Session會話簡介
會話是指在一段時間內(nèi),用戶使用同一個瀏覽器進程與Web應(yīng)用之間的交互過程。
會話(Session)通常用來跟蹤用戶的狀態(tài),緩存用戶在此瀏覽器進程中的信息。
當用戶關(guān)閉瀏覽器,上一個Session也就無法再次獲得了(Cookie的maxAge為-1的情況)。再次打開新的瀏覽器,將開始一個新的會話。
類javax.servlet.http.HttpSession。每一個HttpSession代表用戶的一個會話。
每一個Session的過期時間默認為30分鐘。
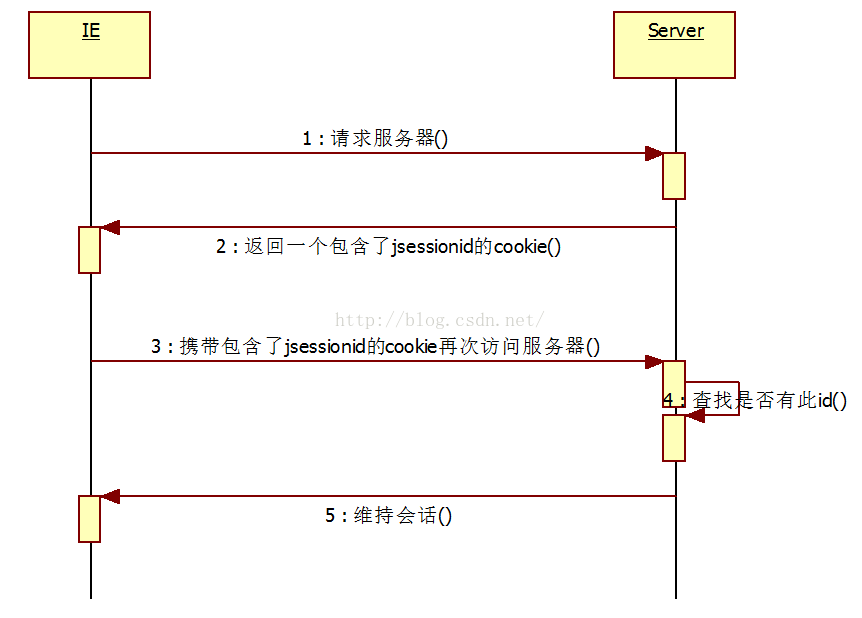
當瀏覽器第一次訪問服務(wù)器時,無論先訪問哪一個頁面,服務(wù)器就會給用戶分配一個唯一的會話標識,即jsessionid然后以cookie的形式返回給用戶。
下圖是一個響應(yīng)頭(下圖是基于Servlet3.0的,在Servlet2.5中沒有HttpOnly屬性)
服務(wù)器給每個用戶創(chuàng)建一個會話,即HttpSession對象,保存在服務(wù)器端。
那么,當用戶再次訪問服務(wù)器時,服務(wù)器是如何知道還是當前用戶呢?
當瀏覽器再次訪問服務(wù)器時,會攜帶包含了jsessionid的cookie訪問服務(wù)器。服務(wù)器根據(jù)此id返回此用戶的HttpSession對象,就保持了會話。
( 那么,是否可以在不同的瀏覽器上實現(xiàn)同一個同一個會話呢?
下面是一個典型的URL,它帶有一定的欺騙作用,可以在不同的瀏覽器上實現(xiàn)同一個會話:
http://localhost:8080/day07_2/CNCookieServlet;jsessionid=F8692D61CD46D094DBB7A8FC7387649C )
瀏覽器和服務(wù)器的關(guān)系如下兩圖:

HttpSession:
在Servlet中,通過HttpServletRequest.getSession方法獲取會話對像。
HttpSession接口的以下方法用于向會話范圍內(nèi)共享數(shù)據(jù):
|
1
2
3
4
|
getAttribute(“name”)setAttribute(“name”,object);getAttributeNames()removeAttrubute(“name”) |
Invalidate(); - 此方法強力刪除服務(wù)器緩存的session.
示例:
在一個Servlet的向httpSession中setAttribute設(shè)置某些值。
通過超連接,或其他方式轉(zhuǎn)到其他servlet并通過getAttribute顯示信息。
在任意Servlet中調(diào)用getAttribute顯示信息。
關(guān)閉此瀏覽器,重新訪問獲取信息的servlet,你會發(fā)現(xiàn)已經(jīng)沒有信息了。
如下:
|
1
2
3
4
|
String name=request.getParameter("name"); request.setAttribute("name", "request---"+name); request.getSession().setAttribute("name", "session---"+name); getServletContext().setAttribute("name", "application---"+name); |
Session的唯一標識Id:
每一個Session都一個唯一標識,即ID。
當瀏覽器獲取一個新的Session時,用戶即可以通過session.geId();打印出ID的值 。
在不關(guān)閉瀏覽器的情況下,在多個頁面上跳轉(zhuǎn),使用的是同一個Session。
如:
|
1
|
request.getSession().getId() |
何為安全退出:
用戶退出時,應(yīng)該當將自己的信息從Session中清除-即安全退出。
安全退出是為了將自己在服務(wù)器上留下的信息清除干凈,以防被黑
Session.invalidate();
1、request.getSession().invalidate();
如此可將session池中的相對應(yīng)的對象刪除
2、Session.removeAttribute(…)
如:
request.getSession().removeAttribute("realCode");
用于刪除session對象中的屬性
通過重寫URL來跟蹤會話:
前面已經(jīng)說過,Servlet容器先在客戶端保存一個SessionID,以后,在瀏覽器發(fā)出HTTP請求時,都會包含這個SessionID.Servlet容器讀取HTTP請求中的這個SessionID,根據(jù)這個SessionID從容器中取出HttpSession對像,以便于跟蹤HTTP請求屬于哪一個會話,這一過程稱為會話的跟蹤。
如果瀏覽器支持Cookie,Servlet容器就將SessionID作為Cookie保存在瀏覽器的客戶端。但如果出于安全的考慮,用戶禁用了Cookie,那么Servlet容器又如何來跟蹤會話呢?
首先讓我們在IE中禁用Cookie(注意:對于某些GHOST的系統(tǒng)不起作用)。
IE>工具>Internet選項>隱私>高級,然后禁用Cookie:
我們可以在主頁加上這樣的超鏈接:(與下面代碼中相關(guān)的SaveServlet.java GetServlet.java LogoutServlet.java的代碼我放在最后面貼)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
<h2>演示重寫url技術(shù)---破解用戶禁用cookie之后,我們session無效的問題</h2> <form action="<%=response.encodeURL("saveServlet") %>" method="post"> name:<input type="text" name="name"/><br/> <input type="submit"/> </form> <a href="<%=response.encodeURL("getServlet") %>">重寫url-讀取幾個容器中的數(shù)據(jù)</a><br/> <a href="<%=response.encodeURL("logoutServlet") %>">重寫url-安全退出</a> |
這句<form action=“<%=response.encodeURL(“/aa”)%>”>就可以實現(xiàn)這一功能
在這里禁用了cookie以后,瀏覽器仍然能夠接收到服務(wù)器發(fā)送過來的cookie,但是瀏覽器只能接受不能發(fā)送出去給服務(wù)器,不能發(fā)送cookie的話也就不能夠去session池中去取相應(yīng)的對象了。
上面的代碼在表單里面輸入想要的值之后,再到下面的getServlet這里的超鏈接處訪問看是不是仍然能夠顯示出輸入的值,答案是肯定的。這里的訪問路徑就相當于類似
http://localhost:8080/day07_2/CNCookieServlet;jsessionid=F8692D61CD46D094DBB7A8FC7387649C 的,后面帶的jsessionid=F8692D61CD46D094DBB7A8FC7387649C就是其id,如此,你到另一個瀏覽器中去輸入這個網(wǎng)址也能夠訪問的到。
這里我要補充一下:(以下情況是在我將session池中HttpSession對象將對應(yīng)session的JSESSIONID值和value值寫入cookie中,這個cookie會覆蓋系統(tǒng)造的那個,就相當于是我自己造的,我將存在時間設(shè)置成了十分鐘,如果不覆蓋的話,cookie在瀏覽器關(guān)閉時就會消亡,下面的現(xiàn)象也就不會出現(xiàn)了)
在是否禁用了cookie這兩種情況下在session池中新建的對象的id是不一樣的,即假如你在禁用了cookie時在表單中輸入了一個name的值,查詢結(jié)果如下:

并且jsessionid為2BB51EBDEAAF14D19656C71E1B6F9FF6
然后馬上換成不禁用cookie模式,輸入另一個名字如Tom,查詢結(jié)果自然會是兩個Tom,jsessionid為
203F9E4DB5D874476B81DAF350661B6A,與禁用是不一樣,這就使出現(xiàn)下面的結(jié)果了
然后此時我們將瀏覽器關(guān)閉,再次進入瀏覽器,在不禁用cookie模式下查看訪問結(jié)果,如下:

下面我將主要的代碼貼上來:
SaveServlet.java
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
|
package cn.hncu.servlets.session; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.PrintWriter; import javax.servlet.ServletException; import javax.servlet.http.Cookie; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; public class SaveServlet extends HttpServlet { public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { doPost(request, response); } public void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { response.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8"); PrintWriter out = response.getWriter(); request.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8"); String name=request.getParameter("name"); request.setAttribute("name", "request---"+name); request.getSession().setAttribute("name", "session---"+name); getServletContext().setAttribute("name", "application---"+name); //把cookie技術(shù)和session技術(shù)聯(lián)合起來做應(yīng)用的一個例子---※功能:讓用戶在關(guān)閉瀏覽器之后,如果10分鐘之內(nèi)能夠登錄本站,還能訪問到session中的信息 //向客戶端寫一個key為"JSESSIONID"用value為sessionid的cookie, Cookie c=new Cookie("JSESSIONID", request.getSession().getId()); c.setMaxAge(60*10);//上面的現(xiàn)象就是這一句造成的,沒有這一句的話就不會有上面說的現(xiàn)象了 c.setPath(request.getContextPath()); response.addCookie(c); out.println("保存成功..."); out.flush(); out.close(); } } |
GetServlet.java
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
|
package cn.hncu.servlets.session; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.PrintWriter; import javax.servlet.ServletException; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; public class GetServlet extends HttpServlet { public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { response.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8"); PrintWriter out = response.getWriter(); out.println("<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC \"-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN\">"); out.println("<HTML>"); out.println(" <HEAD><TITLE>A Servlet</TITLE></HEAD>"); out.println(" <BODY>"); String reqName=(String) request.getAttribute("name"); String seName=(String) request.getSession().getAttribute("name"); String appName=(String) getServletContext().getAttribute("name"); out.println(reqName+"<br/>"); out.println(seName+"<br/>"); out.println(appName+"<br/>"); out.println(" </BODY>"); out.println("</HTML>"); out.flush(); out.close(); } } |
LogoutServlet.java
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
package cn.hncu.servlets.session; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.PrintWriter; import javax.servlet.ServletException; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; public class LogoutServlet extends HttpServlet { public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { response.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8"); PrintWriter out = response.getWriter(); //安全退出---只要讓session對象無效就可以了 request.getSession().invalidate(); out.println("已安全退出..."); } } |
以上所述是小編給大家介紹的JavaWeb Session 會話管理,希望對大家有所幫助,如果大家有任何疑問歡迎給我留言,小編會及時回復(fù)大家的!












