最近遇到一項需求,要求把properties文件中的內容讀取出來供用戶修改,修改完后需要再重新保存到properties文件中。很簡單的需求吧,可問題是properties是繼承自hashtable的,直接通過keyset()、keys()或entryset()方法對properties中的元素進行遍歷時取出來的內容順序與properties文件中的順序不一致,這是問題一;問題二是就算取出來的時候是有序的,保存到文件中時又是無序的了。
當然,解決這兩個問題的方法有很多。我最終采用的方法是自定義一個propertiesutil類,該類繼承自properties。propertiesutil提供一個返回由key按照存入順序組成的list的方法,getkeylist(),這樣問題一就解決了。那如何保證getkeylist()方法返回的就是有序的key組成的集合呢?我查看了一下properties方法的源碼,發現其setproperty()方法實際上就是調用了父類hashtable的put()方法,其次properties在從文件中加載內容時是按照文件順序進行讀取,然后調用父類hashtable的put()方法進行儲存。所以問題的解決辦法就是propertiesutil持有一個私有的可以有序存儲key的集合,然后重寫父類的put()方法,在方法體中照常通過super.put()進行屬性的存儲,同時將key添加到存儲key的集合中。
properties提供有save()方法和store()方法可以將當前對象的內容存放到指定的輸出流中,但它們的底層邏輯都是一樣的。通過調用keys()方法獲取一個enumeration,然后對該enumeration進行遍歷,依次將對應的key和value寫入到輸出流中,所以要保證寫入是有序的,就要保證遍歷keys()返回的enumeration時取出的元素key是有序的。所以解決方法是重寫keys()方法,保證遍歷返回的enumeration時得到的key是有序的。
下面就示范怎么按順序讀properties文件,以及還得按原來的順序寫properties文件。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
|
package com.lxk.propertyfiletest; import java.util.*; /** * created by lxk on 2017/5/2 */public class orderedproperties extends properties { private static final long serialversionuid = -4627607243846121965l; /** * 因為linkedhashset有序,所以,key在調用put()的時候,存放到這里也就有序。 */ private final linkedhashset<object> keys = new linkedhashset<>(); @override public enumeration<object> keys() { return collections.enumeration(keys); } /** * 在put的時候,只是把key有序的存到{@link orderedproperties#keys} * 取值的時候,根據有序的keys,可以有序的取出所有value * 依然調用父類的put方法,也就是key value 鍵值對還是存在hashtable里. * 只是現在多了個存key的屬性{@link orderedproperties#keys} */ @override public object put(object key, object value) { keys.add(key); return super.put(key, value); } /** * 因為復寫了這個方法,在(方式一)的時候,才輸出有序。 * {@link mainorder#printprop} */ @override public set<string> stringpropertynames() { set<string> set = new linkedhashset<>(); for (object key : this.keys) { set.add((string) key); } return set; } /** * 因為復寫了這個方法,在(方式二)的時候,才輸出有序。 * {@link mainorder#printprop} */ @override public set<object> keyset() { return keys; } //這個就不設置有序了,因為涉及到hashtable內部類:entryset,不好復寫。 //public linkedhashset<map.entry<object, object>> entryset() { // linkedhashset<map.entry<object, object>> entryset = new linkedhashset<>(); // for (object key : keys) { // // } // return entryset; //} /** * 因為復寫了這個方法,在(方式四)的時候,才輸出有序。 * {@link mainorder#printprop} */ @override public enumeration<?> propertynames() { return collections.enumeration(keys); } } |
上面是繼承java自帶的類,我們做的主要是實現有序,其他的還是原來的樣子就行。
看下整個的類繼承關系:如下圖:

下面是main方法的類。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
|
package com.lxk.propertyfiletest; import java.io.*; import java.util.enumeration; import java.util.map; import java.util.properties; import java.util.set; /** * 讀寫properties文件測試(帶順序的讀和寫) * <p> * created by lxk on 2017/5/2 */public class mainorder { public static void main(string[] args) { properties prop = readorderedpropertiesfile(); printprop(prop); writeorderedpropertiesfile(prop); } /** * 輸出properties的key和value */ public static void printprop(properties properties) { system.out.println("---------(方式一)------------"); for (string key : properties.stringpropertynames()) { system.out.println(key + "=" + properties.getproperty(key)); } system.out.println("---------(方式二)------------"); set<object> keys = properties.keyset();//返回屬性key的集合 for (object key : keys) { system.out.println(key.tostring() + "=" + properties.get(key)); } system.out.println("---------(方式三)------------"); set<map.entry<object, object>> entryset = properties.entryset();//返回的屬性鍵值對實體 for (map.entry<object, object> entry : entryset) { system.out.println(entry.getkey() + "=" + entry.getvalue()); } system.out.println("---------(方式四)------------"); enumeration<?> e = properties.propertynames(); while (e.hasmoreelements()) { string key = (string) e.nextelement(); string value = properties.getproperty(key); system.out.println(key + "=" + value); } } /** * 讀properties文件(有序) */ private static properties readorderedpropertiesfile() { properties properties = new orderedproperties(); inputstreamreader inputstreamreader = null; try { inputstream inputstream = new bufferedinputstream(new fileinputstream("d:testorder.properties")); //prop.load(in);//直接這么寫,如果properties文件中有漢子,則漢字會亂碼。因為未設置編碼格式。 inputstreamreader = new inputstreamreader(inputstream, "utf-8"); properties.load(inputstreamreader); } catch (exception e) { system.out.println(e.getmessage()); } finally { if (inputstreamreader != null) { try { inputstreamreader.close(); } catch (ioexception e) { system.out.println(e.getmessage()); } } } return properties; } /** * 寫properties文件(有序) */ private static void writeorderedpropertiesfile(properties properties) { properties.setproperty("phone", "10086"); outputstreamwriter outputstreamwriter = null; try { //保存屬性到b.properties文件 fileoutputstream fileoutputstream = new fileoutputstream("order.properties", false);//true表示追加打開,false每次都是清空再重寫 //prop.store(ofile, "此參數是保存生成properties文件中第一行的注釋說明文字");//這個會兩個地方亂碼 //prop.store(new outputstreamwriter(ofile, "utf-8"), "漢字亂碼");//這個就是生成的properties文件中第一行的注釋文字亂碼 outputstreamwriter = new outputstreamwriter(fileoutputstream, "utf-8"); properties.store(outputstreamwriter, "lll"); } catch (exception e) { system.out.println(e.getmessage()); } finally { if (outputstreamwriter != null) { try { outputstreamwriter.close(); } catch (ioexception e) { system.out.println(e.getmessage()); } } } } } |
其實讀和寫,都和使用系統提供的類的差別不大,只是現在讀到了我們自己寫的子類里面去了。
其他的代碼都是一樣樣的。
下面是讀的文件的內容截圖:
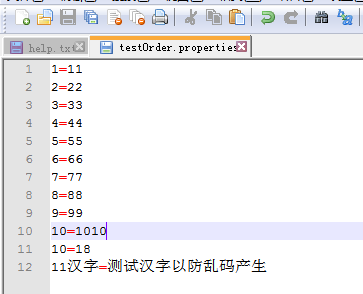
再然后是,實際代碼運行的結果截圖:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
|
---------(方式一)------------ 1=112=223=334=445=556=667=778=889=9910=1811漢字=測試漢字以防亂碼產生 ---------(方式二)------------ 1=112=223=334=445=556=667=778=889=9910=1811漢字=測試漢字以防亂碼產生 ---------(方式三)------------ 11漢字=測試漢字以防亂碼產生 9=998=887=776=665=554=443=332=2210=181=11---------(方式四)------------ 1=112=223=334=445=556=667=778=889=9910=1811漢字=測試漢字以防亂碼產生 |
額,太長了,就不截圖了吧,就給把打印結果給展示一下得了。
可以看到,只有第三次是無序的,具體原因,我也在代碼里面解釋過了。
還有,就是生成的文件的截圖:
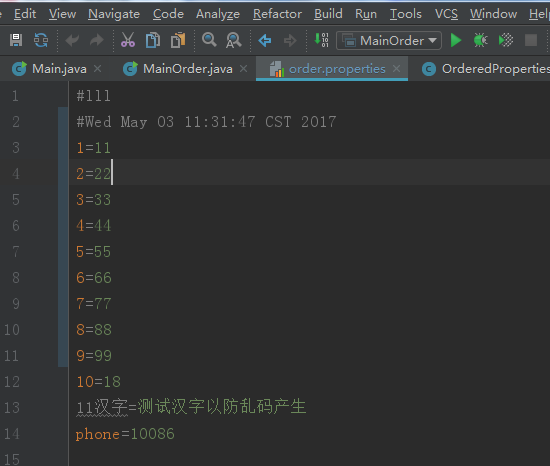
以上就是本文的全部內容,希望對大家的學習有所幫助,也希望大家多多支持服務器之家。
原文鏈接:http://blog.csdn.net/qq_27093465/article/details/71108520















