Mongo DB ,是目前在IT行業(yè)非常流行的一種非關(guān)系型數(shù)據(jù)庫(NoSql),其靈活的數(shù)據(jù)存儲(chǔ)方式,備受當(dāng)前IT從業(yè)人員的青睞。Mongo DB很好的實(shí)現(xiàn)了面向?qū)ο蟮乃枷?OO思想),在Mongo DB中 每一條記錄都是一個(gè)Document對象。Mongo DB最大的優(yōu)勢在于所有的數(shù)據(jù)持久操作都無需開發(fā)人員手動(dòng)編寫SQL語句,直接調(diào)用方法就可以輕松的實(shí)現(xiàn)CRUD操作。
一、下載mongodb
前往mongodb官網(wǎng)下載頁面:https://www.mongodb.org/downloads下載相應(yīng)的版本,比如目前的Linux x64位最新版:mongodb-linux-x86_64-2.6.4.tgz
不過有點(diǎn)坑爹是,下載鏈接明明是tgz格式,結(jié)果下載后變成了gz格式:
先下載看看好了。
二、解壓mongodb
|
1
|
[root@test6 ~]# gzip -d mongodb-linux-x86_64-2.6.4.gz |
得到的是mongodb-linux-x86_64-2.6.4,居然是個(gè)文件,而不是文件夾,和網(wǎng)上說的大相徑庭:

看來前面下載的確實(shí)存在問題!實(shí)際上應(yīng)該是tgz文件才對,按經(jīng)驗(yàn)分析了一下,下載的實(shí)際上還是tgz文件,顯示為gz文件只是形式上的假象!所以,gzip只解壓了壓縮包的外層,實(shí)際上還需要解壓一層tar存檔屬性!
于是,先將解壓后的文件重命名加上tar格式:
|
1
|
[root@test6 ~]# mv mongodb-linux-x86_64-2.6.4 mongodb-linux-x86_64-2.6.4.tar |
然后,使用tar解壓即可:
|
1
|
[root@test6 ~]# tar xvf mongodb-linux-x86_64-2.6.4.tar |

將解壓后的文件夾移動(dòng)&重命名至/usr/local/mongodb
|
1
2
3
|
[root@test6 ~]# mv mongodb-linux-x86_64-2.6.4 /usr/local/mongodb[root@test6 ~]# cd /usr/local/mongodb/bin/[root@test6 ~]# ll |

bin下的mongod就是MongoDB的服務(wù)端進(jìn)程,mongo就是其客戶端,其它的命令用于MongoDB的其它用途如MongoDB文件導(dǎo)出等。
三、啟動(dòng)mongodb
啟動(dòng)前,先指定mongodb的data目錄,如果沒有就創(chuàng)建一個(gè):
|
1
2
|
[root@test6 ~]# cd /usr/local/mongodb[root@test6 mongodb]# mkdir data |
然后,執(zhí)行如下命令即可啟動(dòng)mongodb:
|
1
|
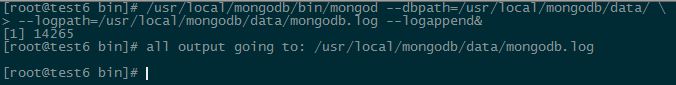
[root@test6 mongodb]# /usr/local/mongodb/bin/mongod --dbpath=/usr/local/mongodb/data/ --logpath=/usr/local/mongodb/data/mongodb.log --logappend& |
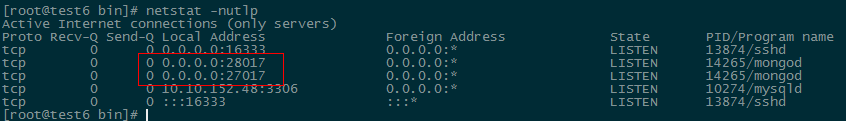
啟動(dòng)成功后,可查看是否啟動(dòng)成功了,默認(rèn)端口號(hào)是27017,當(dāng)然在啟動(dòng)時(shí)也可以指定未使用的其它端口。
最后,將客戶端mogo文件在/bin下軟鏈接,方便隨處執(zhí)行:
|
1
|
ln -s /usr/local/mongodb/bin/mongo /bin/mongo |

現(xiàn)在使用mongo客戶端訪問一下該數(shù)據(jù)庫:
|
1
2
3
4
|
[root@test6 bin]# ./mongoMongoDB shell version: 2.6.4connecting to: test> |
安裝成功!
四、附:基本操作
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
227
228
229
230
231
232
233
234
235
236
237
238
239
240
241
242
243
244
245
246
247
248
249
250
251
252
253
254
255
256
257
258
259
260
261
262
263
264
265
266
267
268
269
270
271
272
273
274
275
276
277
278
279
280
281
282
283
284
285
286
287
288
289
290
291
292
293
294
295
296
297
298
299
300
301
302
303
304
305
306
307
308
309
310
311
|
MongoDB數(shù)據(jù)庫基本用法show dbs:顯示數(shù)據(jù)庫列表 show collections:顯示當(dāng)前數(shù)據(jù)庫中的集合(類似關(guān)系數(shù)據(jù)庫中的表) show users:顯示用戶use <db name>:切換當(dāng)前數(shù)據(jù)庫,這和MS-SQL里面的意思一樣 db.help():顯示數(shù)據(jù)庫操作命令,里面有很多的命令 db.foo.help():顯示集合操作命令,同樣有很多的命令,foo指的是當(dāng)前數(shù)據(jù)庫下,一個(gè)叫foo的集合,并非真正意義上的命令 db.foo.find():對于當(dāng)前數(shù)據(jù)庫中的foo集合進(jìn)行數(shù)據(jù)查找(由于沒有條件,會(huì)列出所有數(shù)據(jù)) db.foo.find( { a : 1 } ):對于當(dāng)前數(shù)據(jù)庫中的foo集合進(jìn)行查找,條件是數(shù)據(jù)中有一個(gè)屬性叫a,且a的值為1MongoDB沒有創(chuàng)建數(shù)據(jù)庫的命令,但有類似的命令。如:如果你想創(chuàng)建一個(gè)“myTest”的數(shù)據(jù)庫,先運(yùn)行use myTest命令,之后就做一些操作(如:db.createCollection('user')),這樣就可以創(chuàng)建一個(gè)名叫“myTest”的數(shù)據(jù)庫。數(shù)據(jù)庫常用命令1、Help查看命令提示 help db.help(); db.yourColl.help(); db.youColl.find().help(); rs.help();2、切換/創(chuàng)建數(shù)據(jù)庫 use yourDB; 當(dāng)創(chuàng)建一個(gè)集合(table)的時(shí)候會(huì)自動(dòng)創(chuàng)建當(dāng)前數(shù)據(jù)庫3、查詢所有數(shù)據(jù)庫 show dbs;4、刪除當(dāng)前使用數(shù)據(jù)庫 db.dropDatabase();5、從指定主機(jī)上克隆數(shù)據(jù)庫 db.cloneDatabase(“127.0.0.1”); 將指定機(jī)器上的數(shù)據(jù)庫的數(shù)據(jù)克隆到當(dāng)前數(shù)據(jù)庫6、從指定的機(jī)器上復(fù)制指定數(shù)據(jù)庫數(shù)據(jù)到某個(gè)數(shù)據(jù)庫 db.copyDatabase("mydb", "temp", "127.0.0.1");將本機(jī)的mydb的數(shù)據(jù)復(fù)制到temp數(shù)據(jù)庫中7、修復(fù)當(dāng)前數(shù)據(jù)庫 db.repairDatabase();8、查看當(dāng)前使用的數(shù)據(jù)庫 db.getName(); db; db和getName方法是一樣的效果,都可以查詢當(dāng)前使用的數(shù)據(jù)庫9、顯示當(dāng)前db狀態(tài) db.stats();10、當(dāng)前db版本 db.version();11、查看當(dāng)前db的鏈接機(jī)器地址 db.getMongo();Collection聚集集合1、創(chuàng)建一個(gè)聚集集合(table) db.createCollection(“collName”, {size: 20, capped: 5, max: 100});2、得到指定名稱的聚集集合(table) db.getCollection("account");3、得到當(dāng)前db的所有聚集集合 db.getCollectionNames();4、顯示當(dāng)前db所有聚集索引的狀態(tài) db.printCollectionStats();用戶相關(guān)1、添加一個(gè)用戶 db.addUser("name"); db.addUser("userName", "pwd123", true); 添加用戶、設(shè)置密碼、是否只讀2、數(shù)據(jù)庫認(rèn)證、安全模式 db.auth("userName", "123123");3、顯示當(dāng)前所有用戶 show users;4、刪除用戶 db.removeUser("userName");其他1、查詢之前的錯(cuò)誤信息 db.getPrevError();2、清除錯(cuò)誤記錄 db.resetError(); 查看聚集集合基本信息1、查看幫助 db.yourColl.help();2、查詢當(dāng)前集合的數(shù)據(jù)條數(shù) db.yourColl.count();3、查看數(shù)據(jù)空間大小 db.userInfo.dataSize();4、得到當(dāng)前聚集集合所在的db db.userInfo.getDB();5、得到當(dāng)前聚集的狀態(tài) db.userInfo.stats();6、得到聚集集合總大小 db.userInfo.totalSize();7、聚集集合儲(chǔ)存空間大小 db.userInfo.storageSize();8、Shard版本信息 db.userInfo.getShardVersion()9、聚集集合重命名 db.userInfo.renameCollection("users"); 將userInfo重命名為users10、刪除當(dāng)前聚集集合 db.userInfo.drop();聚集集合查詢1、查詢所有記錄db.userInfo.find();相當(dāng)于:select* from userInfo;默認(rèn)每頁顯示20條記錄,當(dāng)顯示不下的情況下,可以用it迭代命令查詢下一頁數(shù)據(jù)。注意:鍵入it命令不能帶“;”但是你可以設(shè)置每頁顯示數(shù)據(jù)的大小,用DBQuery.shellBatchSize= 50;這樣每頁就顯示50條記錄了。 2、查詢?nèi)サ艉蟮漠?dāng)前聚集集合中的某列的重復(fù)數(shù)據(jù)db.userInfo.distinct("name");會(huì)過濾掉name中的相同數(shù)據(jù)相當(dāng)于:select distict name from userInfo; 3、查詢age = 22的記錄db.userInfo.find({"age": 22});相當(dāng)于: select * from userInfo where age = 22; 4、查詢age > 22的記錄db.userInfo.find({age: {$gt: 22}});相當(dāng)于:select * from userInfo where age >22; 5、查詢age < 22的記錄db.userInfo.find({age: {$lt: 22}});相當(dāng)于:select * from userInfo where age <22; 6、查詢age >= 25的記錄db.userInfo.find({age: {$gte: 25}});相當(dāng)于:select * from userInfo where age >= 25; 7、查詢age <= 25的記錄db.userInfo.find({age: {$lte: 25}}); 8、查詢age >= 23 并且 age <= 26db.userInfo.find({age: {$gte: 23, $lte: 26}}); 9、查詢name中包含 mongo的數(shù)據(jù)db.userInfo.find({name: /mongo/});//相當(dāng)于%%select * from userInfo where name like ‘%mongo%'; 10、查詢name中以mongo開頭的db.userInfo.find({name: /^mongo/});select * from userInfo where name like ‘mongo%'; 11、查詢指定列name、age數(shù)據(jù)db.userInfo.find({}, {name: 1, age: 1});相當(dāng)于:select name, age from userInfo;當(dāng)然name也可以用true或false,當(dāng)用ture的情況下河name:1效果一樣,如果用false就是排除name,顯示name以外的列信息。 12、查詢指定列name、age數(shù)據(jù), age > 25db.userInfo.find({age: {$gt: 25}}, {name: 1, age: 1});相當(dāng)于:select name, age from userInfo where age >25; 13、按照年齡排序升序:db.userInfo.find().sort({age: 1});降序:db.userInfo.find().sort({age: -1}); 14、查詢name = zhangsan, age = 22的數(shù)據(jù)db.userInfo.find({name: 'zhangsan', age: 22});相當(dāng)于:select * from userInfo where name = ‘zhangsan' and age = ‘22'; 15、查詢前5條數(shù)據(jù)db.userInfo.find().limit(5);相當(dāng)于:selecttop 5 * from userInfo; 16、查詢10條以后的數(shù)據(jù)db.userInfo.find().skip(10);相當(dāng)于:select * from userInfo where id not in (selecttop 10 * from userInfo); 17、查詢在5-10之間的數(shù)據(jù)db.userInfo.find().limit(10).skip(5);可用于分頁,limit是pageSize,skip是第幾頁*pageSize 18、or與 查詢db.userInfo.find({$or: [{age: 22}, {age: 25}]});相當(dāng)于:select * from userInfo where age = 22 or age = 25; 19、查詢第一條數(shù)據(jù)db.userInfo.findOne();相當(dāng)于:selecttop 1 * from userInfo;db.userInfo.find().limit(1); 20、查詢某個(gè)結(jié)果集的記錄條數(shù)db.userInfo.find({age: {$gte: 25}}).count();相當(dāng)于:select count(*) from userInfo where age >= 20; 21、按照某列進(jìn)行排序db.userInfo.find({***: {$exists: true}}).count();相當(dāng)于:select count(***) from userInfo;索引1、創(chuàng)建索引db.userInfo.ensureIndex({name: 1});db.userInfo.ensureIndex({name: 1, ts: -1}); 2、查詢當(dāng)前聚集集合所有索引db.userInfo.getIndexes(); 3、查看總索引記錄大小db.userInfo.totalIndexSize(); 4、讀取當(dāng)前集合的所有index信息db.users.reIndex(); 5、刪除指定索引db.users.dropIndex("name_1"); 6、刪除所有索引索引db.users.dropIndexes(); 修改、添加、刪除集合數(shù)據(jù)1、添加db.users.save({name: ‘zhangsan', age: 25, ***: true});添加的數(shù)據(jù)的數(shù)據(jù)列,沒有固定,根據(jù)添加的數(shù)據(jù)為準(zhǔn) 2、修改db.users.update({age: 25}, {$set: {name: 'changeName'}}, false, true);相當(dāng)于:update users set name = ‘changeName' where age = 25; db.users.update({name: 'Lisi'}, {$inc: {age: 50}}, false, true);相當(dāng)于:update users set age = age + 50 where name = ‘Lisi'; db.users.update({name: 'Lisi'}, {$inc: {age: 50}, $set: {name: 'hoho'}}, false, true);相當(dāng)于:update users set age = age + 50, name = ‘hoho' where name = ‘Lisi'; 3、刪除db.users.remove({age: 132}); 4、查詢修改刪除db.users.findAndModify({ query: {age: {$gte: 25}}, sort: {age: -1}, update: {$set: {name: 'a2'}, $inc: {age: 2}}, remove: true}); db.runCommand({ findandmodify : "users", query: {age: {$gte: 25}}, sort: {age: -1}, update: {$set: {name: 'a2'}, $inc: {age: 2}}, remove: true});update 或 remove 其中一個(gè)是必須的參數(shù); 其他參數(shù)可選。參數(shù)詳解默認(rèn)值query查詢過濾條件{}sort如果多個(gè)文檔符合查詢過濾條件,將以該參數(shù)指定的排列方式選擇出排在首位的對象,該對象將被操作{}remove若為true,被選中對象將在返回前被刪除N/Aupdate一個(gè) 修改器對象N/Anew若為true,將返回修改后的對象而不是原始對象。在刪除操作中,該參數(shù)被忽略。falsefields參見Retrieving a Subset of Fields (1.5.0+)All fieldsupsert創(chuàng)建新對象若查詢結(jié)果為空。 示例 (1.5.4+)false語句塊操作1、簡單Hello Worldprint("Hello World!");這種寫法調(diào)用了print函數(shù),和直接寫入"Hello World!"的效果是一樣的; 2、將一個(gè)對象轉(zhuǎn)換成jsontojson(new Object());tojson(new Object('a')); 3、循環(huán)添加數(shù)據(jù)> for (var i = 0; i < 30; i++) {... db.users.save({name: "u_" + i, age: 22 + i, ***: i % 2});... };這樣就循環(huán)添加了30條數(shù)據(jù),同樣也可以省略括號(hào)的寫法> for (var i = 0; i < 30; i++) db.users.save({name: "u_" + i, age: 22 + i, ***: i % 2});也是可以的,當(dāng)你用db.users.find()查詢的時(shí)候,顯示多條數(shù)據(jù)而無法一頁顯示的情況下,可以用it查看下一頁的信息; 4、find 游標(biāo)查詢>var cursor = db.users.find();> while (cursor.hasNext()) { printjson(cursor.next()); }這樣就查詢所有的users信息,同樣可以這樣寫var cursor = db.users.find();while (cursor.hasNext()) { printjson(cursor.next); }同樣可以省略{}號(hào) 5、forEach迭代循環(huán)db.users.find().forEach(printjson);forEach中必須傳遞一個(gè)函數(shù)來處理每條迭代的數(shù)據(jù)信息 6、將find游標(biāo)當(dāng)數(shù)組處理var cursor = db.users.find();cursor[4];取得下標(biāo)索引為4的那條數(shù)據(jù)既然可以當(dāng)做數(shù)組處理,那么就可以獲得它的長度:cursor.length();或者cursor.count();那樣我們也可以用循環(huán)顯示數(shù)據(jù)for (var i = 0, len = c.length(); i < len; i++) printjson(c[i]); 7、將find游標(biāo)轉(zhuǎn)換成數(shù)組> var arr = db.users.find().toArray();> printjson(arr[2]);用toArray方法將其轉(zhuǎn)換為數(shù)組 8、定制我們自己的查詢結(jié)果只顯示age <= 28的并且只顯示age這列數(shù)據(jù)db.users.find({age: {$lte: 28}}, {age: 1}).forEach(printjson);db.users.find({age: {$lte: 28}}, {age: true}).forEach(printjson);排除age的列db.users.find({age: {$lte: 28}}, {age: false}).forEach(printjson); 9、forEach傳遞函數(shù)顯示信息db.things.find({x:4}).forEach(function(x) {print(tojson(x));}); |
參考文章①:http://blog.csdn.net/ssyan/article/details/6927307
參考文章②:http://blog.chinaunix.net/uid-26558059-id-3211264.html