在我們編程時(shí),有一些代碼是固定的,例如Socket連接的代碼,讀取文件內(nèi)容的代碼,一般情況下我都是到網(wǎng)上搜一下然后直接粘貼下來改一改,當(dāng)然如果你能自己記住所有的代碼那更厲害,但是自己寫畢竟不如粘貼來的快,而且自己寫的代碼還要測試,而一段經(jīng)過測試的代碼則可以多次使用,所以這里我就自己總結(jié)了一下python中常用的編程模板,如果還有哪些漏掉了請大家及時(shí)補(bǔ)充哈。
一、讀寫文件
1、讀文件
(1)、一次性讀取全部內(nèi)容
|
1
2
3
4
|
filepath='D:/data.txt' #文件路徑with open(filepath, 'r') as f: print f.read() |
(2)讀取固定字節(jié)大小
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-filepath='D:/data.txt' #文件路徑f = open(filepath, 'r')content=""try: while True: chunk = f.read(8) if not chunk: break content+=chunkfinally: f.close() print content |
(3)每次讀取一行
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-filepath='D:/data.txt' #文件路徑f = open(filepath, "r")content=""try: while True: line = f.readline() if not line: break content+=linefinally: f.close() print content |
(4)一次讀取所有的行
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-filepath='D:/data.txt' #文件路徑with open(filepath, "r") as f: txt_list = f.readlines()for i in txt_list: print i, |
2、寫文件
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-filepath='D:/data1.txt' #文件路徑with open(filepath, "w") as f: #w會(huì)覆蓋原來的文件,a會(huì)在文件末尾追加 f.write('1234') |
二、連接Mysql數(shù)據(jù)庫
1、連接
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
#!/usr/bin/python# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-import MySQLdbDB_URL='localhost'USER_NAME='root'PASSWD='1234'DB_NAME='test'# 打開數(shù)據(jù)庫連接db = MySQLdb.connect(DB_URL,USER_NAME,PASSWD,DB_NAME)# 使用cursor()方法獲取操作游標(biāo) cursor = db.cursor()# 使用execute方法執(zhí)行SQL語句cursor.execute("SELECT VERSION()")# 使用 fetchone() 方法獲取一條數(shù)據(jù)庫。data = cursor.fetchone()print "Database version : %s " % data# 關(guān)閉數(shù)據(jù)庫連接db.close() |
2、創(chuàng)建表
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
<p>#!/usr/bin/python# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-import MySQLdb# 打開數(shù)據(jù)庫連接db = MySQLdb.connect("localhost","testuser","test123","TESTDB" )# 使用cursor()方法獲取操作游標(biāo) cursor = db.cursor()# 如果數(shù)據(jù)表已經(jīng)存在使用 execute() 方法刪除表。cursor.execute("DROP TABLE IF EXISTS EMPLOYEE")# 創(chuàng)建數(shù)據(jù)表SQL語句sql = """CREATE TABLE EMPLOYEE ( FIRST_NAME CHAR(20) NOT NULL, LAST_NAME CHAR(20), AGE INT, SEX CHAR(1), INCOME FLOAT )"""cursor.execute(sql)# 關(guān)閉數(shù)據(jù)庫連接db.close()</p> |
3、插入
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
#!/usr/bin/python# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-import MySQLdb# 打開數(shù)據(jù)庫連接db = MySQLdb.connect("localhost","testuser","test123","TESTDB" )# 使用cursor()方法獲取操作游標(biāo) cursor = db.cursor()# SQL 插入語句sql = """INSERT INTO EMPLOYEE(FIRST_NAME, LAST_NAME, AGE, SEX, INCOME) VALUES ('Mac', 'Mohan', 20, 'M', 2000)"""try: # 執(zhí)行sql語句 cursor.execute(sql) # 提交到數(shù)據(jù)庫執(zhí)行 db.commit()except: # Rollback in case there is any error db.rollback()# 關(guān)閉數(shù)據(jù)庫連接db.close() |
4、查詢
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
|
<p>#!/usr/bin/python# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-import MySQLdb# 打開數(shù)據(jù)庫連接db = MySQLdb.connect("localhost","testuser","test123","TESTDB" )# 使用cursor()方法獲取操作游標(biāo) cursor = db.cursor()# SQL 查詢語句sql = "SELECT * FROM EMPLOYEE \ WHERE INCOME > '%d'" % (1000)try: # 執(zhí)行SQL語句 cursor.execute(sql) # 獲取所有記錄列表 results = cursor.fetchall() for row in results: fname = row[0] lname = row[1] age = row[2] sex = row[3] income = row[4] # 打印結(jié)果 print "fname=%s,lname=%s,age=%d,sex=%s,income=%d" % \ (fname, lname, age, sex, income )except: print "Error: unable to fecth data"# 關(guān)閉數(shù)據(jù)庫連接db.close()</p> |
5、更新
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
#!/usr/bin/python# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-import MySQLdb# 打開數(shù)據(jù)庫連接db = MySQLdb.connect("localhost","testuser","test123","TESTDB" )# 使用cursor()方法獲取操作游標(biāo) cursor = db.cursor()# SQL 更新語句sql = "UPDATE EMPLOYEE SET AGE = AGE + 1 WHERE SEX = '%c'" % ('M')try: # 執(zhí)行SQL語句 cursor.execute(sql) # 提交到數(shù)據(jù)庫執(zhí)行 db.commit()except: # 發(fā)生錯(cuò)誤時(shí)回滾 db.rollback()# 關(guān)閉數(shù)據(jù)庫連接db.close() |
三、Socket
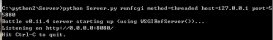
1、服務(wù)器
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
|
from socket import *from time import ctimeHOST = ''PORT = 21568BUFSIZ = 1024ADDR = (HOST, PORT)tcpSerSock = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM)tcpSerSock.bind(ADDR)tcpSerSock.listen(5)while True: print 'waiting for connection...' tcpCliSock, addr = tcpSerSock.accept() print '...connected from:', addr while True: try: data = tcpCliSock.recv(BUFSIZ) print '<', data tcpCliSock.send('[%s] %s' % (ctime(), data)) except: print 'disconnect from:', addr tcpCliSock.close() breaktcpSerSock.close() |
2、客戶端
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
from socket import *HOST = 'localhost'PORT = 21568BUFSIZ = 1024ADDR = (HOST, PORT)tcpCliSock = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM)tcpCliSock.connect(ADDR) try: while True: data = raw_input('>') if data == 'close': break if not data: continue tcpCliSock.send(data) data = tcpCliSock.recv(BUFSIZ) print dataexcept: tcpCliSock.close() |
四、多線程
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
import time, threading# 新線程執(zhí)行的代碼:def loop(): print 'thread %s is running...' % threading.current_thread().name n = 0 while n < 5: n = n + 1 print 'thread %s >>> %s' % (threading.current_thread().name, n) time.sleep(1) print 'thread %s ended.' % threading.current_thread().nameprint 'thread %s is running...' % threading.current_thread().namet = threading.Thread(target=loop, name='LoopThread')t.start()t.join()print 'thread %s ended.' % threading.current_thread().name |
還請大家積極補(bǔ)充!