java中方法的參數(shù)傳遞方式只有一種:值傳遞。
java內(nèi)存分配:
1.棧:存放 基本類(lèi)型的數(shù)據(jù)、對(duì)象的引用(類(lèi)似于c語(yǔ)言中的指針)
2.堆:存放用new產(chǎn)生的數(shù)據(jù)
3.靜態(tài)域:存放在對(duì)象中用static定義的靜態(tài)成員
4.常量池:存放常量
5.寄存器
6.非ram存儲(chǔ)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
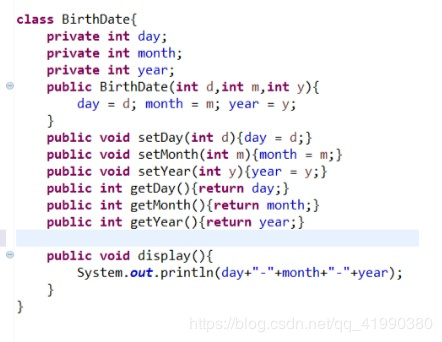
class birthdate{ private int day; private int month; private int year; public birthdate(int d,int m,int y){ day=d; month=m; year=y; }} |
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
public class test{ public static void main(string[] args){ int date=9; test test=new test(); test.change(date); birthdate d1=new birthdate(7,7,1970); } public void change(int i){ i=1234; }} |
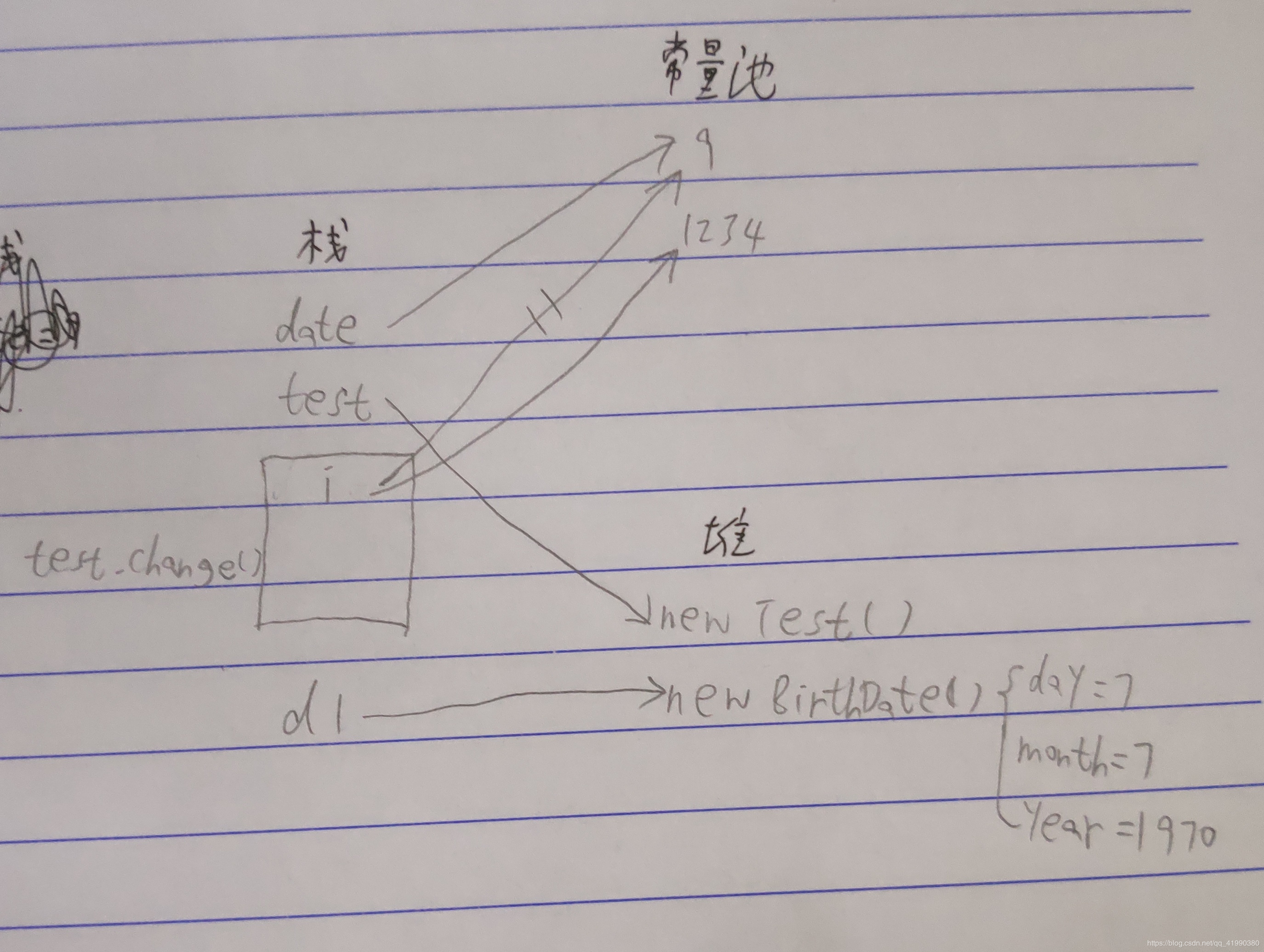
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
public class testtransfer{ public static void main(string[] args){ int a=6; int b=9; swap(a,b); system.out.println("交換結(jié)束后,a的值是"+a+";b的值是"+b); //a=9,b=6 } public static void swap(int a,int b){ int tmp=a; a=b; b=tmp; system.out.println("swap方法里,a的值是"+a+";b的值是"+b); //a=6,b=9 }} |
前


|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
public class testtransfer{ public static void main(string[] args){ dataswap ds=new dataswap(); ds.a=6; ds.b=9; swap(ds); system.out.println("交換結(jié)束后,ds.a的值是"+ds.a+";ds.b的值是"+ds.b); //a=9,b=6 } public static void swap(dataswap ds){ int tmp=ds.a; ds.a=ds.b; ds.b=tmp; system.out.println("swap方法里,ds.a的值是"+ds.a+";ds.b的值是"+ds.b); //a=9,b=6 }} class dataswap{ public int a; public int b;} |




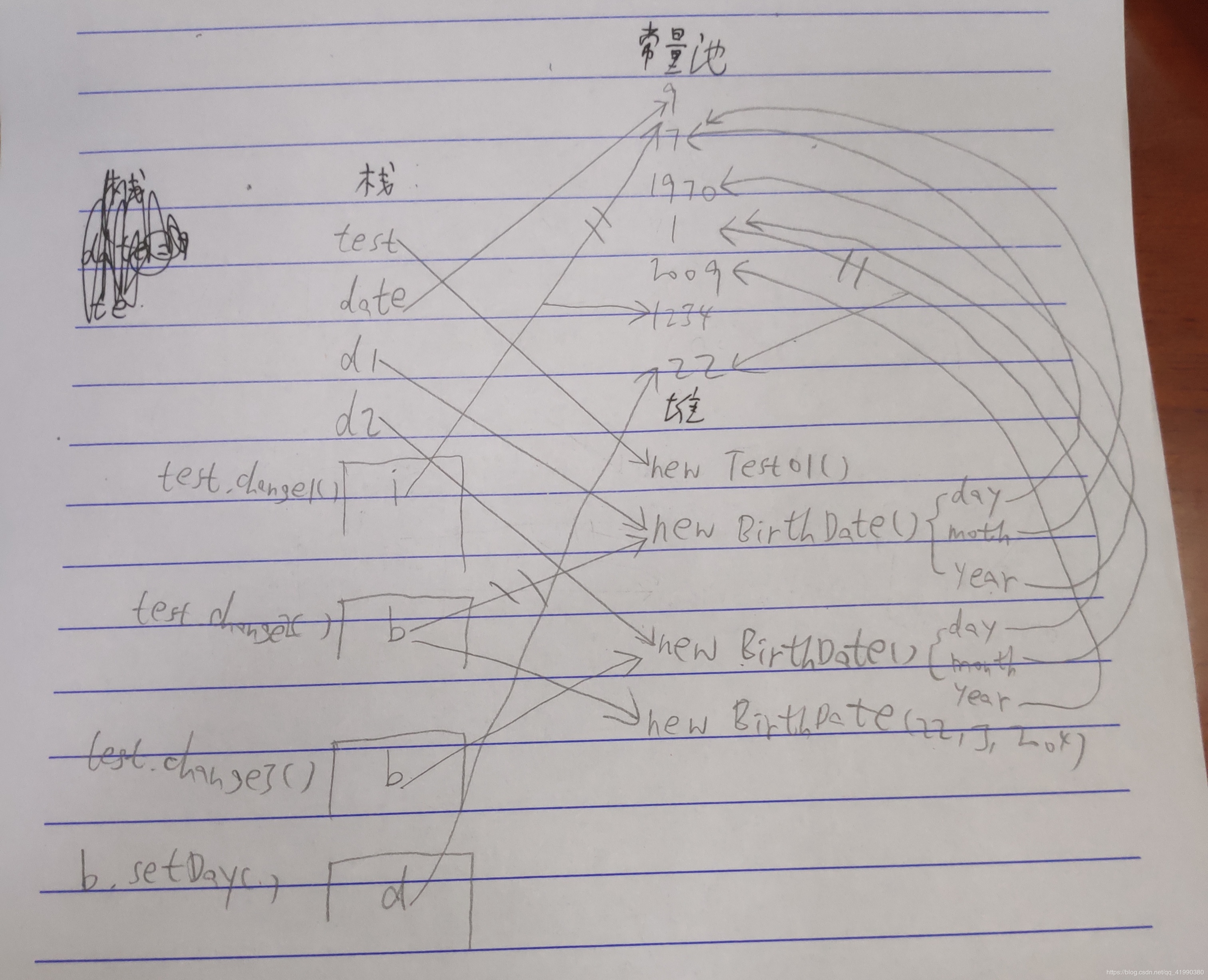
以上所述是小編給大家介紹的java內(nèi)存分配與參數(shù)傳遞詳解整合,希望對(duì)大家有所幫助,如果大家有任何疑問(wèn)請(qǐng)給我留言,小編會(huì)及時(shí)回復(fù)大家的。在此也非常感謝大家對(duì)服務(wù)器之家網(wǎng)站的支持!
原文鏈接:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41990380/article/details/88669624














