localhost:3030/security/api/v1/user/delete/"; private String userUpdateUrl = "http://localhost:3030/security/api/v1/user/update"; private String userMatchUrl = "http://localhost:3030/security/api/v1/user/match/"; JSONObject addUser = new JSONObject(); Long addUserId = null; List<Long> userIds = new ArrayList<>(); @Before public void before() throws Exception { addUser.put("name", "美羊羊"); JSONObject addResultJson = new JSONObject(new HttpClientHelper().httpPostRequest(userAddUrl, addUser.toString(), null)); assert ("success".equals(addResultJson.getString("result"))); addUserId = addResultJson.getJSONObject("item").getLong("id"); JSONObject user = new JSONObject(); user.put("name", "喜羊羊"); addResultJson = new JSONObject(new HttpClientHelper().httpPostRequest(userAddUrl, user.toString(), null)); assert ("success".equals(addResultJson.getString("result"))); userIds.add(addResultJson.getJSONObject("item").getLong("id")); user.put("name", "灰太狼"); addResultJson = new JSONObject(new HttpClientHelper().httpPostRequest(userAddUrl, user.toString(), null)); assert ("success".equals(addResultJson.getString("result"))); userIds.add(addResultJson.getJSONObject("item").getLong("id")); } @Test public void testUpdateUser() throws Exception { JSONObject user = new JSONObject(); user.put("name", "霉羊羊"); user.put("id", addUserId); new HttpClientHelper().httpPostRequest(userUpdateUrl, user.toString(), null); JSONObject locateResultJson = new JSONObject(new HttpClientHelper().httpGetRequest(userLocateUrl + addUserId, null)); assert (user.getString("name").equals(locateResultJson.getJSONObject("item").getString("name"))); } @Test public void testMatchUser() throws Exception { JSONObject matchResultJson = new JSONObject(new HttpClientHelper().httpGetRequest(userMatchUrl + URLEncoder.encode("羊","UTF-8"), null)); assert (matchResultJson.has("items") && matchResultJson.getJSONArray("items").length() == 2); matchResultJson = new JSONObject(new HttpClientHelper().httpGetRequest(userMatchUrl + URLEncoder.encode("狼","UTF-8"), null)); assert (matchResultJson.has("items") && matchResultJson.getJSONArray("items").length() == 1); } @After public void after() throws Exception { if (addUserId != null) { JSONObject deleteResultJson = new JSONObject(new HttpClientHelper().httpGetRequest(userDeleteUrl + addUserId, null)); assert ("success".equals(deleteResultJson.getString("result"))); } for (Long userId : userIds) { JSONObject deleteResultJson = new JSONObject(new HttpClientHelper().httpGetRequest(userDeleteUrl + userId, null)); assert ("success".equals(deleteResultJson.getString("result"))); } }} |
這里在 @Test 聲明了兩個測試用例,一個測試了用戶修改功能,一個測試了用戶模糊查詢功能。 @Before 聲明了在執行每個測試用例之前要做的準備工作。這里首先往數據庫中插入三條數據,同時也測試了數據的增加功能、精確查詢的功能。@After 聲明了執行每個測試用例后的清理工作。這里主要是將之前插入的數據給刪除了。這里同步測試了用戶刪除的功能。
后記
這里就展示了一個完整的 SpringBoot 使用 JDBC Templet 的完整樣例。如果有在 Spring 下使用 JDBC Templet 的經歷,那么在 Spring 里面主要是減少了很多配置的工作。
本文涉及的代碼已經上傳到 GitHUB 上下載
總結
以上就是這篇文章的全部內容了,希望本文的內容對大家的學習或者工作具有一定的參考學習價值,如果有疑問大家可以留言交流,謝謝大家對服務器之家的支持。
原文鏈接:https://www.jianshu.com/p/6f97dbdfc537















