阻塞隊列 (BlockingQueue)是Java util.concurrent包下重要的數據結構,BlockingQueue提供了線程安全的隊列訪問方式:當阻塞隊列進行插入數據時,如果隊列已滿,線程將會阻塞等待直到隊列非滿;從阻塞隊列取數據時,如果隊列已空,線程將會阻塞等待直到隊列非空。并發包下很多高級同步類的實現都是基于BlockingQueue實現的。
BlockingQueue 的操作方法
BlockingQueue 具有 4 組不同的方法用于插入、移除以及對隊列中的元素進行檢查。如果請求的操作不能得到立即執行的話,每個方法的表現也不同。這些方法如下:
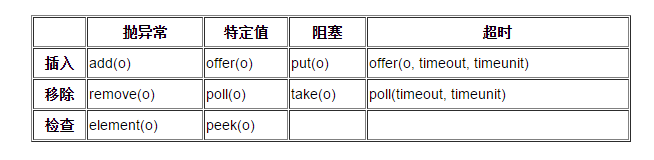
四組不同的行為方式解釋:
- 拋異常:如果試圖的操作無法立即執行,拋一個異常。
- 特定值:如果試圖的操作無法立即執行,返回一個特定的值(常常是 true / false)。
- 阻塞:如果試圖的操作無法立即執行,該方法調用將會發生阻塞,直到能夠執行。
- 超時:如果試圖的操作無法立即執行,該方法調用將會發生阻塞,直到能夠執行,但等待時間不會超過給定值。返回一個特定值以告知該操作是否成功(典型的是true / false)。
無法向一個 BlockingQueue 中插入 null。如果你試圖插入 null,BlockingQueue 將會拋出一個 NullPointerException。
可以訪問到 BlockingQueue 中的所有元素,而不僅僅是開始和結束的元素。比如說,你將一個對象放入隊列之中以等待處理,但你的應用想要將其取消掉。那么你可以調用諸如 remove(o) 方法來將隊列之中的特定對象進行移除。但是這么干效率并不高(譯者注:基于隊列的數據結構,獲取除開始或結束位置的其他對象的效率不會太高),因此你盡量不要用這一類的方法,除非你確實不得不那么做。
BlockingQueue 的實現類
BlockingQueue 是個接口,你需要使用它的實現之一來使用BlockingQueue,Java.util.concurrent包下具有以下 BlockingQueue 接口的實現類:
- ArrayBlockingQueue:ArrayBlockingQueue 是一個有界的阻塞隊列,其內部實現是將對象放到一個數組里。有界也就意味著,它不能夠存儲無限多數量的元素。它有一個同一時間能夠存儲元素數量的上限。你可以在對其初始化的時候設定這個上限,但之后就無法對這個上限進行修改了(譯者注:因為它是基于數組實現的,也就具有數組的特性:一旦初始化,大小就無法修改)。
- DelayQueue:DelayQueue 對元素進行持有直到一個特定的延遲到期。注入其中的元素必須實現 java.util.concurrent.Delayed 接口。
- LinkedBlockingQueue:LinkedBlockingQueue 內部以一個鏈式結構(鏈接節點)對其元素進行存儲。如果需要的話,這一鏈式結構可以選擇一個上限。如果沒有定義上限,將使用 Integer.MAX_VALUE 作為上限。
- PriorityBlockingQueue:PriorityBlockingQueue 是一個無界的并發隊列。它使用了和類 java.util.PriorityQueue 一樣的排序規則。你無法向這個隊列中插入 null 值。所有插入到 PriorityBlockingQueue 的元素必須實現 java.lang.Comparable 接口。因此該隊列中元素的排序就取決于你自己的 Comparable 實現。
- SynchronousQueue:SynchronousQueue 是一個特殊的隊列,它的內部同時只能夠容納單個元素。如果該隊列已有一元素的話,試圖向隊列中插入一個新元素的線程將會阻塞,直到另一個線程將該元素從隊列中抽走。同樣,如果該隊列為空,試圖向隊列中抽取一個元素的線程將會阻塞,直到另一個線程向隊列中插入了一條新的元素。據此,把這個類稱作一個隊列顯然是夸大其詞了。它更多像是一個匯合點。
使用例子:
阻塞隊列的最長使用的例子就是生產者消費者模式,也是各種實現生產者消費者模式方式中首選的方式。使用者不用關心什么阻塞生產,什么時候阻塞消費,使用非常方便,代碼如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
|
package MyThread;import java.util.Random;import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue;import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingQueue;import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;public class BlockingQueueTest { //生產者 public static class Producer implements Runnable{ private final BlockingQueue<Integer> blockingQueue; private volatile boolean flag; private Random random; public Producer(BlockingQueue<Integer> blockingQueue) { this.blockingQueue = blockingQueue; flag=false; random=new Random(); } public void run() { while(!flag){ int info=random.nextInt(100); try { blockingQueue.put(info); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" produce "+info); Thread.sleep(50); } catch (InterruptedException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } } public void shutDown(){ flag=true; } } //消費者 public static class Consumer implements Runnable{ private final BlockingQueue<Integer> blockingQueue; private volatile boolean flag; public Consumer(BlockingQueue<Integer> blockingQueue) { this.blockingQueue = blockingQueue; } public void run() { while(!flag){ int info; try { info = blockingQueue.take(); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" consumer "+info); Thread.sleep(50); } catch (InterruptedException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } } public void shutDown(){ flag=true; } } public static void main(String[] args){ BlockingQueue<Integer> blockingQueue = new LinkedBlockingQueue<Integer>(10); Producer producer=new Producer(blockingQueue); Consumer consumer=new Consumer(blockingQueue); //創建5個生產者,5個消費者 for(int i=0;i<10;i++){ if(i<5){ new Thread(producer,"producer"+i).start(); }else{ new Thread(consumer,"consumer"+(i-5)).start(); } } try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } producer.shutDown(); consumer.shutDown(); }} |
阻塞隊列原理:
其實阻塞隊列實現阻塞同步的方式很簡單,使用的就是是lock鎖的多條件(condition)阻塞控制。使用BlockingQueue封裝了根據條件阻塞線程的過程,而我們就不用關心繁瑣的await/signal操作了。
下面是Jdk 1.7中ArrayBlockingQueue部分代碼:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
|
public ArrayBlockingQueue(int capacity, boolean fair) { if (capacity <= 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException(); //創建數組 this.items = new Object[capacity]; //創建鎖和阻塞條件 lock = new ReentrantLock(fair); notEmpty = lock.newCondition(); notFull = lock.newCondition(); }//添加元素的方法public void put(E e) throws InterruptedException { checkNotNull(e); final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock; lock.lockInterruptibly(); try { while (count == items.length) notFull.await(); //如果隊列不滿就入隊 enqueue(e); } finally { lock.unlock(); } } //入隊的方法 private void enqueue(E x) { final Object[] items = this.items; items[putIndex] = x; if (++putIndex == items.length) putIndex = 0; count++; notEmpty.signal(); } //移除元素的方法 public E take() throws InterruptedException { final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock; lock.lockInterruptibly(); try { while (count == 0) notEmpty.await(); return dequeue(); } finally { lock.unlock(); } } //出隊的方法 private E dequeue() { final Object[] items = this.items; @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E x = (E) items[takeIndex]; items[takeIndex] = null; if (++takeIndex == items.length) takeIndex = 0; count--; if (itrs != null) itrs.elementDequeued(); notFull.signal(); return x; |
雙端阻塞隊列(BlockingDeque)
concurrent包下還提供雙端阻塞隊列(BlockingDeque),和BlockingQueue是類似的,只不過BlockingDeque提供從任意一端插入或者抽取元素的隊列。
以上就是本文的全部內容,希望對大家的學習有所幫助,也希望大家多多支持服務器之家。















