一、poi的定義
java中操作excel的有兩種比較主流的工具包: jxl 和 poi 。jxl 只能操作excel 95, 97, 2000也即以.xls為后綴的excel。而poi可以操作excel 95及以后的版本,即可操作后綴為 .xls 和 .xlsx兩種格式的excel。
poi全稱 poor obfuscation implementation,直譯為“可憐的模糊實(shí)現(xiàn)”,利用poi接口可以通過java操作microsoft office 套件工具的讀寫功能。官網(wǎng):http://poi.apache.org ,poi支持office的所有版本,首先去官網(wǎng)下載如下界面:
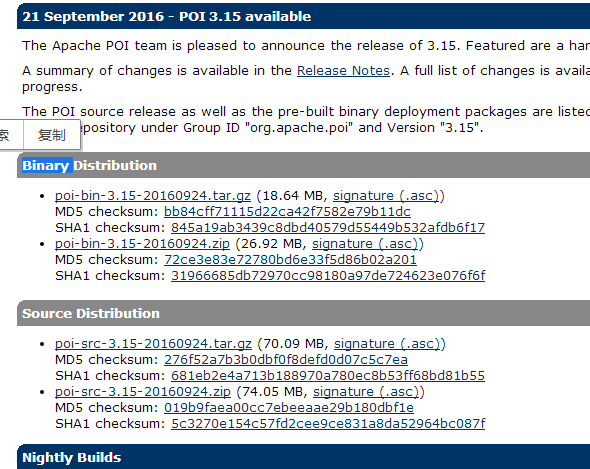
下載完后,打開“poi-bin-3.15-20160924.tar.gz”獲取操作excel需要的jar包,并將這些jar包復(fù)制到項(xiàng)目中。對于只操作2003 及以前版本的excel,只需要poi-3.15.jar ,如果需要同時對2007及以后版本進(jìn)行操作則需要復(fù)制
poi-ooxml-3.15.jar
poi-ooxml-schemas-3.15.jar
以及復(fù)制在ooxml-lib目錄下的xmlbeans-2.6.0.jar(但不知為何,我下的jar文件中沒有dom4j.jar)這個文件,還是加上dom4j.jar,防止報(bào)錯.
二、使用junit進(jìn)行操作excel測試
首先明確excel工作簿對象、工作表對象、行對象、以及單元格對象。
具體代碼如下注意要分清楚究竟是2007版本以前,還是2007版本以后(包括2007版本):下面這段代碼是2007版本以前的:
這段代碼只是將數(shù)據(jù)寫入到excel文件中創(chuàng)建
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
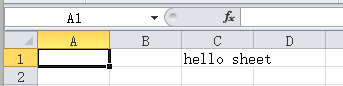
public static void main(string[] args) throws exception { /** * 注意這只是07版本以前的做法對應(yīng)的excel文件的后綴名為.xls * 07版本和07版本以后的做法excel文件的后綴名為.xlsx */ //創(chuàng)建新工作簿 hssfworkbook workbook = new hssfworkbook(); //新建工作表 hssfsheet sheet = workbook.createsheet("hello"); //創(chuàng)建行,行號作為參數(shù)傳遞給createrow()方法,第一行從0開始計(jì)算 hssfrow row = sheet.createrow(0); //創(chuàng)建單元格,row已經(jīng)確定了行號,列號作為參數(shù)傳遞給createcell(),第一列從0開始計(jì)算 hssfcell cell = row.createcell(2); //設(shè)置單元格的值,即c1的值(第一行,第三列) cell.setcellvalue("hello sheet"); //輸出到磁盤中 fileoutputstream fos = new fileoutputstream(new file("e:\\root\\sheet\\11.xls")); workbook.write(fos); workbook.close(); fos.close(); } |
結(jié)果如下圖:
同樣也可以對讀取excel文件,得到excel文件的數(shù)據(jù),并將其打印出來,代碼如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
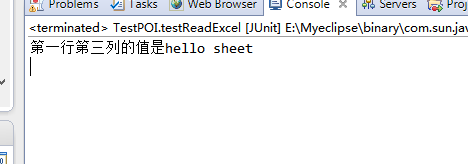
@test public void testreadexcel() throws exception { //創(chuàng)建輸入流 fileinputstream fis = new fileinputstream(new file("e:\\root\\sheet\\11.xls")); //通過構(gòu)造函數(shù)傳參 hssfworkbook workbook = new hssfworkbook(fis); //獲取工作表 hssfsheet sheet = workbook.getsheetat(0); //獲取行,行號作為參數(shù)傳遞給getrow方法,第一行從0開始計(jì)算 hssfrow row = sheet.getrow(0); //獲取單元格,row已經(jīng)確定了行號,列號作為參數(shù)傳遞給getcell,第一列從0開始計(jì)算 hssfcell cell = row.getcell(2); //設(shè)置單元格的值,即c1的值(第一行,第三列) string cellvalue = cell.getstringcellvalue(); system.out.println("第一行第三列的值是"+cellvalue); workbook.close(); fis.close(); } |
結(jié)果如下圖:
上面操作的都是07版本以前的excel文件,即后綴名為.xls,07和07版本以后的excel文件后綴名為.xlsx相應(yīng)的工作簿的對象名也改為:
|
1
2
|
//創(chuàng)建工作簿xssfworkbook workbook = new xssfworkbook(); |
代碼如下,創(chuàng)建excel文件并保存數(shù)據(jù)到excel文件:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
@test public void write07() throws exception { //創(chuàng)建工作簿 xssfworkbook workbook = new xssfworkbook(); //新建工作表 xssfsheet sheet = workbook.createsheet("hello"); //創(chuàng)建行,0表示第一行 xssfrow row = sheet.createrow(0); //創(chuàng)建單元格行號由row確定,列號作為參數(shù)傳遞給createcell;第一列從0開始計(jì)算 xssfcell cell = row.createcell(2); //給單元格賦值 cell.setcellvalue("hello sheet"); //創(chuàng)建輸出流 fileoutputstream fos = new fileoutputstream(new file("e:\\root\\sheet\\hello.xlsx")); workbook.write(fos); workbook.close(); fos.close(); } |
與之對應(yīng)的讀取數(shù)據(jù),代碼如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
|
@test public void read07() throws exception { //創(chuàng)建輸入流 fileinputstream fis = new fileinputstream(new file("e:\\root\\sheet\\hello.xlsx")); //由輸入流得到工作簿 xssfworkbook workbook = new xssfworkbook(fis); //得到工作表 xssfsheet sheet = workbook.getsheet("hello"); //得到行,0表示第一行 xssfrow row = sheet.getrow(0); //創(chuàng)建單元格行號由row確定,列號作為參數(shù)傳遞給createcell;第一列從0開始計(jì)算 xssfcell cell = row.getcell(2); //給單元格賦值 string cellvalue = cell.getstringcellvalue(); system.out.println("c1的值是"+cellvalue); int a[][] = new int[10][30]; for(int i=0;i<a.length;i++) { system.out.println(i); } workbook.close(); fis.close(); } |
問題出現(xiàn)了,也可以解釋為需求:當(dāng)不能確定究竟是讀取07以前(例如2003,95,97,2000)還是07版本以后的excel文件,我們當(dāng)然希望程序能夠自動識別,并創(chuàng)建相應(yīng)的對象,去操作excel文件,代碼如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
@test public void reda03and07() throws exception { //讀取03或07的版本 string filepath = "e:\\root\\sheet\\hello.xlsx"; if(filepath.matches("^.+\\.(?i)((xls)|(xlsx))$")) { fileinputstream fis = new fileinputstream(filepath); boolean is03excell = filepath.matches("^.+\\.(?i)(xls)$")?true:false; workbook workbook = is03excell ? new hssfworkbook(fis):new xssfworkbook(fis); sheet sheet = workbook.getsheetat(0); row row = sheet.getrow(0); cell cell = row.getcell(2); system.out.println("第一行第一列的數(shù)據(jù)是:"+cell.getstringcellvalue()); } } |
學(xué)完了上面幾個例子,接下來就是應(yīng)用它了,我們經(jīng)常需要在一個頁面中批量導(dǎo)出和批量導(dǎo)出數(shù)據(jù),這里就涉及到對excel文件的操作,當(dāng)然還有其它的文件格式,我們使用一個llist<user> list 來保存,在這里我們寫了一個excelutil這個工具類:代碼如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
|
package com.ittax.core.util;import java.util.list;import javax.servlet.servletoutputstream;import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.hssfcell;import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.hssfcellstyle;import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.hssffont;import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.hssfheader;import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.hssfrow;import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.hssfsheet;import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.hssfworkbook;import org.apache.poi.ss.util.cellrangeaddress;import com.ittax.nsfw.user.entity.user;/** * excel工具類,支持批量導(dǎo)出 * @author lizewu * */public class excelutil { /** * 將用戶的信息導(dǎo)入到excel文件中去 * @param userlist 用戶列表 * @param out 輸出表 */ public static void exportuserexcel(list<user> userlist,servletoutputstream out) { try{ //1.創(chuàng)建工作簿 hssfworkbook workbook = new hssfworkbook(); //1.1創(chuàng)建合并單元格對象 cellrangeaddress callrangeaddress = new cellrangeaddress(0,0,0,4);//起始行,結(jié)束行,起始列,結(jié)束列 //1.2頭標(biāo)題樣式 hssfcellstyle headstyle = createcellstyle(workbook,(short)16); //1.3列標(biāo)題樣式 hssfcellstyle colstyle = createcellstyle(workbook,(short)13); //2.創(chuàng)建工作表 hssfsheet sheet = workbook.createsheet("用戶列表"); //2.1加載合并單元格對象 sheet.addmergedregion(callrangeaddress); //設(shè)置默認(rèn)列寬 sheet.setdefaultcolumnwidth(25); //3.創(chuàng)建行 //3.1創(chuàng)建頭標(biāo)題行;并且設(shè)置頭標(biāo)題 hssfrow row = sheet.createrow(0); hssfcell cell = row.createcell(0); //加載單元格樣式 cell.setcellstyle(headstyle); cell.setcellvalue("用戶列表"); //3.2創(chuàng)建列標(biāo)題;并且設(shè)置列標(biāo)題 hssfrow row2 = sheet.createrow(1); string[] titles = {"用戶名","賬號","所屬部門","性別","電子郵箱"}; for(int i=0;i<titles.length;i++) { hssfcell cell2 = row2.createcell(i); //加載單元格樣式 cell2.setcellstyle(colstyle); cell2.setcellvalue(titles[i]); } //4.操作單元格;將用戶列表寫入excel if(userlist != null) { for(int j=0;j<userlist.size();j++) { //創(chuàng)建數(shù)據(jù)行,前面有兩行,頭標(biāo)題行和列標(biāo)題行 hssfrow row3 = sheet.createrow(j+2); hssfcell cell1 = row3.createcell(0); cell1.setcellvalue(userlist.get(j).getname()); hssfcell cell2 = row3.createcell(1); cell2.setcellvalue(userlist.get(j).getaccount()); hssfcell cell3 = row3.createcell(2); cell3.setcellvalue(userlist.get(j).getdept()); hssfcell cell4 = row3.createcell(3); cell4.setcellvalue(userlist.get(j).isgender()?"男":"女"); hssfcell cell5 = row3.createcell(4); cell5.setcellvalue(userlist.get(j).getemail()); } } //5.輸出 workbook.write(out); workbook.close(); //out.close(); }catch(exception e) { e.printstacktrace(); } } /** * * @param workbook * @param fontsize * @return 單元格樣式 */ private static hssfcellstyle createcellstyle(hssfworkbook workbook, short fontsize) { // todo auto-generated method stub hssfcellstyle style = workbook.createcellstyle(); style.setalignment(hssfcellstyle.align_center);//水平居中 style.setverticalalignment(hssfcellstyle.vertical_center);//垂直居中 //創(chuàng)建字體 hssffont font = workbook.createfont(); font.setboldweight(hssffont.boldweight_bold); font.setfontheightinpoints(fontsize); //加載字體 style.setfont(font); return style; }} |
緊接著就是在useservice中調(diào)用方法并寫出exportexcel方法:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
|
@override public void exportexcel(list<user> userlist, servletoutputstream out) { // todo auto-generated method stub excelutil.exportuserexcel(userlist, out); } @override public void importexcel(file file, string excelfilename) { // todo auto-generated method stub //1.創(chuàng)建輸入流 try { fileinputstream inputstream = new fileinputstream(file); boolean is03excel = excelfilename.matches("^.+\\.(?i)(xls)$"); //1.讀取工作簿 workbook workbook = is03excel?new hssfworkbook(inputstream):new xssfworkbook(inputstream); //2.讀取工作表 sheet sheet = workbook.getsheetat(0); //3.讀取行 //判斷行數(shù)大于二,是因?yàn)閿?shù)據(jù)從第三行開始插入 if(sheet.getphysicalnumberofrows() > 2) { user user = null; //跳過前兩行 for(int k=2;k<sheet.getphysicalnumberofrows();k++ ) { //讀取單元格 row row0 = sheet.getrow(k); user = new user(); //用戶名 cell cell0 = row0.getcell(0); user.setname(cell0.getstringcellvalue()); //賬號 cell cell1 = row0.getcell(1); user.setaccount(cell1.getstringcellvalue()); //所屬部門 cell cell2 = row0.getcell(2); user.setdept(cell2.getstringcellvalue()); //設(shè)置性別 cell cell3 = row0.getcell(3); boolean gender = cell3.getstringcellvalue() == "男"?true:false; user.setgender(gender); //設(shè)置手機(jī) string mobile = ""; cell cell4 = row0.getcell(4); try { mobile = cell4.getstringcellvalue(); } catch (exception e) { // todo auto-generated catch block double dmoblie = cell4.getnumericcellvalue(); mobile = bigdecimal.valueof(dmoblie).tostring(); } user.setmobile(mobile); //設(shè)置電子郵箱 cell cell5 = row0.getcell(5); user.setemail(cell5.getstringcellvalue()); //默認(rèn)用戶密碼是123456 user.setpassword("123456"); //用戶默認(rèn)狀態(tài)是有效 user.setstate(user.user_state_valide); //保存用戶 save(user); } } workbook.close(); inputstream.close(); } catch (exception e) { // todo auto-generated catch block e.printstacktrace(); } } |
最后就是在action中調(diào)用service方法:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
|
//導(dǎo)出用戶列表 public void exportexcel() { try { //1.查找用戶列表 userlist = userservice.findobjects(); //2.導(dǎo)出 httpservletresponse response = servletactioncontext.getresponse(); //這里設(shè)置的文件格式是application/x-excel response.setcontenttype("application/x-excel"); response.setheader("content-disposition", "attachment;filename=" + new string("用戶列表.xls".getbytes(), "iso-8859-1")); servletoutputstream outputstream = response.getoutputstream(); userservice.exportexcel(userlist, outputstream); if(outputstream != null) outputstream.close(); }catch(exception e) { e.printstacktrace(); } } public string importexcel() { if(userexcel!= null) { //判斷是否是excel文件 if(userexcelfilename.matches("^.+\\.(?i)((xls)|(xlsx))$")) { userservice.importexcel(userexcel, userexcelfilename); } } return"list"; } |
注意的是應(yīng)該使用servletoutputstream這個類,最后實(shí)現(xiàn)了批量導(dǎo)出和導(dǎo)入數(shù)據(jù)。
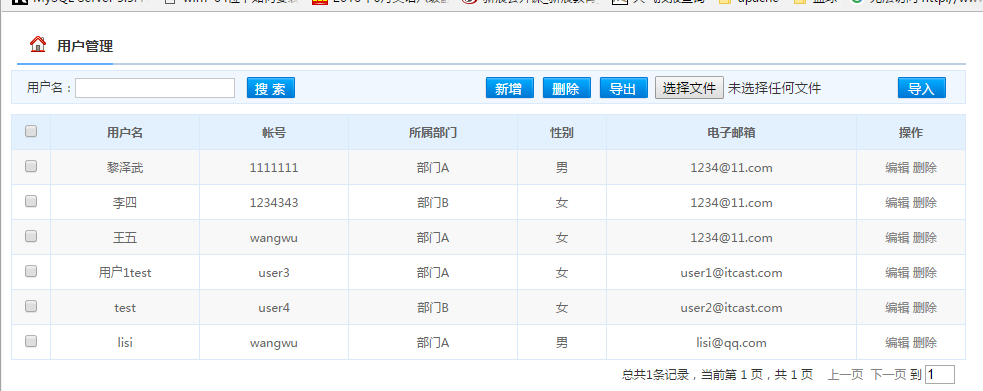
導(dǎo)出用戶結(jié)果如下圖;
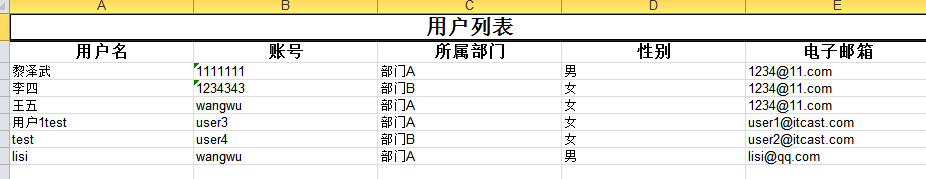
導(dǎo)入結(jié)果如下圖;
導(dǎo)入前:

導(dǎo)入后的結(jié)果;
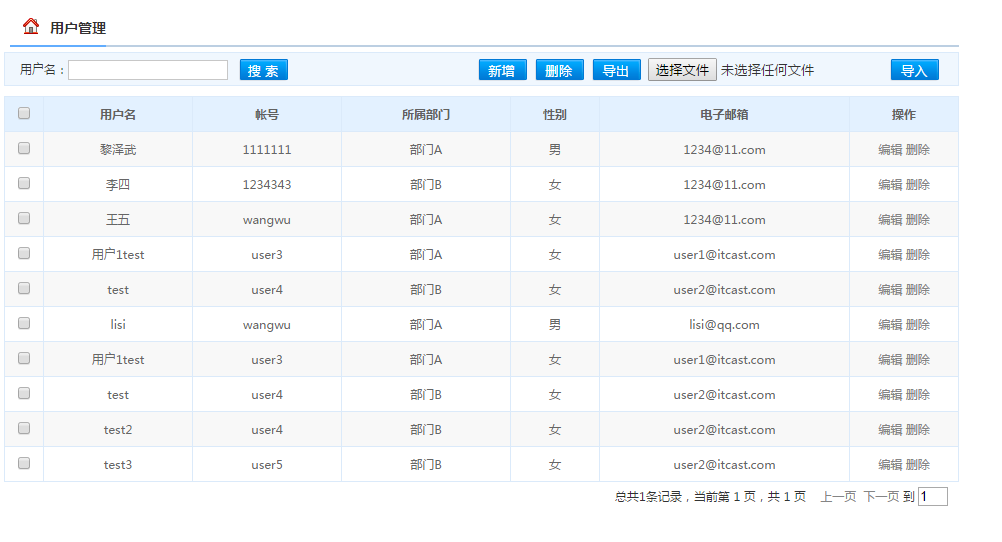
ok,關(guān)于poi操作excel文件就暫時到此為止了
以上就是本文的全部內(nèi)容,希望本文的內(nèi)容對大家的學(xué)習(xí)或者工作能帶來一定的幫助,同時也希望多多支持服務(wù)器之家!
原文鏈接:http://www.cnblogs.com/zhuixun/p/6600331.html















