前言
現在流行的通用授權框架有apache的shiro和spring家族的spring security,在涉及今天的微服務鑒權時,需要利用我們的授權框架搭建自己的鑒權服務,今天總理了spring security。
spring security 主要實現了authentication(認證,解決who are you? ) 和 access control(訪問控制,也就是what are you allowed to do?,也稱為authorization)。spring security在架構上將認證與授權分離,并提供了擴展點。
核心對象
主要代碼在spring-security-core包下面。要了解spring security,需要先關注里面的核心對象。
securitycontextholder, securitycontext 和 authentication
securitycontextholder 是 securitycontext的存放容器,默認使用threadlocal 存儲,意味securitycontext在相同線程中的方法都可用。
securitycontext主要是存儲應用的principal信息,在spring security中用authentication 來表示。
獲取principal:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
object principal = securitycontextholder.getcontext().getauthentication().getprincipal();if (principal instanceof userdetails) {string username = ((userdetails)principal).getusername();} else {string username = principal.tostring();} |
在spring security中,可以看一下authentication定義:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
public interface authentication extends principal, serializable { collection<? extends grantedauthority> getauthorities(); /** * 通常是密碼 */ object getcredentials(); /** * stores additional details about the authentication request. these might be an ip * address, certificate serial number etc. */ object getdetails(); /** * 用來標識是否已認證,如果使用用戶名和密碼登錄,通常是用戶名 */ object getprincipal(); /** * 是否已認證 */ boolean isauthenticated(); void setauthenticated(boolean isauthenticated) throws illegalargumentexception;} |
在實際應用中,通常使用usernamepasswordauthenticationtoken:
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
public abstract class abstractauthenticationtoken implements authentication, credentialscontainer { }public class usernamepasswordauthenticationtoken extends abstractauthenticationtoken {} |
一個常見的認證過程通常是這樣的,創建一個usernamepasswordauthenticationtoken,然后交給authenticationmanager認證(后面詳細說明),認證通過則通過securitycontextholder存放authentication信息。
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
usernamepasswordauthenticationtoken authenticationtoken = new usernamepasswordauthenticationtoken(loginvm.getusername(), loginvm.getpassword());authentication authentication = this.authenticationmanager.authenticate(authenticationtoken);securitycontextholder.getcontext().setauthentication(authentication); |
userdetails與userdetailsservice
userdetails 是spring security里的一個關鍵接口,他用來表示一個principal。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
public interface userdetails extends serializable { /** * 用戶的授權信息,可以理解為角色 */ collection<? extends grantedauthority> getauthorities(); /** * 用戶密碼 * * @return the password */ string getpassword(); /** * 用戶名 * */ string getusername(); boolean isaccountnonexpired(); boolean isaccountnonlocked(); boolean iscredentialsnonexpired(); boolean isenabled();} |
userdetails提供了認證所需的必要信息,在實際使用里,可以自己實現userdetails,并增加額外的信息,比如email、mobile等信息。
在authentication中的principal通常是用戶名,我們可以通過userdetailsservice來通過principal獲取userdetails:
|
1
2
3
|
public interface userdetailsservice { userdetails loaduserbyusername(string username) throws usernamenotfoundexception;} |
grantedauthority
在userdetails里說了,grantedauthority可以理解為角色,例如 role_administrator or role_hr_supervisor。
小結
- securitycontextholder, 用來訪問 securitycontext.
- securitycontext, 用來存儲authentication .
- authentication, 代表憑證.
- grantedauthority, 代表權限.
- userdetails, 用戶信息.
- userdetailsservice,獲取用戶信息.
authentication認證
authenticationmanager
實現認證主要是通過authenticationmanager接口,它只包含了一個方法:
|
1
2
3
4
|
public interface authenticationmanager { authentication authenticate(authentication authentication) throws authenticationexception;} |
authenticate()方法主要做三件事:
- 如果驗證通過,返回authentication(通常帶上authenticated=true)。
- 認證失敗拋出authenticationexception
- 如果無法確定,則返回null
authenticationexception是運行時異常,它通常由應用程序按通用方式處理,用戶代碼通常不用特意被捕獲和處理這個異常。
authenticationmanager的默認實現是providermanager,它委托一組authenticationprovider實例來實現認證。
authenticationprovider和authenticationmanager類似,都包含authenticate,但它有一個額外的方法supports,以允許查詢調用方是否支持給定authentication類型:
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
public interface authenticationprovider { authentication authenticate(authentication authentication) throws authenticationexception; boolean supports(class<?> authentication);} |
providermanager包含一組authenticationprovider,執行authenticate時,遍歷providers,然后調用supports,如果支持,則執行遍歷當前provider的authenticate方法,如果一個provider認證成功,則break。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
|
public authentication authenticate(authentication authentication) throws authenticationexception { class<? extends authentication> totest = authentication.getclass(); authenticationexception lastexception = null; authentication result = null; boolean debug = logger.isdebugenabled(); for (authenticationprovider provider : getproviders()) { if (!provider.supports(totest)) { continue; } if (debug) { logger.debug("authentication attempt using " + provider.getclass().getname()); } try { result = provider.authenticate(authentication); if (result != null) { copydetails(authentication, result); break; } } catch (accountstatusexception e) { prepareexception(e, authentication); // sec-546: avoid polling additional providers if auth failure is due to // invalid account status throw e; } catch (internalauthenticationserviceexception e) { prepareexception(e, authentication); throw e; } catch (authenticationexception e) { lastexception = e; } } if (result == null && parent != null) { // allow the parent to try. try { result = parent.authenticate(authentication); } catch (providernotfoundexception e) { // ignore as we will throw below if no other exception occurred prior to // calling parent and the parent // may throw providernotfound even though a provider in the child already // handled the request } catch (authenticationexception e) { lastexception = e; } } if (result != null) { if (erasecredentialsafterauthentication && (result instanceof credentialscontainer)) { // authentication is complete. remove credentials and other secret data // from authentication ((credentialscontainer) result).erasecredentials(); } eventpublisher.publishauthenticationsuccess(result); return result; } // parent was null, or didn't authenticate (or throw an exception). if (lastexception == null) { lastexception = new providernotfoundexception(messages.getmessage( "providermanager.providernotfound", new object[] { totest.getname() }, "no authenticationprovider found for {0}")); } prepareexception(lastexception, authentication); throw lastexception; } |
從上面的代碼可以看出, providermanager有一個可選parent,如果parent不為空,則調用parent.authenticate(authentication)
authenticationprovider
authenticationprovider有多種實現,大家最關注的通常是daoauthenticationprovider,繼承于abstractuserdetailsauthenticationprovider,核心是通過userdetails來實現認證,daoauthenticationprovider默認會自動加載,不用手動配。
先來看abstractuserdetailsauthenticationprovider,看最核心的authenticate:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
|
public authentication authenticate(authentication authentication) throws authenticationexception { // 必須是usernamepasswordauthenticationtoken assert.isinstanceof(usernamepasswordauthenticationtoken.class, authentication, messages.getmessage( "abstractuserdetailsauthenticationprovider.onlysupports", "only usernamepasswordauthenticationtoken is supported")); // 獲取用戶名 string username = (authentication.getprincipal() == null) ? "none_provided" : authentication.getname(); boolean cachewasused = true; // 從緩存獲取 userdetails user = this.usercache.getuserfromcache(username); if (user == null) { cachewasused = false; try { // retrieveuser 抽象方法,獲取用戶 user = retrieveuser(username, (usernamepasswordauthenticationtoken) authentication); } catch (usernamenotfoundexception notfound) { logger.debug("user '" + username + "' not found"); if (hideusernotfoundexceptions) { throw new badcredentialsexception(messages.getmessage( "abstractuserdetailsauthenticationprovider.badcredentials", "bad credentials")); } else { throw notfound; } } assert.notnull(user, "retrieveuser returned null - a violation of the interface contract"); } try { // 預先檢查,defaultpreauthenticationchecks,檢查用戶是否被lock或者賬號是否可用 preauthenticationchecks.check(user); // 抽象方法,自定義檢驗 additionalauthenticationchecks(user, (usernamepasswordauthenticationtoken) authentication); } catch (authenticationexception exception) { if (cachewasused) { // there was a problem, so try again after checking // we're using latest data (i.e. not from the cache) cachewasused = false; user = retrieveuser(username, (usernamepasswordauthenticationtoken) authentication); preauthenticationchecks.check(user); additionalauthenticationchecks(user, (usernamepasswordauthenticationtoken) authentication); } else { throw exception; } } // 后置檢查 defaultpostauthenticationchecks,檢查iscredentialsnonexpired postauthenticationchecks.check(user); if (!cachewasused) { this.usercache.putuserincache(user); } object principaltoreturn = user; if (forceprincipalasstring) { principaltoreturn = user.getusername(); } return createsuccessauthentication(principaltoreturn, authentication, user); } |
上面的檢驗主要基于userdetails實現,其中獲取用戶和檢驗邏輯由具體的類去實現,默認實現是daoauthenticationprovider,這個類的核心是讓開發者提供userdetailsservice來獲取userdetails以及 passwordencoder來檢驗密碼是否有效:
|
1
2
|
private userdetailsservice userdetailsservice;private passwordencoder passwordencoder; |
看具體的實現,retrieveuser,直接調用userdetailsservice獲取用戶:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
|
protected final userdetails retrieveuser(string username, usernamepasswordauthenticationtoken authentication) throws authenticationexception { userdetails loadeduser; try { loadeduser = this.getuserdetailsservice().loaduserbyusername(username); } catch (usernamenotfoundexception notfound) { if (authentication.getcredentials() != null) { string presentedpassword = authentication.getcredentials().tostring(); passwordencoder.ispasswordvalid(usernotfoundencodedpassword, presentedpassword, null); } throw notfound; } catch (exception repositoryproblem) { throw new internalauthenticationserviceexception( repositoryproblem.getmessage(), repositoryproblem); } if (loadeduser == null) { throw new internalauthenticationserviceexception( "userdetailsservice returned null, which is an interface contract violation"); } return loadeduser; } |
再來看驗證:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
|
protected void additionalauthenticationchecks(userdetails userdetails, usernamepasswordauthenticationtoken authentication) throws authenticationexception { object salt = null; if (this.saltsource != null) { salt = this.saltsource.getsalt(userdetails); } if (authentication.getcredentials() == null) { logger.debug("authentication failed: no credentials provided"); throw new badcredentialsexception(messages.getmessage( "abstractuserdetailsauthenticationprovider.badcredentials", "bad credentials")); } // 獲取用戶密碼 string presentedpassword = authentication.getcredentials().tostring(); // 比較passwordencoder后的密碼是否和userdetails的密碼一致 if (!passwordencoder.ispasswordvalid(userdetails.getpassword(), presentedpassword, salt)) { logger.debug("authentication failed: password does not match stored value"); throw new badcredentialsexception(messages.getmessage( "abstractuserdetailsauthenticationprovider.badcredentials", "bad credentials")); } } |
小結:要自定義認證,使用daoauthenticationprovider,只需要為其提供passwordencoder和userdetailsservice就可以了。
定制 authentication managers
spring security提供了一個builder類authenticationmanagerbuilder,借助它可以快速實現自定義認證。
看官方源碼說明:
securitybuilder used to create an authenticationmanager . allows for easily building in memory authentication, ldap authentication, jdbc based authentication, adding userdetailsservice , and adding authenticationprovider's.
authenticationmanagerbuilder可以用來build一個authenticationmanager,可以創建基于內存的認證、ldap認證、 jdbc認證,以及添加userdetailsservice和authenticationprovider。
簡單使用:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
|
@configuration@enablewebsecurity@enableglobalmethodsecurity(prepostenabled = true, securedenabled = true)public class applicationsecurity extends websecurityconfigureradapter { public securityconfiguration(authenticationmanagerbuilder authenticationmanagerbuilder, userdetailsservice userdetailsservice,tokenprovider tokenprovider,corsfilter corsfilter, securityproblemsupport problemsupport) { this.authenticationmanagerbuilder = authenticationmanagerbuilder; this.userdetailsservice = userdetailsservice; this.tokenprovider = tokenprovider; this.corsfilter = corsfilter; this.problemsupport = problemsupport; } @postconstruct public void init() { try { authenticationmanagerbuilder .userdetailsservice(userdetailsservice) .passwordencoder(passwordencoder()); } catch (exception e) { throw new beaninitializationexception("security configuration failed", e); } } @override protected void configure(httpsecurity http) throws exception { http .addfilterbefore(corsfilter, usernamepasswordauthenticationfilter.class) .exceptionhandling() .authenticationentrypoint(problemsupport) .accessdeniedhandler(problemsupport) .and() .csrf() .disable() .headers() .frameoptions() .disable() .and() .sessionmanagement() .sessioncreationpolicy(sessioncreationpolicy.stateless) .and() .authorizerequests() .antmatchers("/api/register").permitall() .antmatchers("/api/activate").permitall() .antmatchers("/api/authenticate").permitall() .antmatchers("/api/account/reset-password/init").permitall() .antmatchers("/api/account/reset-password/finish").permitall() .antmatchers("/api/profile-info").permitall() .antmatchers("/api/**").authenticated() .antmatchers("/management/health").permitall() .antmatchers("/management/**").hasauthority(authoritiesconstants.admin) .antmatchers("/v2/api-docs/**").permitall() .antmatchers("/swagger-resources/configuration/ui").permitall() .antmatchers("/swagger-ui/index.html").hasauthority(authoritiesconstants.admin) .and() .apply(securityconfigureradapter()); }} |
授權與訪問控制
一旦認證成功,我們可以繼續進行授權,授權是通過accessdecisionmanager來實現的。框架有三種實現,默認是affirmativebased,通過accessdecisionvoter決策,有點像providermanager委托給authenticationproviders來認證。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
|
public void decide(authentication authentication, object object, collection<configattribute> configattributes) throws accessdeniedexception { int deny = 0; // 遍歷decisionvoter for (accessdecisionvoter voter : getdecisionvoters()) { // 投票 int result = voter.vote(authentication, object, configattributes); if (logger.isdebugenabled()) { logger.debug("voter: " + voter + ", returned: " + result); } switch (result) { case accessdecisionvoter.access_granted: return; case accessdecisionvoter.access_denied: deny++; break; default: break; } } // 一票否決 if (deny > 0) { throw new accessdeniedexception(messages.getmessage( "abstractaccessdecisionmanager.accessdenied", "access is denied")); } // to get this far, every accessdecisionvoter abstained checkallowifallabstaindecisions(); } |
來看accessdecisionvoter:
|
1
2
3
4
|
boolean supports(configattribute attribute);boolean supports(class<?> clazz);int vote(authentication authentication, s object, collection<configattribute> attributes); |
object是用戶要訪問的資源,configattribute則是訪問object要滿足的條件,通常payload是字符串,比如role_admin 。所以我們來看下rolevoter的實現,其核心就是從authentication提取出grantedauthority,然后和configattribute比較是否滿足條件。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
|
public boolean supports(configattribute attribute) { if ((attribute.getattribute() != null) && attribute.getattribute().startswith(getroleprefix())) { return true; } else { return false; } } public boolean supports(class<?> clazz) { return true; }public int vote(authentication authentication, object object, collection<configattribute> attributes) { if(authentication == null) { return access_denied; } int result = access_abstain; // 獲取grantedauthority信息 collection<? extends grantedauthority> authorities = extractauthorities(authentication); for (configattribute attribute : attributes) { if (this.supports(attribute)) { // 默認拒絕訪問 result = access_denied; // attempt to find a matching granted authority for (grantedauthority authority : authorities) { // 判斷是否有匹配的 authority if (attribute.getattribute().equals(authority.getauthority())) { // 可訪問 return access_granted; } } } } return result; } |
這里要疑問,configattribute哪來的?其實就是上面applicationsecurity的configure里的。
web security 如何實現
web層中的spring security(用于ui和http后端)基于servlet filters,下圖顯示了單個http請求的處理程序的典型分層。
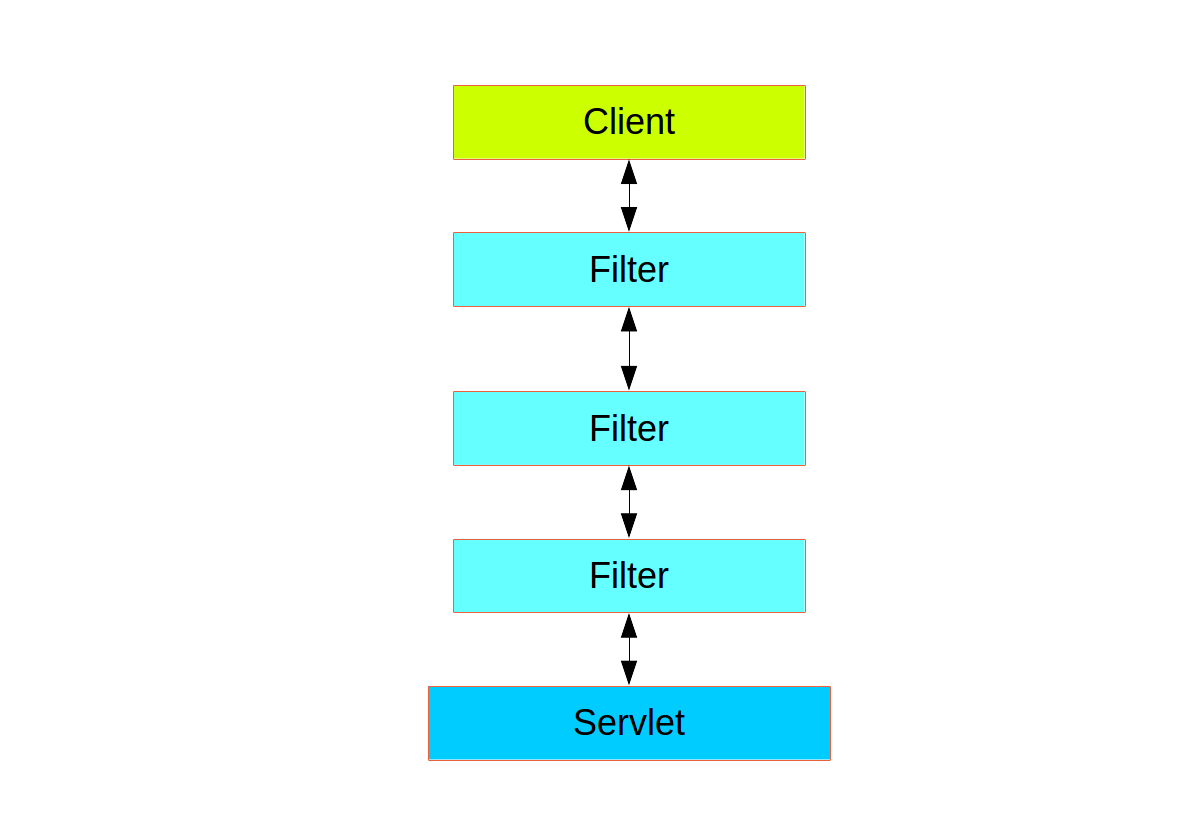
spring security通過filterchainproxy作為單一的filter注冊到web層,proxy內部的filter。

filterchainproxy相當于一個filter的容器,通過virtualfilterchain來依次調用各個內部filter
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
|
public void dofilter(servletrequest request, servletresponse response, filterchain chain) throws ioexception, servletexception { boolean clearcontext = request.getattribute(filter_applied) == null; if (clearcontext) { try { request.setattribute(filter_applied, boolean.true); dofilterinternal(request, response, chain); } finally { securitycontextholder.clearcontext(); request.removeattribute(filter_applied); } } else { dofilterinternal(request, response, chain); } } private void dofilterinternal(servletrequest request, servletresponse response, filterchain chain) throws ioexception, servletexception { firewalledrequest fwrequest = firewall .getfirewalledrequest((httpservletrequest) request); httpservletresponse fwresponse = firewall .getfirewalledresponse((httpservletresponse) response); list<filter> filters = getfilters(fwrequest); if (filters == null || filters.size() == 0) { if (logger.isdebugenabled()) { logger.debug(urlutils.buildrequesturl(fwrequest) + (filters == null ? " has no matching filters" : " has an empty filter list")); } fwrequest.reset(); chain.dofilter(fwrequest, fwresponse); return; } virtualfilterchain vfc = new virtualfilterchain(fwrequest, chain, filters); vfc.dofilter(fwrequest, fwresponse); } private static class virtualfilterchain implements filterchain { private final filterchain originalchain; private final list<filter> additionalfilters; private final firewalledrequest firewalledrequest; private final int size; private int currentposition = 0; private virtualfilterchain(firewalledrequest firewalledrequest, filterchain chain, list<filter> additionalfilters) { this.originalchain = chain; this.additionalfilters = additionalfilters; this.size = additionalfilters.size(); this.firewalledrequest = firewalledrequest; } public void dofilter(servletrequest request, servletresponse response) throws ioexception, servletexception { if (currentposition == size) { if (logger.isdebugenabled()) { logger.debug(urlutils.buildrequesturl(firewalledrequest) + " reached end of additional filter chain; proceeding with original chain"); } // deactivate path stripping as we exit the security filter chain this.firewalledrequest.reset(); originalchain.dofilter(request, response); } else { currentposition++; filter nextfilter = additionalfilters.get(currentposition - 1); if (logger.isdebugenabled()) { logger.debug(urlutils.buildrequesturl(firewalledrequest) + " at position " + currentposition + " of " + size + " in additional filter chain; firing filter: '" + nextfilter.getclass().getsimplename() + "'"); } nextfilter.dofilter(request, response, this); } } } |
參考
https://spring.io/guides/topicals/spring-security-architecture/
https://docs.spring.io/spring-security/site/docs/5.0.5.release/reference/htmlsingle/#overall-architecture
總結
以上就是這篇文章的全部內容了,希望本文的內容對大家的學習或者工作具有一定的參考學習價值,如果有疑問大家可以留言交流,謝謝大家對服務器之家的支持。
原文鏈接:http://www.cnblogs.com/xiaoqi/p/spring-security.html