Pre
本篇博文我們開始梳理下Spring 提供的測試解決方案。
對于 Web 應用程序而言, 一個應用程序中涉及數據層、服務層、Web 層,以及各種外部服務之間的交互關系時,我們除了對各層組件的單元測試之外,還需要充分引入集成測試保證服務的正確性和穩定性。
Spring Boot 中的測試解決方案
和 Spring Boot 1.x 版本一樣,Spring Boot 2.x 也提供了一個用于測試的 spring-boot-starter-test 組件。
在 Spring Boot 中,集成該組件的方法是在 pom 文件中添加如下所示依賴:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId> <scope>test</scope></dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.junit.platform</groupId> <artifactId>junit-platform-launcher</artifactId> <scope>test</scope></dependency> |
其中,最后一個依賴用于導入與 JUnit 相關的功能組件。
然后,通過 Maven 查看 spring-boot-starter-test 組件的依賴關系,我們可以得到如下所示的組件依賴圖:
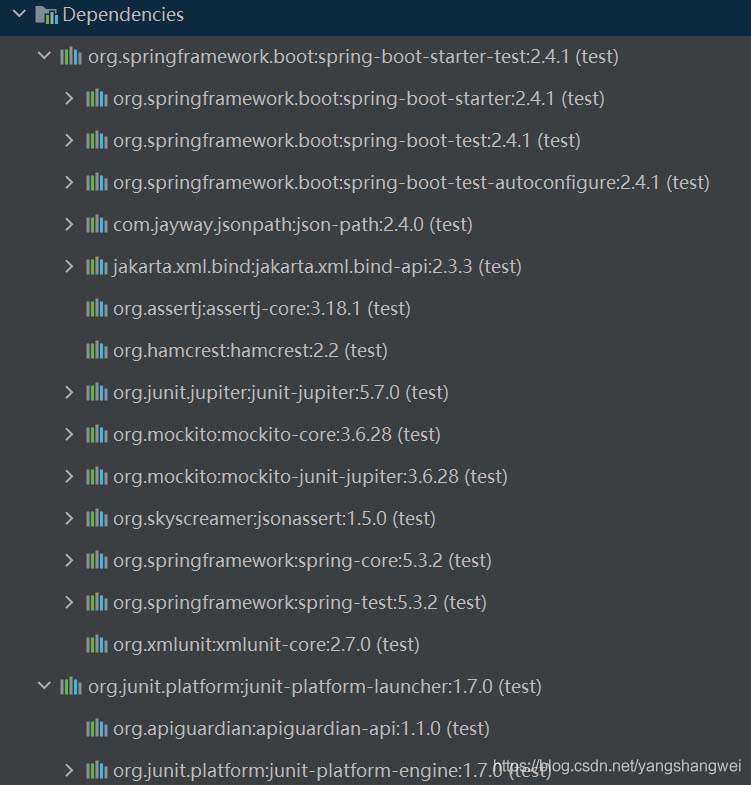
從上圖中可以看到,在代碼工程的構建路徑中,我們引入了一系列組件初始化測試環境。比如 JUnit、JSON Path、AssertJ、Mockito、Hamcrest 等
-
JUnit:JUnit 是一款非常流行的基于 Java 語言的單元測試框架 -
JSON Path:類似于 XPath 在 XML 文檔中的定位,JSON Path 表達式通常用來檢索路徑或設置 JSON 文件中的數據。 -
AssertJ:AssertJ 是一款強大的流式斷言工具,它需要遵守 3A 核心原則,即 Arrange(初始化測試對象或準備測試數據)——> Actor(調用被測方法)——>Assert(執行斷言)。 -
Mockito:Mockito 是 Java 世界中一款流行的 Mock 測試框架,它主要使用簡潔的 API 實現模擬操作。在實施集成測試時,我們將大量使用到這個框架。 -
Hamcrest:Hamcrest 提供了一套匹配器(Matcher),其中每個匹配器的設計用于執行特定的比較操作。 -
JSONassert:JSONassert 是一款專門針對 JSON 提供的斷言框架。 -
Spring Test & Spring Boot Test:為 Spring 和 Spring Boot 框架提供的測試工具。
以上組件的依賴關系都是自動導入, 無須做任何變動。
測試 Spring Boot 應用程序
接下來,我們將初始化 Spring Boot 應用程序的測試環境,并介紹如何在單個服務內部完成單元測試的方法和技巧。
導入 spring-boot-starter-test 依賴后,我們就可以使用它提供的各項功能應對復雜的測試場景了。
初始化測試環境
對于 Spring Boot 應用程序而言,我們知道其 Bootstrap 類中的 main() 入口將通過 SpringApplication.run() 方法啟動 Spring 容器.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;@SpringBootApplicationpublic class Application { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args); }} |
針對上述 Bootstrap 類,我們可以通過編寫測試用例的方式,驗證 Spring 容器能否正常啟動。

基于 Maven 的默認風格,我們將在 src/test/java 和 src/test/resources 包下添加各種測試用例代碼和配置文件。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
import org.junit.Assert;import org.junit.Test;import org.junit.runner.RunWith;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner; @SpringBootTest@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)public class ApplicationContextTests { @Autowired private ApplicationContext applicationContext; @Test public void testContextLoads() throws Throwable { Assert.assertNotNull(this.applicationContext); }} |
該用例對 Spring 中的 ApplicationContext 作了簡單非空驗證。
執行該測試用例后,從輸出的控制臺信息中,我們可以看到 Spring Boot 應用程序被正常啟動,同時測試用例本身也會給出執行成功的提示。
上述測試用例雖然簡單,但是已經包含了測試 Spring Boot 應用程序的基本代碼框架。其中,最重要的是 ApplicationContextTests 類上的 @SpringBootTest 和 @RunWith 注解,對于 Spring Boot 應用程序而言,這兩個注解構成了一套完成的測試方案。
接下來我們對這兩個注解進行詳細展開。
@SpringBootTest
因為 SpringBoot 程序的入口是 Bootstrap 類,所以 SpringBoot 專門提供了一個 @SpringBootTest 注解測試 Bootstrap 類。同時 @SpringBootTest 注解也可以引用 Bootstrap 類的配置,因為所有配置都會通過 Bootstrap 類去加載。
在上面的例子中,我們是通過直接使用 @SpringBootTest 注解提供的默認功能對作為 Bootstrap 類的 Application 類進行測試。
而更常見的做法是在 @SpringBootTest 注解中指定該 Bootstrap 類,并設置測試的 Web 環境,如下代碼所示。
|
1
2
|
@SpringBootTest(classes = CustomerApplication.class, webEnvironment = SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.MOCK) |
在以上代碼中,@SpringBootTest 注解中的 webEnvironment 可以有四個選項,分別是 MOCK、RANDOM_PORT、DEFINED_PORT 和 NONE。
@SpringBootTest - webEnvironment
-
MOCK:加載 WebApplicationContext 并提供一個 Mock 的 Servlet 環境,此時內置的 Servlet 容器并沒有正式啟動。 -
RANDOM_PORT:加載 EmbeddedWebApplicationContext 并提供一個真實的 Servlet 環境,然后使用一個隨機端口啟動內置容器。 -
DEFINED_PORT:這個配置也是通過加載 EmbeddedWebApplicationContext 提供一個真實的 Servlet 環境,但使用的是默認端口,如果沒有配置端口就使用 8080。 -
NONE:加載 ApplicationContext 但并不提供任何真實的 Servlet 環境。
在 Spring Boot 中,@SpringBootTest 注解主要用于測試基于自動配置的 ApplicationContext,它允許我們設置測試上下文中的 Servlet 環境。
在多數場景下,一個真實的 Servlet 環境對于測試而言過于重量級,通過 MOCK 環境則可以緩解這種環境約束所帶來的困擾
@RunWith 注解與 SpringRunner
在上面的示例中,我們還看到一個由 JUnit 框架提供的 @RunWith 注解,它用于設置測試運行器。例如,我們可以通過 @RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class) 讓測試運行于 Spring 測試環境。
雖然這我們指定的是 SpringRunner.class,實際上,SpringRunner 就是 SpringJUnit4ClassRunner 的簡化,它允許 JUnit 和 Spring TestContext 整合運行,而 Spring TestContext 則提供了用于測試 Spring 應用程序的各項通用的支持功能。
執行測試用例
接下來我們將通過代碼示例回顧如何使用 JUnit 框架執行單元測試的過程和實踐,同時提供驗證異常和驗證正確性的測試方法。
單元測試的應用場景是一個獨立的類,如下所示的 CustomerTicket 類就是一個非常典型的獨立類:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
public class CustomTicket { private Long id; private Long accountId; private String orderNumber; private String description; private Date createTime; public CustomTicket (Long accountId, String orderNumber) { super(); Assert.notNull(accountId, "Account Id must not be null"); Assert.notNull(orderNumber, "Order Number must not be null"); Assert.isTrue(orderNumber.length() == 10, "Order Number must be exactly 10 characters"); this.accountId = accountId; this.orderNumber = orderNumber; } …} |
我們可以看到,該類對CustomTicket 做了封裝,并在其構造函數中添加了校驗機制。
下面我們先來看看如何對正常場景進行測試。
例如 ArtisanTicket 中orderNumber 的長度問題,我們可以使用如下測試用例,通過在構造函數中傳入字符串來驗證規則的正確性:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)public class CustomerTicketTests { private static final String ORDER_NUMBER = "Order00001"; @Test public void testOrderNumberIsExactly10Chars() throws Exception { CustomerTicket customerTicket = new CustomerTicket(100L, ORDER_NUMBER); assertThat(customerTicket.getOrderNumber().toString()).isEqualTo(ORDER_NUMBER); }} |
使用 @DataJpaTest 注解測試數據訪問組件
數據需要持久化,接下來我們將從數據持久化的角度出發,討論如何對 Repository 層進行測試的方法。
首先,我們討論一下使用關系型數據庫的場景,并引入針對 JPA 數據訪問技術的 @DataJpaTest 注解。
@DataJpaTest 注解會自動注入各種 Repository 類,并初始化一個內存數據庫和及訪問該數據庫的數據源。在測試場景下,一般我們可以使用 H2 作為內存數據庫,并通過 MySQL 實現數據持久化,因此我們需要引入以下所示的 Maven 依賴:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
<dependency> <groupId>com.h2database</groupId> <artifactId>h2</artifactId></dependency><dependency> <groupId>mysql</groupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> <scope>runtime</scope></dependency> |
另一方面,我們需要準備數據庫 DDL 用于初始化數據庫表,并提供 DML 腳本完成數據初始化。其中,schema-mysql.sql 和 data-h2.sql 腳本分別充當了 DDL 和 DML 的作用。
在 customer-service 的 schema-mysql.sql 中包含了 CUSTOMER 表的創建語句,如下代碼所示:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `customerticket`;create table `customerticket` ( `id` bigint(20) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `account_id` bigint(20) not null, `order_number` varchar(50) not null, `description` varchar(100) not null, `create_time` timestamp not null DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP, PRIMARY KEY (`id`)); |
而在 data-h2.sql 中,我們插入了一條測試需要使用的數據,具體的初始化數據過程如下代碼所示:
|
1
|
INSERT INTO customerticket (`account_id`, `order_number`,`description`) values (1, 'Order00001', ' DemoCustomerTicket1'); |
接下來是提供具體的 Repository 接口,我們先通過如下所示代碼回顧一下 CustomerRepository 接口的定義。
|
1
2
3
|
public interface CustomerTicketRepository extends JpaRepository<CustomerTicket, Long> { List<CustomerTicket> getCustomerTicketByOrderNumber(String orderNumber);} |
這里存在一個方法名衍生查詢 getCustomerTicketByOrderNumber,它會根據 OrderNumber 獲取 CustomerTicket。
基于上述 CustomerRepository,我們可以編寫如下所示的測試用例:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
|
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)@DataJpaTestpublic class CustomerRepositoryTest { @Autowired private TestEntityManager entityManager; @Autowired private CustomerTicketRepository customerTicketRepository; @Test public void testFindCustomerTicketById() throws Exception { this.entityManager.persist(new CustomerTicket(1L, "Order00001", "DemoCustomerTicket1", new Date())); CustomerTicket customerTicket = this.customerTicketRepository.getOne(1L); assertThat(customerTicket).isNotNull(); assertThat(customerTicket.getId()).isEqualTo(1L); } @Test public void testFindCustomerTicketByOrderNumber() throws Exception { String orderNumber = "Order00001"; this.entityManager.persist(new CustomerTicket(1L, orderNumber, "DemoCustomerTicket1", new Date())); this.entityManager.persist(new CustomerTicket(2L, orderNumber, "DemoCustomerTicket2", new Date())); List<CustomerTicket> customerTickets = this.customerTicketRepository.getCustomerTicketByOrderNumber(orderNumber); assertThat(customerTickets).size().isEqualTo(2); CustomerTicket actual = customerTickets.get(0); assertThat(actual.getOrderNumber()).isEqualTo(orderNumber); } @Test public void testFindCustomerTicketByNonExistedOrderNumber() throws Exception { this.entityManager.persist(new CustomerTicket(1L, "Order00001", "DemoCustomerTicket1", new Date())); this.entityManager.persist(new CustomerTicket(2L, "Order00002", "DemoCustomerTicket2", new Date())); List<CustomerTicket> customerTickets = this.customerTicketRepository.getCustomerTicketByOrderNumber("Order00003"); assertThat(customerTickets).size().isEqualTo(0); }} |
這里可以看到,我們使用了 @DataJpaTest 實現 CustomerRepository 的注入。同時,我們還注意到另一個核心測試組件 TestEntityManager,它的效果相當于不使用真正的 CustomerRepository 完成數據的持久化,從而提供了一種數據與環境之間的隔離機制。
執行這些測試用例后,我們需要關注它們的控制臺日志輸入,其中核心日志如下所示(為了顯示做了簡化處理):
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
Hibernate: drop table customer_ticket if existsHibernate: drop sequence if exists hibernate_sequenceHibernate: create sequence hibernate_sequence start with 1 increment by 1Hibernate: create table customer_ticket (id bigint not null, account_id bigint, create_time timestamp, description varchar(255), order_number varchar(255), primary key (id))Hibernate: create table localaccount (id bigint not null, account_code varchar(255), account_name varchar(255), primary key (id))…Hibernate: call next value for hibernate_sequenceHibernate: call next value for hibernate_sequenceHibernate: insert into customer_ticket (account_id, create_time, description, order_number, id) values (?, ?, ?, ?, ?)Hibernate: insert into customer_ticket (account_id, create_time, description, order_number, id) values (?, ?, ?, ?, ?)Hibernate: select customerti0_.id as id1_0_, customerti0_.account_id as account_2_0_, customerti0_.create_time as create_t3_0_, customerti0_.description as descript4_0_, customerti0_.order_number as order_nu5_0_ from customer_ticket customerti0_ where customerti0_.order_number=?…Hibernate: drop table customer_ticket if existsHibernate: drop sequence if exists hibernate_sequence |
從以上日志中,我們不難看出執行各種 SQL 語句的效果。
Service層和Controller的測試
與位于底層的數據訪問層不同,這兩層的組件都依賴于它的下一層組件,即 Service 層依賴于數據訪問層,而 Controller 層依賴于 Service 層。因此,對這兩層進行測試時,我們將使用不同的方案和技術。
使用 Environment 測試配置信息
在 Spring Boot 應用程序中,Service 層通常依賴于配置文件,所以我們也需要對配置信息進行測試。
配置信息的測試方案分為兩種,第一種依賴于物理配置文件,第二種則是在測試時動態注入配置信息。
第一種測試方案比較簡單,在 src/test/resources 目錄下添加配置文件時,Spring Boot 能讀取這些配置文件中的配置項并應用于測試案例中。
在介紹具體的實現過程之前,我們有必要先來了解一下 Environment 接口,該接口定義如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
public interface Environment extends PropertyResolver { String[] getActiveProfiles(); String[] getDefaultProfiles(); boolean acceptsProfiles(String... profiles);} |
在上述代碼中我們可以看到,Environment 接口的主要作用是處理 Profile,而它的父接口 PropertyResolver 定義如下代碼所示:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
public interface PropertyResolver { boolean containsProperty(String key); String getProperty(String key); String getProperty(String key, String defaultValue); <T> T getProperty(String key, Class<T> targetType); <T> T getProperty(String key, Class<T> targetType, T defaultValue); String getRequiredProperty(String key) throws IllegalStateException; <T> T getRequiredProperty(String key, Class<T> targetType) throws IllegalStateException; String resolvePlaceholders(String text); String resolveRequiredPlaceholders(String text) throws IllegalArgumentException;} |
顯然,PropertyResolver 的作用是根據各種配置項的 Key 獲取配置屬性值。
現在,假設 src/test/resources 目錄中的 application.properties 存在如下配置項:
|
1
|
springcss.order.point = 10 |
那么,我們就可以設計如下所示的測試用例了。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)@SpringBootTestpublic class EnvironmentTests{ @Autowired public Environment environment; @Test public void testEnvValue(){ Assert.assertEquals(10, Integer.parseInt(environment.getProperty("springcss.order.point"))); }} |
這里我們注入了一個 Environment 接口,并調用了它的 getProperty 方法來獲取測試環境中的配置信息。
除了在配置文件中設置屬性,我們也可以使用 @SpringBootTest 注解指定用于測試的屬性值,示例代碼如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)@SpringBootTest(properties = {" springcss.order.point = 10"})public class EnvironmentTests{ @Autowired public Environment environment; @Test public void testEnvValue(){ Assert.assertEquals(10, Integer.parseInt(environment.getProperty("springcss.order.point"))); }} |
使用 Mock 測試 Service 層
Service 層依賴于數據訪問層。因此,對 Service 層進行測試時,我們還需要引入新的技術體系,也就是應用非常廣泛的 Mock 機制。
接下來,我們先看一下 Mock 機制的基本概念。
Mock 機制
Mock 的意思是模擬,它可以用來對系統、組件或類進行隔離。
在測試過程中,我們通常關注測試對象本身的功能和行為,而對測試對象涉及的一些依賴,僅僅關注它們與測試對象之間的交互(比如是否調用、何時調用、調用的參數、調用的次數和順序,以及返回的結果或發生的異常等),并不關注這些被依賴對象如何執行這次調用的具體細節。
因此,Mock 機制就是使用 Mock 對象替代真實的依賴對象,并模擬真實場景來開展測試工作。
使用 Mock 對象完成依賴關系測試的示意圖如下所示:
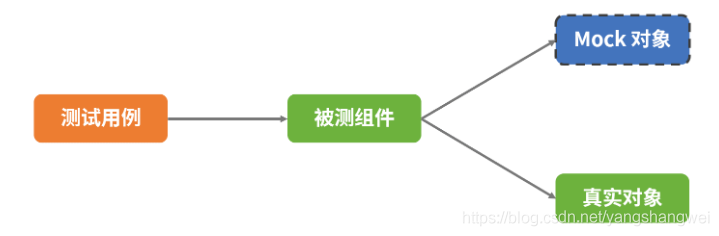
可以看出,在形式上,Mock 是在測試代碼中直接 Mock 類和定義 Mock 方法的行為,通常測試代碼和 Mock 代碼放一起。因此,測試代碼的邏輯從測試用例的代碼上能很容易地體現出來。
下面我們一起看一下如何使用 Mock 測試 Service 層。
使用 Mock
@SpringBootTest 注解中的 SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.MOCK 選項,該選項用于加載 WebApplicationContext 并提供一個 Mock 的 Servlet 環境,內置的 Servlet 容器并沒有真實啟動。接下來,我們針對 Service 層演示一下這種測試方式。
首先,我們來看一種簡單場景,在 customer-service 中存在如下 CustomerTicketService 類:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
@Servicepublic class CustomerTicketService { @Autowired private CustomerTicketRepository customerTicketRepository; public CustomerTicket getCustomerTicketById(Long id) { return customerTicketRepository.getOne(id); } …} |
這里我們可以看到,以上方法只是簡單地通過 CustomerTicketRepository 完成了數據查詢操作。
顯然,對以上 CustomerTicketService 進行集成測試時,還需要我們提供一個 CustomerTicketRepository 依賴。
下面,我們通過以下代碼演示一下如何使用 Mock 機制完成對 CustomerTicketRepository 的隔離。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)@SpringBootTest(webEnvironment = SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.MOCK)public class CustomerServiceTests { @MockBean private CustomerTicketRepository customerTicketRepository; @Test public void testGetCustomerTicketById() throws Exception { Long id = 1L; Mockito.when(customerTicketRepository.getOne(id)).thenReturn(new CustomerTicket(1L, 1L, "Order00001", "DemoCustomerTicket1", new Date())); CustomerTicket actual = customerTicketService.getCustomerTicketById(id); assertThat(actual).isNotNull(); assertThat(actual.getOrderNumber()).isEqualTo("Order00001"); }} |
首先,我們通過 @MockBean 注解注入了 CustomerTicketRepository;然后,基于第三方 Mock 框架 Mockito 提供的 when/thenReturn 機制完成了對 CustomerTicketRepository 中 getCustomerTicketById() 方法的 Mock。
當然,如果你希望在測試用例中直接注入真實的CustomerTicketRepository,這時就可以使用@SpringBootTest 注解中的 SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.RANDOM_PORT 選項,示例代碼如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)@SpringBootTest(webEnvironment = SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.RANDOM_PORT)public class CustomerServiceTests { @Autowired private CustomerTicketRepository customerTicketRepository; @Test public void testGetCustomerTicketById() throws Exception { Long id = 1L; CustomerTicket actual = customerTicketService.getCustomerTicketById(id); assertThat(actual).isNotNull(); assertThat(actual.getOrderNumber()).isEqualTo("Order00001"); }} |
運行上述代碼后就會以一個隨機的端口啟動整個 Spring Boot 工程,并從數據庫中真實獲取目標數據進行驗證。
以上集成測試的示例中只包含了對 Repository 層的依賴,而有時候一個 Service 中可能同時包含 Repository 和其他 Service 類或組件,下面回到如下所示的 CustomerTicketService 類:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
@Servicepublic class CustomerTicketService { @Autowired private OrderClient orderClient; private OrderMapper getRemoteOrderByOrderNumber(String orderNumber) { return orderClient.getOrderByOrderNumber(orderNumber); } …} |
這里我們可以看到,在該代碼中,除了依賴 CustomerTicketRepository 之外,還同時依賴了 OrderClient。
請注意:以上代碼中的 OrderClient 是在 customer-service 中通過 RestTemplate 訪問 order-service 的遠程實現類,其代碼如下所示:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
@Componentpublic class OrderClient { @Autowired RestTemplate restTemplate; public OrderMapper getOrderByOrderNumber(String orderNumber) { ResponseEntity<OrderMapper> restExchange = restTemplate.exchange( "http://localhost:8083/orders/{orderNumber}", HttpMethod.GET, null, OrderMapper.class, orderNumber); OrderMapper result = restExchange.getBody(); return result; }} |
CustomerTicketService 類實際上并不關注 OrderClient 中如何實現遠程訪問的具體過程。因為對于集成測試而言,它只關注方法調用返回的結果,所以我們將同樣采用 Mock 機制完成對 OrderClient 的隔離。
對 CustomerTicketService 這部分功能的測試用例代碼如下所示,可以看到,我們采用的是同樣的測試方式。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
@Testpublic void testGenerateCustomerTicket() throws Exception { Long accountId = 100L; String orderNumber = "Order00001"; Mockito.when(this.orderClient.getOrderByOrderNumber("Order00001")) .thenReturn(new OrderMapper(1L, orderNumber, "deliveryAddress")); Mockito.when(this.localAccountRepository.getOne(accountId)) .thenReturn(new LocalAccount(100L, "accountCode", "accountName")); CustomerTicket actual = customerTicketService.generateCustomerTicket(accountId, orderNumber); assertThat(actual.getOrderNumber()).isEqualTo(orderNumber);} |
這里提供的測試用例演示了 Service 層中進行集成測試的各種手段,它們已經能夠滿足一般場景的需要。
測試 Controller 層
對 Controller 層進行測試之前,我們先來提供一個典型的 Controller 類,它來自 customer-service,如下代碼所示:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
@RestController@RequestMapping(value="customers")public class CustomerController { @Autowired private CustomerTicketService customerTicketService; @PostMapping(value = "/{accountId}/{orderNumber}") public CustomerTicket generateCustomerTicket( @PathVariable("accountId") Long accountId, @PathVariable("orderNumber") String orderNumber) { CustomerTicket customerTicket = customerTicketService.generateCustomerTicket(accountId, orderNumber); return customerTicket; }} |
關于上述 Controller 類的測試方法,相對來說比較豐富,比如有 TestRestTemplate、@WebMvcTest 注解和 MockMvc 這三種,下面我們逐一進行講解。
使用 TestRestTemplate
Spring Boot 提供的 TestRestTemplate 與 RestTemplate 非常類似,只不過它專門用在測試環境中。
如果我們想在測試環境中使用 @SpringBootTest,則可以直接使用 TestRestTemplate 來測試遠程訪問過程,示例代碼如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)@SpringBootTest(webEnvironment = SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.RANDOM_PORT)public class CustomerController2Tests { @Autowired private TestRestTemplate testRestTemplate; @MockBean private CustomerTicketService customerTicketService; @Test public void testGenerateCustomerTicket() throws Exception { Long accountId = 100L; String orderNumber = "Order00001"; given(this.customerTicketService.generateCustomerTicket(accountId, orderNumber)) .willReturn(new CustomerTicket(1L, accountId, orderNumber, "DemoCustomerTicket1", new Date())); CustomerTicket actual = testRestTemplate.postForObject("/customers/" + accountId+ "/" + orderNumber, null, CustomerTicket.class); assertThat(actual.getOrderNumber()).isEqualTo(orderNumber); }} |
上述測試代碼中,首先,我們注意到 @SpringBootTest 注解通過使用 SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.RANDOM_PORT 指定了隨機端口的 Web 運行環境。然后,我們基于 TestRestTemplate 發起了 HTTP 請求并驗證了結果。
特別說明:這里使用 TestRestTemplate 發起請求的方式與 RestTemplate 完全一致
使用 @WebMvcTest 注解
接下來測試方法中,我們將引入一個新的注解 @WebMvcTest,該注解將初始化測試 Controller 所必需的 Spring MVC 基礎設施,CustomerController 類的測試用例如下所示:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)@WebMvcTest(CustomerController.class)public class CustomerControllerTestsWithMockMvc { @Autowired private MockMvc mvc; @MockBean private CustomerTicketService customerTicketService; @Test public void testGenerateCustomerTicket() throws Exception { Long accountId = 100L; String orderNumber = "Order00001"; given(this.customerTicketService.generateCustomerTicket(accountId, orderNumber)) .willReturn(new CustomerTicket(1L, 100L, "Order00001", "DemoCustomerTicket1", new Date())); this.mvc.perform(post("/customers/" + accountId+ "/" + orderNumber).accept(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)).andExpect(status().isOk()); }} |
MockMvc 類提供的基礎方法分為以下 6 種,下面一一對應來看下。
-
Perform:執行一個 RequestBuilder 請求,會自動執行 SpringMVC 流程并映射到相應的 Controller 進行處理。 -
get/post/put/delete:聲明發送一個 HTTP 請求的方式,根據 URI 模板和 URI 變量值得到一個 HTTP 請求,支持 GET、POST、PUT、DELETE 等 HTTP 方法。 -
param:添加請求參數,發送 JSON 數據時將不能使用這種方式,而應該采用 @ResponseBody 注解。 -
andExpect:添加 ResultMatcher 驗證規則,通過對返回的數據進行判斷來驗證 Controller 執行結果是否正確。 -
andDo:添加 ResultHandler 結果處理器,比如調試時打印結果到控制臺。 -
andReturn:最后返回相應的 MvcResult,然后執行自定義驗證或做異步處理。
執行該測試用例后,從輸出的控制臺日志中我們不難發現,整個流程相當于啟動了 CustomerController 并執行遠程訪問,而 CustomerController 中使用的 CustomerTicketService 則做了 Mock。
顯然,測試 CustomerController 的目的在于驗證其返回數據的格式和內容。在上述代碼中,我們先定義了 CustomerController 將會返回的 JSON 結果,然后通過 perform、accept 和 andExpect 方法模擬了 HTTP 請求的整個過程,最終驗證了結果的正確性。
請注意 @SpringBootTest 注解不能和 @WebMvcTest 注解同時使用。
使用 @AutoConfigureMockMvc 注解
在使用 @SpringBootTest 注解的場景下,如果我們想使用 MockMvc 對象,那么可以引入 @AutoConfigureMockMvc 注解。
通過將 @SpringBootTest 注解與 @AutoConfigureMockMvc 注解相結合,@AutoConfigureMockMvc 注解將通過 @SpringBootTest 加載的 Spring 上下文環境中自動配置 MockMvc 這個類。
使用 @AutoConfigureMockMvc 注解的測試代碼如下所示:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)@SpringBootTest@AutoConfigureMockMvcpublic class CustomerControllerTestsWithAutoConfigureMockMvc { @Autowired private MockMvc mvc; @MockBean private CustomerTicketService customerTicketService; @Test public void testGenerateCustomerTicket() throws Exception { Long accountId = 100L; String orderNumber = "Order00001"; given(this.customerTicketService.generateCustomerTicket(accountId, orderNumber)) .willReturn(new CustomerTicket(1L, 100L, "Order00001", "DemoCustomerTicket1", new Date())); this.mvc.perform(post("/customers/" + accountId+ "/" + orderNumber).accept(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)).andExpect(status().isOk()); }} |
在上述代碼中,我們使用了 MockMvc 工具類完成了對 HTTP 請求的模擬,并基于返回狀態驗證了 Controller 層組件的正確性。
小結

以上為個人經驗,希望能給大家一個參考,也希望大家多多支持服務器之家。
原文鏈接:https://blog.csdn.net/yangshangwei/article/details/117231037















