1、RetentionPolicy.SOURCE:注解只保留在源文件,當Java文件編譯成class文件的時候,注解被遺棄;
2、RetentionPolicy.CLASS:注解被保留到class文件,但jvm加載class文件時候被遺棄,這是默認的生命周期;
3、RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME:注解不僅被保存到class文件中,jvm加載class文件之后,仍然存在;
這3個生命周期分別對應于:Java源文件(.java文件)--->.class文件--->內存中的字節碼。
那怎么來選擇合適的注解生命周期呢?
首先要明確生命周期長度SOURCE<CLASS<RUNTIME,所以前者能作用的地方后者一定也能作用。一般如果需要在運行時去動態獲取注解信息,那只能用RUNTIME注解;如果要在編譯時進行一些預處理操作,比如生成一些輔助代碼(如ButterKnife),就用CLASS注解;如果只是做一些檢查性的操作,比如@Override和@SuppressWarnings,則可選用SOURCE注解。
下面來介紹下運行時注解的簡單運用。
獲取注解
你需要通過反射來獲取運行時注解,可以從Package、Class、Field、Method...上面獲取,基本方法都一樣,幾個常見的方法如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
/** * 獲取指定類型的注解 */public <A extends Annotation> A getAnnotation(Class<A> annotationType);/** * 獲取所有注解,如果有的話 */public Annotation[] getAnnotations();/** * 獲取所有注解,忽略繼承的注解 */public Annotation[] getDeclaredAnnotations();/** * 指定注解是否存在該元素上,如果有則返回true,否則false */public Boolean isAnnotationPresent(Class<? extends Annotation> annotationType);/** * 獲取Method中參數的所有注解 */public Annotation[][] getParameterAnnotations(); |
要使用這些函數必須先通過反射獲取到對應的元素:Class、Field、Method等。
自定義注解
來看下自定義注解的簡單使用方式,這里先定義3個運行時注解:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
// 適用類、接口(包括注解類型)或枚舉 @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Target(ElementType.TYPE) public @interface ClassInfo { String value(); } // 適用field屬性,也包括enum常量 @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Target(ElementType.FIELD) public @interface FieldInfo { int[] value(); } // 適用方法 @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Target(ElementType.METHOD) public @interface MethodInfo { String name() default "long"; String data(); int age() default 27; } |
這3個注解分別適用于不同的元素,并都帶有不同的屬性,在使用注解是需要設置這些屬性值。
再定義一個測試類來使用這些注解:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
/** * 測試運行時注解 */@ClassInfo("Test Class") public class TestRuntimeAnnotation { @FieldInfo(value = {1, 2}) public String fieldInfo = "FiledInfo"; @FieldInfo(value = {10086}) public int i = 100; @MethodInfo(name = "BlueBird", data = "Big") public static String getMethodInfo() { return TestRuntimeAnnotation.class.getSimpleName(); }} |
使用還是很簡單的,最后來看怎么在代碼中獲取注解信息:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
|
/** * 測試運行時注解 */private void _testRuntimeAnnotation() { StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer(); Class<?> cls = TestRuntimeAnnotation.class; Constructor<?>[] constructors = cls.getConstructors(); // 獲取指定類型的注解 sb.append("Class注解:").append("\n"); ClassInfo classInfo = cls.getAnnotation(ClassInfo.class); if (classInfo != null) { sb.append(Modifier.toString(cls.getModifiers())).append(" ") .append(cls.getSimpleName()).append("\n"); sb.append("注解值: ").append(classInfo.value()).append("\n\n"); } sb.append("Field注解:").append("\n"); Field[] fields = cls.getDeclaredFields(); for (Field field : fields) { FieldInfo fieldInfo = field.getAnnotation(FieldInfo.class); if (fieldInfo != null) { sb.append(Modifier.toString(field.getModifiers())).append(" ") .append(field.getType().getSimpleName()).append(" ") .append(field.getName()).append("\n"); sb.append("注解值: ").append(Arrays.toString(fieldInfo.value())).append("\n\n"); } } sb.append("Method注解:").append("\n"); Method[] methods = cls.getDeclaredMethods(); for (Method method : methods) { MethodInfo methodInfo = method.getAnnotation(MethodInfo.class); if (methodInfo != null) { sb.append(Modifier.toString(method.getModifiers())).append(" ") .append(method.getReturnType().getSimpleName()).append(" ") .append(method.getName()).append("\n"); sb.append("注解值: ").append("\n"); sb.append("name: ").append(methodInfo.name()).append("\n"); sb.append("data: ").append(methodInfo.data()).append("\n"); sb.append("age: ").append(methodInfo.age()).append("\n"); } } System.out.print(sb.toString());} |
所做的操作都是通過反射獲取對應元素,再獲取元素上面的注解,最后得到注解的屬性值。
看一下輸出情況,這里我直接顯示在手機上:
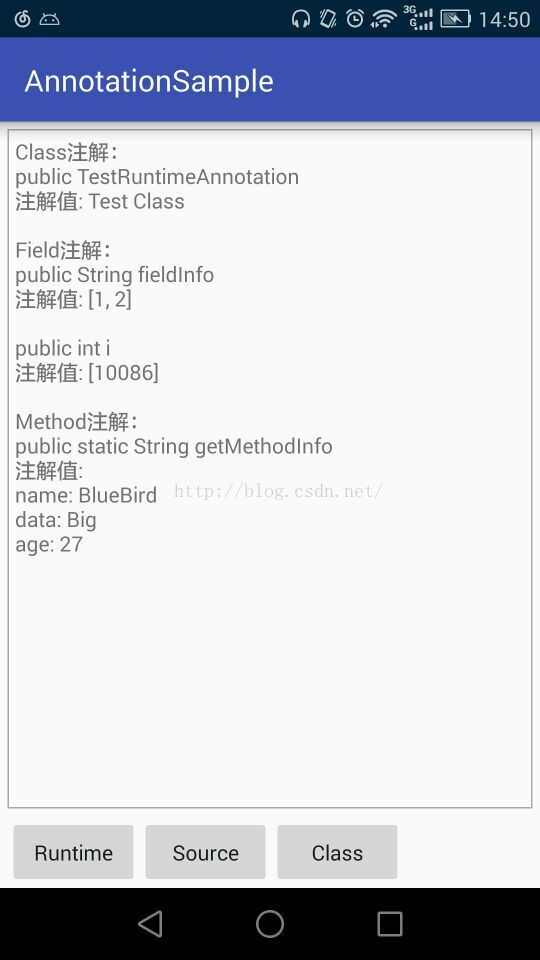
總結
以上就是本文關于java語言注解基礎概念詳解的全部內容,希望對大家有所幫助。感興趣的朋友可以繼續參閱本站其他相關專題,如有不足之處,歡迎留言指出。感謝朋友們對本站的支持!
原文鏈接:http://blog.csdn.net/hypmxy/article/details/72676331















