1、安裝pymysql庫
如果你想要使用python操作MySQL數據庫,就必須先要安裝pymysql庫,這個庫的安裝很簡單,直接使用pip install pymysql;進行安裝。
假如上面這種方式還是安裝不上,就用如下鏈接找一個合適的安裝包進行安裝,這個就不細說了,請自行百度。
https://www.lfd.uci.edu/~gohlke/pythonlibs/
學習本篇文章,最好是先看我另外一篇關于游標cursor講解的文章,這樣會有更好的效果
2、使用python連接mysql數據庫
1)六個常用的連接參數
- 參數host:mysql服務器所在的主機的ip;
- 參數user:用戶名
- 參數password:密碼
- 參數port:連接的mysql主機的端口,默認是3306
- 參數db:連接的數據庫名
- 參數charset:當讀取數據出現中文會亂碼的時候,需要我們設置一下編碼;我們使用python操作數據庫的時候,那么python就相當于是client,我們是用這個client來操作mysql的server服務器,python3默認采用的utf8字符集,我的mysql服務器默認采用latin1字符集,因此mysql中創建的每張表,都是建表的時候加了utf8編碼的,因此這里設置的應該就是connection連接器的編碼。
什么是connection?可以參考我的另外一篇文章學習。
2)python連接mysql的語法
|
1
2
|
import pymysql db = pymysql.connect(host='localhost',user='root',password='123456',port=3306,db='spiders',charset=' utf8') |
- 最基本的參數是host,user,password和port,必須要有。剩下兩個參數根據你自己的情況決定是否使用。
- host指的是mysql服務器安裝在哪里,由于我的mysql就是安裝在本機上,因此這里可以寫localhost,我也可以寫成主機名或者主機ip。
- db指的是你要操作的是哪一個數據庫,在進行數據庫連接的時候,最好加上這個參數。
3)一個簡單的熱身案例
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
# 導包import pymysql # 使用pymysql連接上mysql數據庫服務器,創建了一個數據庫對象;db = pymysql.connect(host='localhost',user='root', password='123456', port=3306, db='huangwei', charset='utf8')# 開啟mysql的游標功能,創建一個游標對象; cursor = db.cursor()# 要執行的SQL語句;sql = "select * from student"# 使用游標對象執行SQL語句;cursor.execute(sql)# 使用fetchone()方法,獲取返回的結果,但是需要用變量保存返回結果;data = cursor.fetchone()print(data)# 斷開數據庫的連接,釋放資源;db.close() |
結果如下:

3、cursor游標對象的一些常用方法
1)cursor用來執行命令的方法
- execute(query, args):執行單條sql語句,接收的參數為sql語句本身和使用的參數列表,返回值為受影響的行數;
- executemany(query, args):執行單挑sql語句,但是重復執行參數列表里的參數,返回值為受影響的行數;
2)cursor用來接收返回值的方法
- fetchone():返回一條結果行;
- fetchmany(size):接收size條返回結果行。如果size的值大于返回的結果行的數量,則會返回cursor.arraysize條數據;
- fetchall():接收全部的返回結果行;
4、創建表
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
import pymysql db = pymysql.connect(host='localhost',user='root', password='123456',port=3306, db='huangwei', charset='utf8')# 創建一個游標對象;cursor = db.cursor() # 建表語句;sql = """ create table person( id int auto_increment primary key not null, name varchar(10) not null, age int not null )charset=utf8 """# 執行sql語句;cursor.execute(sql) # 斷開數據庫的連接;db.close() |
注意:你在mysql中sql語句怎么寫,在這里就怎么寫。還有一個細節需要注意的是,在python中,將代碼進行多次換行的時候,最好使用“三引號”。
5、查詢數據…查
1)fetchone():一次獲取一條記錄
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
import pymysql db = pymysql.connect(host='localhost',user='root',db='huangwei',password='123456',port=3306,charset='utf8') cursor = db.cursor()cursor.execute('select count(*) from person')aa = cursor.fetchone()print(aa)cursor.execute('select name,age from person') for i in range(aa[0]): a,b = cursor.fetchone() c = "我的名字叫{},今年{}歲".format(a,b) display(c)db.close() |
結果如下:

2)fetchall():一次獲取所有記錄
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
import pymysql db = pymysql.connect(host='localhost',user='root',db='huangwei',password='123456',port=3306,charset='utf8') cursor = db.cursor()cursor.execute('select name,age from person')aa = cursor.fetchall()# print(aa)for a,b in aa: c = "我的名字叫{},今年{}歲".format(a,b) display(c)db.close() |
結果如下:
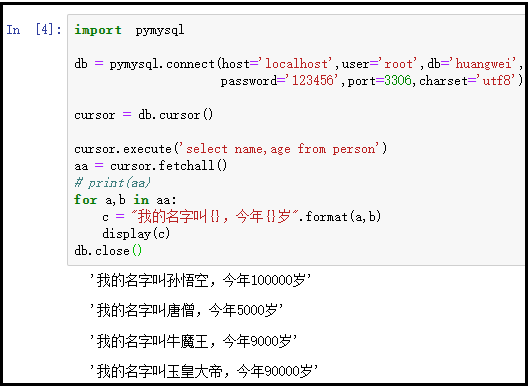
注:還有一個fetchmany()方法,用于一次性獲取指定條數的記錄,請自行下去研究。
3)使用pandas中的read_sql()方法,將提取到的數據直接轉化為DataFrame進行操作
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
import pymysql import pandas as pddb = pymysql.connect(host='localhost',user='root',db='huangwei',password='123456',port=3306,charset='utf8')cursor = db.cursor()df1 = pd.read_sql("select * from student where ssex='男'",db)display(df1)df2 = pd.read_sql("select * from student where ssex='女'",db)display(df2) |
結果如下:
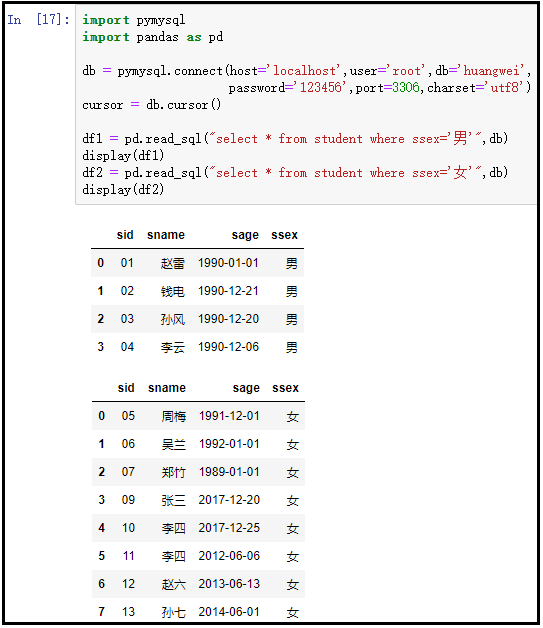
6、插入數據…增
1)一次性插入一條數據
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
import pymysqldb = pymysql.connect(host='localhost',user='root', password='123456',port=3306, db='huangwei', charset='utf8') cursor = db.cursor() # mysql中SQL語句怎么寫,這里就怎么寫;name = "豬八戒"age = 8000sql = 'insert into person(name,age) values ("豬八戒",8000)'try: cursor.execute(sql) db.commit() print("插入成功")except: print("插入失敗") db.rollback()db.close() |
1.1)一次性插入一條數據
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
import pymysql db = pymysql.connect(host='localhost',user='root', password='123456',port=3306, db='huangwei', charset='utf8') cursor = db.cursor() # 插入數據sql = 'insert into person(name,age) values(%s,%s)'try: cursor.execute(sql,('孫悟空',100000)) db.commit() print("插入成功")except: print("插入失敗") db.rollback()db.close() |
2)一次性插入多條數據
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
import pymysql db = pymysql.connect(host='localhost',user='root', password='123456',port=3306, db='huangwei', charset='utf8') cursor = db.cursor() # 插入數據sql = 'insert into person(name,age) values(%s,%s)'# 注意:(('牛魔王',9000),('鐵扇公主',8000),('玉皇大帝',6000))也可以,小括號都可以換為中括號datas = [('牛魔王',9000),('鐵扇公主',8000),('玉皇大帝',6000)]try: cursor.executemany(sql,datas) db.commit() print("插入成功")except: print("插入失敗") db.rollback()db.close() |
總結如下:
① pymysql模塊是默認開啟mysql的事務功能的,因此,進行 “增” “刪” "改"的時候,一定要使用db.commit()提交事務,否則就看不見所插入的數據。
② 進行 “增”、“刪”、"改"的時候,一定要使用try…except…語句,因為萬一沒插入成功,其余代碼都無法執行。當語句執行不成功,我們就db.rollback()回滾到操作之前的狀態;當語句執行成功,我們就db.commit()提交事務。
7、更新數據…改
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
import pymysql db = pymysql.connect(host='localhost',user='root', password='123456',port=3306, db='huangwei', charset='utf8') cursor = db.cursor() # 更新數據sql = 'update person set age=%s where name=%s'try: cursor.execute(sql,[90000,"玉皇大帝"]) db.commit() print("更新成功")except: print("更新失敗") db.rollback()db.close() |
8、刪除數據…刪
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
import pymysql db = pymysql.connect(host='localhost',user='root', password='123456',port=3306, db='huangwei', charset='utf8') cursor = db.cursor() # 刪除數據sql = 'delete from person where age=8000'try: cursor.execute(sql) db.commit() print("刪除成功")except: print("刪除失敗") db.rollback()db.close() |
以上就是本文的全部內容,希望對大家的學習有所幫助,也希望大家多多支持服務器之家。
原文鏈接:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_41261833/article/details/103832017