前言
最近在做一個小的Demo中,在一個界面上兩次調用視圖組件,并且在視圖組件中都調用了數據庫查詢,結果發現,一直報錯,將兩個視圖組件的調用分離,單獨進行,卻又是正常的,尋找一番,發現是配置依賴注入服務時,對于服務的生命周期沒有配置得當導致,特此做一次實驗來認識三者之間(甚至是四者之間的用法及區別)。
本文demo地址(具體見WebApi控制器中):https://gitee.com/530521314/koInstance.git
一、服務的生命周期
在Asp.Net Core中,內置容器負責管理服務的生命周期,從被依賴注入容器創建開始,等我們調用完服務時,到容器釋放該服務的所有實力為止,有幾種形式表現:
1、Transient:每次請求服務時,都會創建一個新實例,這種生命周期適合用于輕量級服務(如Repository和ApplicationService服務)。
2、Scoped:為每個HTTP請求創建一個實例,生命周期將橫貫整次請求。
3、SingleTon:在第一次請求服務時,為該服務創建一個實例,之后每次請求將會使用第一次創建好的服務。
4、Instance:與SingleTon類似,但在應用程序啟動時會將該實例注冊到容器中,可以理解為比SingleTon還早存在。
應用程序中相關服務的控制生命周期的方法時通過相應的Add*指定,如下三種,當然還可以通過擴展方法來簡化ConfigurationServices方法中所見的代碼數量。
|
1
2
3
|
services.AddTransient<IApplicationService, ApplicationService>();services.AddScoped<IApplicationService, ApplicationService>();services.AddSingleton<IApplicationService, ApplicationService>(); |
二、代碼設計服務生命周期
首先設計一些服務相關的操作接口
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
public interface IOperation { Guid GetGuid(); } public interface IOperationTransient: IOperation { } public interface IOperationScoped : IOperation { } public interface IOperationSingleton : IOperation { } public interface IOperationInstance : IOperation { }基礎服務接口 |
其次對這些操作類予以實現并生成相關服務
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
|
/// <summary> /// 常規服務 /// </summary> public class Operation : IOperation { private readonly Guid _guid; public Operation() { _guid = Guid.NewGuid(); } public Operation(Guid guid) { _guid = guid == Guid.Empty ? Guid.NewGuid() : guid; } public Guid GetGuid() { return _guid; } } /// <summary> /// 瞬時服務 /// </summary> public class OperationTransient : IOperationTransient { private readonly Guid _guid; public OperationTransient() { _guid = Guid.NewGuid(); } public OperationTransient(Guid guid) { _guid = guid == Guid.Empty ? Guid.NewGuid() : guid; } public Guid GetGuid() { return _guid; } } /// <summary> /// 單次請求內服務固定 /// </summary> public class OperationScoped : IOperationScoped { private readonly Guid _guid; public OperationScoped() { _guid = Guid.NewGuid(); } public OperationScoped(Guid guid) { _guid = guid == Guid.Empty ? Guid.NewGuid() : guid; } public Guid GetGuid() { return _guid; } } /// <summary> /// 所有請求內固定服務 /// </summary> public class OperationSingleton : IOperationSingleton { private readonly Guid _guid; public OperationSingleton() { _guid = Guid.NewGuid(); } public OperationSingleton(Guid guid) { _guid = guid == Guid.Empty ? Guid.NewGuid() : guid; } public Guid GetGuid() { return _guid; } } /// <summary> /// 應用程序內固定服務 /// </summary> public class OperationInstance : IOperationInstance { private readonly Guid _guid; public OperationInstance() { _guid = Guid.NewGuid(); } public OperationInstance(Guid guid) { _guid = guid == Guid.Empty ? Guid.NewGuid() : guid; } public Guid GetGuid() { return _guid; } }基礎服務具體實現 |
對基礎服務的聚合接口,提供統一服務接口
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
public interface IOperationService { /// <summary> /// 獲取四種形式的Guid碼 /// </summary> /// <returns></returns> List<string> GetGuidString(); }聚合服務接口 |
對基礎服務的聚合實現,將基礎服務全部接入進來作為統一服務
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
|
/// <summary> /// 服務調用 /// </summary> public class OperationService : IOperationService { public IOperationTransient _transientOperation { get; } public IOperationScoped _scopedOperation { get; } public IOperationSingleton _singletonOperation { get; } public IOperationInstance _instanceOperation { get; } public OperationService(IOperationTransient transientOperation, IOperationScoped scopedOperation, IOperationSingleton singletonOperation, IOperationInstance instanceOperation) { _transientOperation = transientOperation; _scopedOperation = scopedOperation; _singletonOperation = singletonOperation; _instanceOperation = instanceOperation; } public List<string> GetGuidString() { return new List<string>() { $"Transient:"+_transientOperation.GetGuid(), $"Scoped:"+_scopedOperation.GetGuid(), $"Singleton:" +_singletonOperation.GetGuid(), $"Instance:"+_instanceOperation.GetGuid(), }; } }聚合服務的實現 |
在控制器中進行服務注入
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
[Route("api/[controller]")] [ApiController] public class ValuesController : ControllerBase { private readonly IOperationService _operationService; public ValuesController(IOperationService operationService) { _operationService = operationService; } [HttpGet] [Route(nameof(GetGuidString))] public ActionResult<string> GetGuidString() { return string.Join("\n", _operationService.GetGuidString()); } } |
在StartUp中完成服務注入邏輯,這里實現服務注入的方式多種均可。
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
services.AddTransient<IOperationTransient, OperationTransient>();services.AddScoped<IOperationScoped, OperationScoped>();services.AddSingleton<IOperationSingleton, OperationSingleton>();//應用程序啟動時便注入該實例services.AddSingleton<IOperationInstance>(new OperationInstance(Guid.Empty));services.AddTransient<IOperationService, OperationService>(); |
通過訪問預期Api地址可以得到不同的四種基礎服務的Guid信息,
第一次啟動程序(不關閉)發起訪問:

第二次(第一次基礎上再次訪問)發起訪問:

可以看見,兩次訪問下,Singleton和Instance是相同的,都是由應用程序啟動時和應用服務加載時決定完畢,Singleton在首次進入服務時進行分配,并始終保持不變,而Instance在應用程序啟動時,便將實例注入,進入服務也保持著最先的實例,沒有重新分配實例。而Transient和Scoped則進行著變化。
關閉程序,重啟,第三次發起訪問:

可以見到,Singleton和Instance都發生了變化,也說明了之前在Singleton和Instance處寫上的作用。
接下來開始設計Transient和Scoped的不同之處,對于已有代碼加上新功能,此次我們只針對Scoped和Transient進行比較。
首先在StartUp中將HttpContextAccessor服務注入,目的是在后期能夠針對Scoped獲取新的服務實例(盡管兩個實例是相同的)。
|
1
|
services.AddHttpContextAccessor(); |
接著在聚合服務中增加一個方法,用來針對Transient、Scoped測試。
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
/// <summary>/// 獲取Transient、Scoped的Guid碼/// </summary>/// <returns></returns>List<string> GetTransientAndScopedGuidString(); |
在聚合服務實現中實現該方法并對已有的服務重新獲取實例,得到不同實例下的Guid碼。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
public List<string> GetTransientAndScopedGuidString() { //var tempTransientService = (IOperationTransient)ServiceLocator.Instance.GetService(typeof(IOperationTransient)); var tempTransientService = (IOperationTransient)_httpContextAccessor.HttpContext.RequestServices.GetService(typeof(IOperationTransient)); var tempScopedService = (IOperationScoped)_httpContextAccessor.HttpContext.RequestServices.GetService(typeof(IOperationScoped)); return new List<string>() { $"原生Transient請求服務:"+_transientOperation.GetGuid(), $"手動Transient請求服務:"+ tempTransientService.GetGuid(), $"原生Scoped請求服務:"+_scopedOperation.GetGuid(), $"手動Scoped請求服務:"+tempScopedService.GetGuid(), }; } |
在控制器部分調用該聚合服務即可,并返回相應的結果,本次我返回的結果:
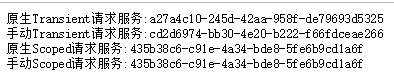
可以看到,對于Scoped來講,一次請求內多次訪問同一個服務是共用一個服務實例的,而對于Transient則是,每次訪問都是新的服務實例。
至此,對于這四種服務生命周期算是掌握的差不多了。
總結
以上就是這篇文章的全部內容了,希望本文的內容對大家的學習或者工作具有一定的參考學習價值,如果有疑問大家可以留言交流,謝謝大家對服務器之家的支持。
原文鏈接:https://www.cnblogs.com/CKExp/p/9823076.html












