一:單向鏈表基本介紹
鏈表是一種數據結構,和數組同級。比如,java中我們使用的arraylist,其實現原理是數組。而linkedlist的實現原理就是鏈表了。鏈表在進行循環遍歷時效率不高,但是插入和刪除時優勢明顯。下面對單向鏈表做一個介紹。
單鏈表的概念
鏈表是最基本的數據結構,其存儲的你原理圖如下圖所示
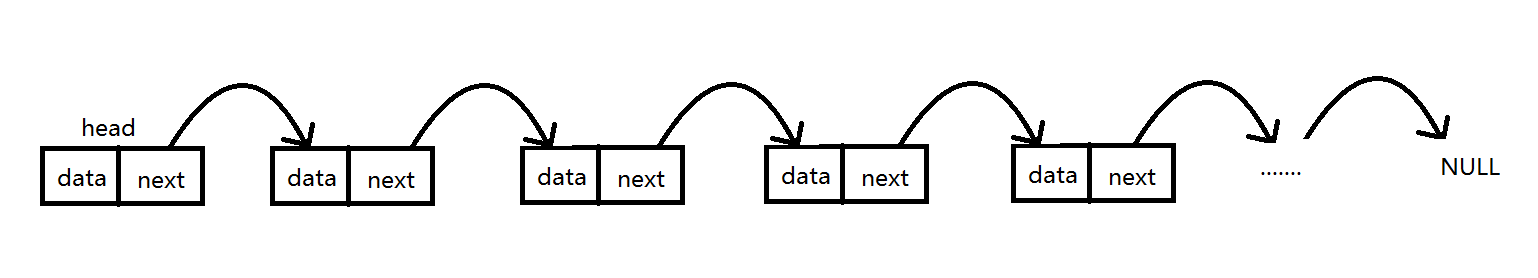
上面展示的是一個單鏈表的存儲原理圖,簡單易懂,head為頭節點,他不存放任何的數據,只是充當一個指向鏈表中真正存放數據的第一個節點的作用,而每個節點中都有一個next引用,指向下一個節點,就這樣一節一節往下面記錄,直到最后一個節點,其中的next指向null。
鏈表有很多種,比如單鏈表,雙鏈表等等。我們就對單鏈表進行學習,其他的懂了原理其實是一樣的。
單向鏈表是一種線性表,實際上是由節點(node)組成的,一個鏈表擁有不定數量的節點。其數據在內存中存儲是不連續的,它存儲的數據分散在內存中,每個結點只能也只有它能知道下一個結點的存儲位置。由n各節點(node)組成單向鏈表,每一個node記錄本node的數據及下一個node。向外暴露的只有一個頭節點(head),我們對鏈表的所有操作,都是直接或者間接地通過其頭節點來進行的。

上圖中最左邊的節點即為頭結點(head),但是添加節點的順序是從右向左的,添加的新節點會被作為新節點。最先添加的節點對下一節點的引用可以為空。引用是引用下一個節點而非下一個節點的對象。因為有著不斷的引用,所以頭節點就可以操作所有節點了。
下圖描述了單向鏈表存儲情況。存儲是分散的,每一個節點只要記錄下一節點,就把所有數據串了起來,形成了一個單向鏈表。

節點(node)是由一個需要儲存的對象及對下一個節點的引用組成的。也就是說,節點擁有兩個成員:儲存的對象、對下一個節點的引用。下面圖是具體的說明:

二、單項鏈表的實現
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
|
package com.zjn.linkandqueue;/** * 自定義鏈表設計 * * @author zjn * */public class mylink { node head = null; // 頭節點 /** * 鏈表中的節點,data代表節點的值,next是指向下一個節點的引用 * * @author zjn * */ class node { node next = null; // 節點的引用,指向下一個節點 int data; // 節點的對象,即內容 public node(int data) { this.data = data; } } /** * 向鏈表中插入數據 * * @param d */ public void addnode(int d) { node newnode = new node(d); // 實例化一個節點 if (head == null) { head = newnode; return; } node tmp = head; while (tmp.next != null) { tmp = tmp.next; } tmp.next = newnode; } /** * * @param index:刪除第index個節點 * @return */ public boolean deletenode(int index) { if (index < 1 || index > length()) { return false; } if (index == 1) { head = head.next; return true; } int i = 1; node prenode = head; node curnode = prenode.next; while (curnode != null) { if (i == index) { prenode.next = curnode.next; return true; } prenode = curnode; curnode = curnode.next; i++; } return false; } /** * * @return 返回節點長度 */ public int length() { int length = 0; node tmp = head; while (tmp != null) { length++; tmp = tmp.next; } return length; } /** * 在不知道頭指針的情況下刪除指定節點 * * @param n * @return */ public boolean deletenode11(node n) { if (n == null || n.next == null) return false; int tmp = n.data; n.data = n.next.data; n.next.data = tmp; n.next = n.next.next; system.out.println("刪除成功!"); return true; } public void printlist() { node tmp = head; while (tmp != null) { system.out.println(tmp.data); tmp = tmp.next; } } public static void main(string[] args) { mylink list = new mylink(); list.addnode(5); list.addnode(3); list.addnode(1); list.addnode(2); list.addnode(55); list.addnode(36); system.out.println("linklength:" + list.length()); system.out.println("head.data:" + list.head.data); list.printlist(); list.deletenode(4); system.out.println("after deletenode(4):"); list.printlist(); }} |
三、鏈表相關的常用操作實現方法
1. 鏈表反轉
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
/** * 鏈表反轉 * * @param head * @return */ public node reverseiteratively(node head) { node preversedhead = head; node pnode = head; node pprev = null; while (pnode != null) { node pnext = pnode.next; if (pnext == null) { preversedhead = pnode; } pnode.next = pprev; pprev = pnode; pnode = pnext; } this.head = preversedhead; return this.head; } |
2. 查找單鏈表的中間節點
采用快慢指針的方式查找單鏈表的中間節點,快指針一次走兩步,慢指針一次走一步,當快指針走完時,慢指針剛好到達中間節點。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
/** * 查找單鏈表的中間節點 * * @param head * @return */ public node searchmid(node head) { node p = this.head, q = this.head; while (p != null && p.next != null && p.next.next != null) { p = p.next.next; q = q.next; } system.out.println("mid:" + q.data); return q; } |
3. 查找倒數第k個元素
采用兩個指針p1,p2,p1先前移k步,然后p1、p2同時移動,當p1移動到尾部時,p2所指位置的元素即倒數第k個元素 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
/** * 查找倒數 第k個元素 * * @param head * @param k * @return */ public node findelem(node head, int k) { if (k < 1 || k > this.length()) { return null; } node p1 = head; node p2 = head; for (int i = 0; i < k; i++)// 前移k步 p1 = p1.next; while (p1 != null) { p1 = p1.next; p2 = p2.next; } return p2; } |
4. 對鏈表進行排序
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
/** * 排序 * * @return */public node orderlist() { node nextnode = null; int tmp = 0; node curnode = head; while (curnode.next != null) { nextnode = curnode.next; while (nextnode != null) { if (curnode.data > nextnode.data) { tmp = curnode.data; curnode.data = nextnode.data; nextnode.data = tmp; } nextnode = nextnode.next; } curnode = curnode.next; } return head;} |
5. 刪除鏈表中的重復節點
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
/** * 刪除重復節點 */ public void deleteduplecate(node head) { node p = head; while (p != null) { node q = p; while (q.next != null) { if (p.data == q.next.data) { q.next = q.next.next; } else q = q.next; } p = p.next; } } |
6. 從尾到頭輸出單鏈表,采用遞歸方式實現
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
/** * 從尾到頭輸出單鏈表,采用遞歸方式實現 * * @param plisthead */ public void printlistreversely(node plisthead) { if (plisthead != null) { printlistreversely(plisthead.next); system.out.println("printlistreversely:" + plisthead.data); } } |
7. 判斷鏈表是否有環,有環情況下找出環的入口節點
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
|
/** * 判斷鏈表是否有環,單向鏈表有環時,尾節點相同 * * @param head * @return */ public boolean isloop(node head) { node fast = head, slow = head; if (fast == null) { return false; } while (fast != null && fast.next != null) { fast = fast.next.next; slow = slow.next; if (fast == slow) { system.out.println("該鏈表有環"); return true; } } return !(fast == null || fast.next == null); } /** * 找出鏈表環的入口 * * @param head * @return */ public node findloopport(node head) { node fast = head, slow = head; while (fast != null && fast.next != null) { slow = slow.next; fast = fast.next.next; if (slow == fast) break; } if (fast == null || fast.next == null) return null; slow = head; while (slow != fast) { slow = slow.next; fast = fast.next; } return slow; } |
總結
以上就是本文關于鏈表的原理及java實現代碼示例的全部內容,希望對大家有所幫助。如有不足之處,歡迎留言指出。
原文鏈接:http://blog.csdn.net/jianyuerensheng/article/details/51200274















