作為Java程序員Mybatis應該是一個必會框架了,其源碼體量只有Spring 的1/5,也是Hibernate的1/5 ,相比于其他流行框架Mybatis源碼無疑是學習成本最低的,當做年輕人看的第一個框架源碼,無疑是非常好的。
整體架構
對于一個陌生的事物切勿一頭扎進細節里,我們先要觀其大概看看架構脈絡,MyBatis 分為三層架構,分別是基礎支撐層、核心處理層和接口層。
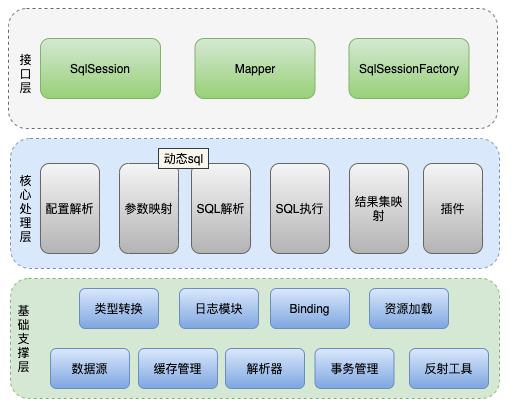
Mybatis 整體架構
基礎支撐層
基礎支撐層是這個Mybatis框架的基建,為整個Mybatis框架提供非常基礎的功能。(篇幅有限下面我們只對部分模塊做簡單的分析)
1.類型轉換模塊,我們在Mybatis中使用< typeAliase >標簽定義一個別名就是使用類型轉換模塊實現的。類型轉換模塊最重要的功能還是實現了Mybatis中JDBC類型和Java類型之間的轉換。主要體現在:
- 在SQL模板綁定用戶參入實參的場景中,將Java類型轉換成JDBC類型
- 在結果集中,將JDBC類型轉換成Java類型。
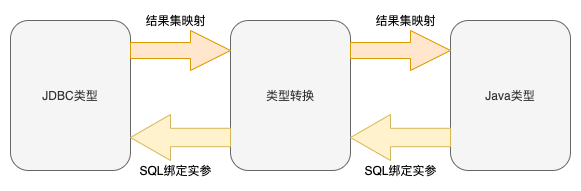
Mybatis類型轉換
2.日志模塊,產生日志,定位異常。
3.反射工具,對原生的Java反射作了一些封裝。
4.Binding模塊,我們在執行Mybatis中的方法時都是通過SqlSession來獲Mapper接口中的代理,這個代理將Mapper.xml文件中SQL進行關聯就是通過Binding模塊來實現的。值得注意點是這個過程是發生在編譯期。可以將錯誤提前到編譯期。
5.數據源模塊,數據源對于一個ORM來說算是非常核心的組件之一了。Mybatis默認的數據源是非常出色的,Mybatis同時也支持集成第三方的數據源。
6.緩存模塊,緩存模塊的好壞直接影響這個ORM的性能。Mybatis提供了兩級緩存,同時也支持第三方緩存中間件集成。
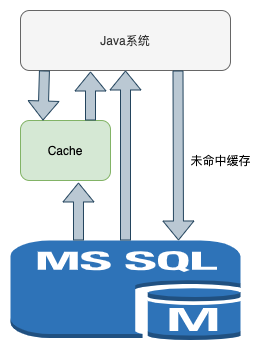
Mybatis緩存
7.解析器模塊,主要是config.xml配置文件解析,和mapper.xml文件解析。
8.事務管理模塊,事務模塊對數據庫的事務機制進行控制,對數據庫事務進行了抽象,同時也對spring框架進行了整合。詳細的處理邏輯下文會結合源碼詳細解析。
核心處理層
核心處理層是我們在學習Mybatis原理的時候需要花80%時間的地方。核心處理層是 MyBatis 核心實現所在,其中涉及 MyBatis 的初始化以及執行一條 SQL 語句的全流程。
配置解析
MyBatis 的初始化以及執行一條 SQL 語句的全流程中也包含了配置解析,我們在現實開發中一般都是使用spring boot starter的自動配置。我們一項目啟動為起點一層一層剝開Mybatis的流程。先打開org.mybatis.spring.boot.autoconfigure.MybatisAutoConfiguration首先明確一點就是MybatisAutoConfiguration的目的就是要得到一個SqlSessionFactory。
- @Bean
- @ConditionalOnMissingBean
- public SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory(DataSource dataSource) throws Exception {
- SqlSessionFactoryBean factory = new SqlSessionFactoryBean();
- factory.setDataSource(dataSource);
- factory.setVfs(SpringBootVFS.class);
- if (StringUtils.hasText(this.properties.getConfigLocation())) {
- factory.setConfigLocation(this.resourceLoader.getResource(this.properties.getConfigLocation()));
- }
- Configuration configuration = this.properties.getConfiguration();
- if (configuration == null && !StringUtils.hasText(this.properties.getConfigLocation())) {
- configuration = new Configuration();
- }
- if (configuration != null && !CollectionUtils.isEmpty(this.configurationCustomizers)) {
- for (ConfigurationCustomizer customizer : this.configurationCustomizers) {
- customizer.customize(configuration);
- }
- }
- factory.setConfiguration(configuration);
- if (this.properties.getConfigurationProperties() != null) {
- factory.setConfigurationProperties(this.properties.getConfigurationProperties());
- }
- if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(this.interceptors)) {
- factory.setPlugins(this.interceptors);
- }
- if (this.databaseIdProvider != null) {
- factory.setDatabaseIdProvider(this.databaseIdProvider);
- }
- if (StringUtils.hasLength(this.properties.getTypeAliasesPackage())) {
- factory.setTypeAliasesPackage(this.properties.getTypeAliasesPackage());
- }
- if (StringUtils.hasLength(this.properties.getTypeHandlersPackage())) {
- factory.setTypeHandlersPackage(this.properties.getTypeHandlersPackage());
- }
- if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(this.properties.resolveMapperLocations())) {
- factory.setMapperLocations(this.properties.resolveMapperLocations());
- }
- return factory.getObject();
- }
這里是通過MybatisProperties里面的配置并放入到SqlSessionFactoryBean中,再由SqlSessionFactoryBean得到SqlSessionFactory。看到最后一行return factory.getObject();我們進去看看這個factory.getObject()的邏輯是如何得到一個SqlSessionFactory。
- @Override
- public SqlSessionFactory getObject() throws Exception {
- if (this.sqlSessionFactory == null) {
- afterPropertiesSet();
- }
- return this.sqlSessionFactory;
- }
這一步沒什么好說的,看看afterPropertiesSet()方法
- @Override
- public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
- notNull(dataSource, "Property 'dataSource' is required");
- notNull(sqlSessionFactoryBuilder, "Property 'sqlSessionFactoryBuilder' is required");
- state((configuration == null && configLocation == null) || !(configuration != null && configLocation != null),
- "Property 'configuration' and 'configLocation' can not specified with together");
- this.sqlSessionFactory = buildSqlSessionFactory();
- }
重點來了,看看這個buildSqlSessionFactory()方法這里的核心目的就是將configurationProperties解析到Configuration對象中。代碼太長了我就不貼出來了, buildSqlSessionFactory()的邏輯我畫了個圖,有興趣的小伙伴自行看一下。

Mybatis配置解析1
我們不要陷入細節之中,我們看看中點看看buildSqlSessionFactory() 方法的最后一行this.sqlSessionFactoryBuilder.build(configuration)點進去
- public SqlSessionFactory build(Configuration config) {
- return new DefaultSqlSessionFactory(config);
- }
通過buildSqlSessionFactory()解析得到的Configuration對象創建一個DefaultSqlSessionFactory(config),到此我們就得到了SqlSessionFactory同時被配置成一個bean了。
我們最終操作都是SqlSession,什么時候會通過SqlSessionFactory得到一個SqlSession呢?
要解決這個問題我們回到最開始的MybatisAutoConfiguration的sqlSessionTemplate(SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory)這個方法,點開SqlSessionTemplate發現它是一個實現了SqlSession到這里我們猜測就是在這里SqlSessionFactory會構建一個SqlSession出來。我們進入new SqlSessionTemplate(sqlSessionFactory)看看源碼。
- public SqlSessionTemplate(SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory) {
- this(sqlSessionFactory, sqlSessionFactory.getConfiguration().getDefaultExecutorType());
- }
再往下看,我們就看到了
- public SqlSessionTemplate(SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory, ExecutorType executorType,
- PersistenceExceptionTranslator exceptionTranslator) {
- notNull(sqlSessionFactory, "Property 'sqlSessionFactory' is required");
- notNull(executorType, "Property 'executorType' is required");
- this.sqlSessionFactory = sqlSessionFactory;
- this.executorType = executorType;
- this.exceptionTranslator = exceptionTranslator;
- this.sqlSessionProxy = (SqlSession) newProxyInstance(
- SqlSessionFactory.class.getClassLoader(),
- new Class[] { SqlSession.class },
- new SqlSessionInterceptor());
- }
這里通過動態代理創建了一個SqlSession。
參數映射、SQL解析
我們先看一下MapperFactoryBean類,這個類實現了FactoryBean在bean初始化的時候會調用getObject()方法我們看看這個類下重寫的getObject()方法里的內容。
- @Override
- public T getObject() throws Exception {
- return getSqlSession().getMapper(this.mapperInterface);
- }
這里調用了sqlSession的getMapper()方法。一層一層點進去里面返回的是一個代理對象。最后的執行是由MapperProxy執行。
- public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
- final MapperProxyFactory<T> mapperProxyFactory = (MapperProxyFactory<T>) knownMappers.get(type);
- if (mapperProxyFactory == null) {
- throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is not known to the MapperRegistry.");
- }
- try {
- return mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession);
- } catch (Exception e) {
- throw new BindingException("Error getting mapper instance. Cause: " + e, e);
- }
- }
接下來的流程我還是畫個流程圖,防止小伙伴們走丟。我這里的內容可能未必完全和小標題一樣,我主要按照sql執行的流程講解的。

Mybatis參數綁定
先看一下MapperProxy中的invoke方法,cachedMapperMethod()方法將MapperMethod緩存起來了。
- @Override
- public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
- try {
- if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
- return method.invoke(this, args);
- } else if (isDefaultMethod(method)) {
- return invokeDefaultMethod(proxy, method, args);
- }
- } catch (Throwable t) {
- throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
- }
- final MapperMethod mapperMethod = cachedMapperMethod(method);
- return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args);
- }
- private MapperMethod cachedMapperMethod(Method method) {
- MapperMethod mapperMethod = methodCache.get(method);
- if (mapperMethod == null) {
- mapperMethod = new MapperMethod(mapperInterface, method, sqlSession.getConfiguration());
- methodCache.put(method, mapperMethod);
- }
- return mapperMethod;
- }
我們在往下看mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args)方法。
- public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
- Object result;
- switch (command.getType()) {
- case INSERT: {
- Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
- result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.insert(command.getName(), param));
- break;
- }
- case UPDATE: {
- Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
- result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.update(command.getName(), param));
- break;
- }
- case DELETE: {
- Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
- result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.delete(command.getName(), param));
- break;
- }
- case SELECT:
- if (method.returnsVoid() && method.hasResultHandler()) {
- executeWithResultHandler(sqlSession, args);
- result = null;
- } else if (method.returnsMany()) {
- result = executeForMany(sqlSession, args);
- } else if (method.returnsMap()) {
- result = executeForMap(sqlSession, args);
- } else if (method.returnsCursor()) {
- result = executeForCursor(sqlSession, args);
- } else {
- Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
- result = sqlSession.selectOne(command.getName(), param);
- }
- break;
- case FLUSH:
- result = sqlSession.flushStatements();
- break;
- default:
- throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + command.getName());
- }
- if (result == null && method.getReturnType().isPrimitive() && !method.returnsVoid()) {
- throw new BindingException("Mapper method '" + command.getName()
- + " attempted to return null from a method with a primitive return type (" + method.getReturnType() + ").");
- }
- return result;
- }
method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args)這里就是處理參數轉換的邏輯。還有很多細節由于篇幅有限以及時間倉促我們不做過多的贅述,感興趣的小伙伴可以結合上面的圖自己看看。下面我們看SQL的執行流程是怎么樣的。整體流程如下圖。

Mybatis執行流程
我們就不對每一個執行器都分析,我只挑一個SimpleExecutor來具體跟一下源碼。我們還是先看看圖吧,防止自己把自己搞蒙。

以simpleExecutor為例的執行流程
- @Override
- public <E> List<E> doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
- Statement stmt = null;
- try {
- Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();
- StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(wrapper, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
- stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog());
- return handler.<E>query(stmt, resultHandler);
- } finally {
- closeStatement(stmt);
- }
- }
這里獲取了Configuration,創建了一個StatementHandler,預處理操作,具體執行的根據創建的預處理方法,最后執行query方法
- @Override
- public <E> List<E> query(Statement statement, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
- String sql = boundSql.getSql();
- statement.execute(sql);
- return resultSetHandler.<E>handleResultSets(statement);
- }
到此我們整理了整個Mybatis的執行流程,分析了其中的源碼,由于篇幅有限很多地方都沒有細致的分析,但是也貼出了圖,希望能幫助到你。
原文鏈接:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/FWGaPN9PV9gcagHS5VyPQA