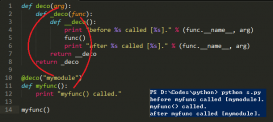
在pytorch下,以數萬首唐詩為素材,訓練雙層LSTM神經網絡,使其能夠以唐詩的方式寫詩。
代碼結構分為四部分,分別為
1.model.py,定義了雙層LSTM模型
2.data.py,定義了從網上得到的唐詩數據的處理方法
3.utlis.py 定義了損失可視化的函數
4.main.py定義了模型參數,以及訓練、唐詩生成函數。
參考:電子工業出版社的《深度學習框架PyTorch:入門與實踐》第九章
main代碼及注釋如下
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
227
228
229
230
231
232
233
234
235
|
import sys, osimport torch as tfrom data import get_datafrom model import PoetryModelfrom torch import nnfrom torch.autograd import Variablefrom utils import Visualizerimport tqdmfrom torchnet import meterimport ipdb class Config(object): data_path = 'data/' pickle_path = 'tang.npz' author = None constrain = None category = 'poet.tang' #or poet.song lr = 1e-3 weight_decay = 1e-4 use_gpu = True epoch = 20 batch_size = 128 maxlen = 125 plot_every = 20 #use_env = True #是否使用visodm env = 'poety' #visdom env max_gen_len = 200 debug_file = '/tmp/debugp' model_path = None prefix_words = '細雨魚兒出,微風燕子斜。' #不是詩歌組成部分,是意境 start_words = '閑云潭影日悠悠' #詩歌開始 acrostic = False #是否藏頭 model_prefix = 'checkpoints/tang' #模型保存路徑opt = Config() def generate(model, start_words, ix2word, word2ix, prefix_words=None): ''' 給定幾個詞,根據這幾個詞接著生成一首完整的詩歌 ''' results = list(start_words) start_word_len = len(start_words) # 手動設置第一個詞為<START> # 這個地方有問題,最后需要再看一下 input = Variable(t.Tensor([word2ix['<START>']]).view(1,1).long()) if opt.use_gpu:input=input.cuda() hidden = None if prefix_words: for word in prefix_words: output,hidden = model(input,hidden) # 下邊這句話是為了把input變成1*1? input = Variable(input.data.new([word2ix[word]])).view(1,1) for i in range(opt.max_gen_len): output,hidden = model(input,hidden) if i<start_word_len: w = results[i] input = Variable(input.data.new([word2ix[w]])).view(1,1) else: top_index = output.data[0].topk(1)[1][0] w = ix2word[top_index] results.append(w) input = Variable(input.data.new([top_index])).view(1,1) if w=='<EOP>': del results[-1] #-1的意思是倒數第一個 break return results def gen_acrostic(model,start_words,ix2word,word2ix, prefix_words = None): ''' 生成藏頭詩 start_words : u'深度學習' 生成: 深木通中岳,青苔半日脂。 度山分地險,逆浪到南巴。 學道兵猶毒,當時燕不移。 習根通古岸,開鏡出清羸。 ''' results = [] start_word_len = len(start_words) input = Variable(t.Tensor([word2ix['<START>']]).view(1,1).long()) if opt.use_gpu:input=input.cuda() hidden = None index=0 # 用來指示已經生成了多少句藏頭詩 # 上一個詞 pre_word='<START>' if prefix_words: for word in prefix_words: output,hidden = model(input,hidden) input = Variable(input.data.new([word2ix[word]])).view(1,1) for i in range(opt.max_gen_len): output,hidden = model(input,hidden) top_index = output.data[0].topk(1)[1][0] w = ix2word[top_index] if (pre_word in {u'。',u'!','<START>'} ): # 如果遇到句號,藏頭的詞送進去生成 if index==start_word_len: # 如果生成的詩歌已經包含全部藏頭的詞,則結束 break else: # 把藏頭的詞作為輸入送入模型 w = start_words[index] index+=1 input = Variable(input.data.new([word2ix[w]])).view(1,1) else: # 否則的話,把上一次預測是詞作為下一個詞輸入 input = Variable(input.data.new([word2ix[w]])).view(1,1) results.append(w) pre_word = w return results def train(**kwargs): for k,v in kwargs.items(): setattr(opt,k,v) #設置apt里屬性的值 vis = Visualizer(env=opt.env) #獲取數據 data, word2ix, ix2word = get_data(opt) #get_data是data.py里的函數 data = t.from_numpy(data) #這個地方出錯了,是大寫的L dataloader = t.utils.data.DataLoader(data, batch_size = opt.batch_size, shuffle = True, num_workers = 1) #在python里,這樣寫程序可以嗎? #模型定義 model = PoetryModel(len(word2ix), 128, 256) optimizer = t.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=opt.lr) criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss() if opt.model_path: model.load_state_dict(t.load(opt.model_path)) if opt.use_gpu: model.cuda() criterion.cuda() #The tnt.AverageValueMeter measures and returns the average value #and the standard deviation of any collection of numbers that are #added to it. It is useful, for instance, to measure the average #loss over a collection of examples. #The add() function expects as input a Lua number value, which #is the value that needs to be added to the list of values to #average. It also takes as input an optional parameter n that #assigns a weight to value in the average, in order to facilitate #computing weighted averages (default = 1). #The tnt.AverageValueMeter has no parameters to be set at initialization time. loss_meter = meter.AverageValueMeter() for epoch in range(opt.epoch): loss_meter.reset() for ii,data_ in tqdm.tqdm(enumerate(dataloader)): #tqdm是python中的進度條 #訓練 data_ = data_.long().transpose(1,0).contiguous() #上邊一句話,把data_變成long類型,把1維和0維轉置,把內存調成連續的 if opt.use_gpu: data_ = data_.cuda() optimizer.zero_grad() input_, target = Variable(data_[:-1,:]), Variable(data_[1:,:]) #上邊一句,將輸入的詩句錯開一個字,形成訓練和目標 output,_ = model(input_) loss = criterion(output, target.view(-1)) loss.backward() optimizer.step() loss_meter.add(loss.data[0]) #為什么是data[0]? #可視化用到的是utlis.py里的函數 if (1+ii)%opt.plot_every ==0: if os.path.exists(opt.debug_file): ipdb.set_trace() vis.plot('loss',loss_meter.value()[0]) # 下面是對目前模型情況的測試,詩歌原文 poetrys = [[ix2word[_word] for _word in data_[:,_iii]] for _iii in range(data_.size(1))][:16] #上面句子嵌套了兩個循環,主要是將詩歌索引的前十六個字變成原文 vis.text('</br>'.join([''.join(poetry) for poetry in poetrys]),win = u'origin_poem') gen_poetries = [] #分別以以下幾個字作為詩歌的第一個字,生成8首詩 for word in list(u'春江花月夜涼如水'): gen_poetry = ''.join(generate(model,word,ix2word,word2ix)) gen_poetries.append(gen_poetry) vis.text('</br>'.join([''.join(poetry) for poetry in gen_poetries]), win = u'gen_poem') t.save(model.state_dict(), '%s_%s.pth' %(opt.model_prefix,epoch)) def gen(**kwargs): ''' 提供命令行接口,用以生成相應的詩 ''' for k,v in kwargs.items(): setattr(opt,k,v) data, word2ix, ix2word = get_data(opt) model = PoetryModel(len(word2ix), 128, 256) map_location = lambda s,l:s # 上邊句子里的map_location是在load里用的,用以加載到指定的CPU或GPU, # 上邊句子的意思是將模型加載到默認的GPU上 state_dict = t.load(opt.model_path, map_location = map_location) model.load_state_dict(state_dict) if opt.use_gpu: model.cuda() if sys.version_info.major == 3: if opt.start_words.insprintable(): start_words = opt.start_words prefix_words = opt.prefix_words if opt.prefix_words else None else: start_words = opt.start_words.encode('ascii',\ 'surrogateescape').decode('utf8') prefix_words = opt.prefix_words.encode('ascii',\ 'surrogateescape').decode('utf8') if opt.prefix_words else None start_words = start_words.replace(',',u',')\ .replace('.',u'。')\ .replace('?',u'?') gen_poetry = gen_acrostic if opt.acrostic else generate result = gen_poetry(model,start_words,ix2word,word2ix,prefix_words) print(''.join(result))if __name__ == '__main__': import fire fire.Fire() |
以上代碼給我一些經驗,
1. 了解python的編程方式,如空格、換行等;進一步了解python的各個基本模塊;
2. 可能出的錯誤:函數名寫錯,大小寫,變量名寫錯,括號不全。
3. 對cuda()的用法有了進一步認識;
4. 學會了調試程序(fire);
5. 學會了訓練結果的可視化(visdom);
6. 進一步的了解了LSTM,對深度學習的架構、實現有了宏觀把控。
這篇pytorch下使用LSTM神經網絡寫詩實例就是小編分享給大家的全部內容了,希望能給大家一個參考,也希望大家多多支持服務器之家。
原文鏈接:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_39845112/article/details/80045091