前言:在前面我們提到數(shù)據(jù)結(jié)構(gòu)的線性表。那么今天我們詳細看下Java源碼是如何實現(xiàn)線性表的,這一篇主要講解順序表ArrayList鏈?zhǔn)奖硐乱黄谔峒啊?/p>
1:ArrayList結(jié)構(gòu)圖
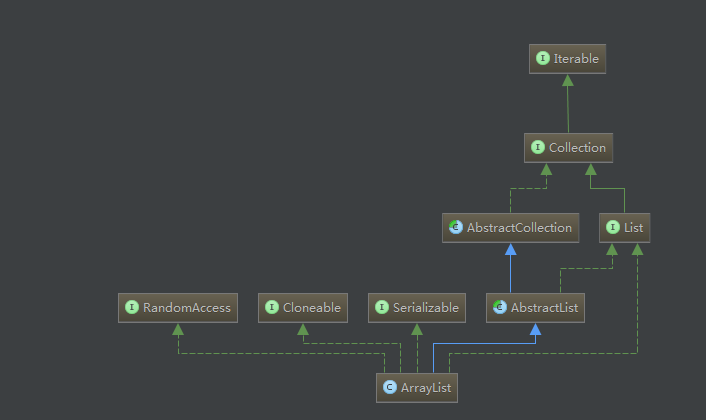
2:關(guān)于Collection和List的區(qū)別
最好的比對就是查看他們的源碼我們先看Collection的所有接口
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
public interface Collection<E> extends Iterable<E> { int size(); boolean contains(Object o); Iterator<E> iterator(); Object[] toArray(); <T> T[] toArray(T[] a); boolean add(E e); boolean remove(Object o); boolean containsAll(Collection<?> c); boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c); boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c); void clear(); boolean equals(Object o); int hashCode();} |
在看List接口
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
public interface List<E> extends Collection<E> { int size(); boolean isEmpty(); Iterator<E> iterator(); Object[] toArray(); <T> T[] toArray(T[] a); boolean add(E e); boolean remove(Object o); boolean containsAll(Collection<?> c); boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c); boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c); boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c); boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c); void clear(); boolean equals(Object o); int hashCode(); E get(int index); E set(int index, E element); void add(int index, E element); E remove(int index); int indexOf(Object o); int lastIndexOf(Object o); ListIterator<E> listIterator(); ListIterator<E> listIterator(int index); List<E> subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex);} |
由于List是繼承Collection,所有具有Collection所有的功能,從Collection接口中我們也可以看出,Collection不具有索引,不可以取元素的值,而List取可以,List是具有索引的,這樣一來在獲取元素方面遠遠好于Collection。
3:Iterable接口
從ArrayList中我們可以看出,最頂端的接口就是Iterable這個接口,這個是一個迭代器,接口如下
|
1
2
3
|
public interface Iterable<T> { Iterator<T> iterator();} |
這個接口主要是返回一個對象,這個對象是Iterator,那么我們在看看Iterator接口里面的方法
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
public interface Iterator<E> { boolean hasNext(); E next(); void remove();} |
那么我們主要看ArrayList是如何實現(xiàn)迭代器Iterator的。Iterator的實現(xiàn)在AbstractList這個抽象類中的一個私有類Itr中。我們看看具體實現(xiàn)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
private class Itr implements Iterator<E> { int cursor = 0; int lastRet = -1; int expectedModCount = modCount; public boolean hasNext() { return cursor != size(); } |
cursor:記錄即將調(diào)用索引的位置
lastRet:最后一個元素的索引
int expectedModCount = modCount;目的是為了驗證modCount后面會單獨說下。
判斷這個集合是否存在最后一個元素,通過cursor != size();size表示數(shù)組的長度,因為數(shù)組中元素索引從0開始,所以當(dāng)最后一個索引等于數(shù)組長度的時候說明已經(jīng)到數(shù)組的尾部了。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
public E next() { checkForComodification(); try { E next = get(cursor); lastRet = cursor++; return next; } catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException e) { checkForComodification(); throw new NoSuchElementException(); } } |
|
1
2
3
4
|
final void checkForComodification() { if (modCount != expectedModCount) throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); } |
modCount:記錄所有數(shù)組數(shù)據(jù)結(jié)構(gòu)變動的次數(shù),包括添加、刪除、更改等,為了避免并發(fā)時候,當(dāng)多個線程同時操作時候,某個線程修改了數(shù)組結(jié)構(gòu),而另一個線程恰恰讀取這個數(shù)組,這樣一來就會產(chǎn)生錯誤。所以在這段代碼中加入了modCount != expectedModCount,比如A線程對數(shù)據(jù)結(jié)構(gòu)修改一次,那么modCount比如+1,而expectedModCount并沒有發(fā)生變化,所以這樣就會拋出異常。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
public void remove() { if (lastRet == -1) throw new IllegalStateException(); checkForComodification(); try { AbstractList.this.remove(lastRet); if (lastRet < cursor) cursor--; lastRet = -1; expectedModCount = modCount; } catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException e) { throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); } } |
我們剛剛說了lastRet記錄的是最后一個元素,所以刪除的時候直接按照索引刪除即可,因為modCount會減一,所以重新對expectedModCount 進行賦值,避免遍歷時候產(chǎn)生錯誤。而且把lastRed在次賦初始值。
4:分析ArrayList
剛剛目的是為了更加連接ArrayList做個鋪墊,ArrayList和我們以前數(shù)據(jù)結(jié)構(gòu)中提到的順序表一樣,采用Object[] 數(shù)組進行存儲元素,用size來記錄元素的元素的個數(shù)。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
/** * The array buffer into which the elements of the ArrayList are stored. * The capacity of the ArrayList is the length of this array buffer. */ private transient Object[] elementData; /** * The size of the ArrayList (the number of elements it contains). * * @serial */ private int size; |
關(guān)于transient,一旦變量被transient修飾,變量將不再是對象持久化的一部分,那么為啥采用transient修飾呢,由于elementData本身是一個緩存數(shù)組,通常會預(yù)留一些容量,當(dāng)容量不夠時然后進行擴充,比如現(xiàn)在elementData容量是10,但是只有5個元素,數(shù)組中的最后五個元素是沒有實際意義的,不需要儲存,所以ArrayList的設(shè)計者將elementData設(shè)計為transient,然后在writeObject方法中手動將其序列化,并且只序列化了實際存儲的那些元素,而不是整個數(shù)組。我們看下writeObject方法
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
private void writeObject(java.io.ObjectOutputStream s) throws java.io.IOException{ // Write out element count, and any hidden stuff int expectedModCount = modCount; s.defaultWriteObject(); // Write out array length s.writeInt(elementData.length); // Write out all elements in the proper order. for (int i=0; i<size; i++) s.writeObject(elementData[i]); if (modCount != expectedModCount) { throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); } } |
關(guān)于ArrayList的初始化。ArrayList的設(shè)計者采用3種方式初始化。(默認(rèn)數(shù)組容量是10)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) { super(); if (initialCapacity < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+initialCapacity); this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity]; } public ArrayList() { this(10); } public ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c) { elementData = c.toArray(); size = elementData.length; // c.toArray might (incorrectly) not return Object[] (see 6260652) if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class) elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, Object[].class); } |
trimToSize方法,這個方法可能我們好多人用的少,其實意義蠻大的,它主要把沒用的容量去除掉,這樣一來可以減少內(nèi)存的開銷
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
public void trimToSize() {modCount++;int oldCapacity = elementData.length;if (size < oldCapacity) { elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size);} |
ensureCapacity方法,我們知道數(shù)組如果滿了就會進行擴容,這個方法就是擴容的。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
public void ensureCapacity(int minCapacity) { modCount++; int oldCapacity = elementData.length; if (minCapacity > oldCapacity) { Object oldData[] = elementData; int newCapacity = (oldCapacity * 3)/2 + 1; if (newCapacity < minCapacity) newCapacity = minCapacity; // minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win: elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity); } |
modCount就是增加因子,記錄操作數(shù)組結(jié)構(gòu)的次數(shù),首先和容量進行比對,如果不夠了進行擴容。這是Java1.6版本的就是在原來的基礎(chǔ)上擴容1.5倍。1.7采用>>1也就是所有元素像右邊移動一位然后加上原來的容量。其中
indexOf方法,這個方法是獲取元素索引。通過索引然后進行查詢元素
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
public int indexOf(Object o) { if (o == null) { for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) if (elementData[i]==null) return i; } else { for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) if (o.equals(elementData[i])) return i; } return -1; } |
從中我們也可以看出ArrayList是支持null的插入的。同樣采用的是循環(huán)遍歷來進行查找,時間復(fù)雜的為n。
contains方法,驗證數(shù)組是否包含某元素,直接通過indexOf驗證返回值即可
|
1
2
3
|
public boolean contains(Object o) { return indexOf(o) >= 0; } |
lastIndexOf方法,和indexOf相對,indexOf是從前往后,lastIndexOf是從后面往前查找如下
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
public int lastIndexOf(Object o) { if (o == null) { for (int i = size-1; i >= 0; i--) if (elementData[i]==null) return i; } else { for (int i = size-1; i >= 0; i--) if (o.equals(elementData[i])) return i; } return -1; } |
toArray方法,就是把List轉(zhuǎn)換成數(shù)組形式
|
1
2
3
|
public Object[] toArray() { return Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size); } |
get和set方法,這個就很簡單了大家看下就行
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
public E get(int index) { RangeCheck(index); return (E) elementData[index]; } public E set(int index, E element) { RangeCheck(index); E oldValue = (E) elementData[index]; elementData[index] = element; return oldValue; } |
RangeCheck方法是進行驗證的,查詢的索引不可以超過數(shù)組的長度如下
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
private void RangeCheck(int index) {if (index >= size)throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Index: "+index+", Size: "+size);} |
add(E e)添加一個元素,這個采用尾插入,先驗證容量,size+1是加入1個元素后長度,看原來數(shù)組容量是否夠。
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
public boolean add(E e) {ensureCapacity(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!elementData[size++] = e;return true;} |
add(int index, E element)按照索引進行插入,第一個還是一樣進行擴容,然后把索引index后面的元素全部向后面移一位。System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1,
size - index);的意思就是將elementData的第index個元素移到第index+1個元素上,長度為size-index。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
public void add(int index, E element) { if (index > size || index < 0) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException( "Index: "+index+", Size: "+size); ensureCapacity(size+1); // Increments modCount!! System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1, size - index); elementData[index] = element; size++; } |
addAll(Collection<? extends E> c)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) { Object[] a = c.toArray(); int numNew = a.length; ensureCapacity(size + numNew); // Increments modCount System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, size, numNew); size += numNew; return numNew != 0; } |
首先把集合c轉(zhuǎn)換成a數(shù)組,然后計算要進行添加的數(shù)組長度,其它的基本和添加元素一致。arraycopy(Object src, int srcPos,Object dest, int destPos,int length)
參數(shù)次數(shù)依次 源數(shù)組,源數(shù)組起始位置,目標(biāo)數(shù)組,目標(biāo)數(shù)組起始位置,復(fù)制數(shù)組元素數(shù)目。
addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c)把數(shù)組插入到指定位置
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) { if (index > size || index < 0) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException( "Index: " + index + ", Size: " + size); Object[] a = c.toArray(); int numNew = a.length; ensureCapacity(size + numNew); // Increments modCount int numMoved = size - index; if (numMoved > 0) System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + numNew, numMoved); System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, index, numNew); size += numNew; return numNew != 0; } |
首先判斷是是否越界,然后和上面的基本一樣,就是進行擴容判斷,然后index后面的值進行后移包括index,然后留下的空間插入集合a。所以2次進行復(fù)制元素。
E remove(int index)和add相對,刪除這個元素然后把index后面的元素往前面移一位size - index - 1其中-1是因為index這個元素會被刪除,會少一位元素。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
public E remove(int index) { RangeCheck(index); modCount++; E oldValue = (E) elementData[index]; int numMoved = size - index - 1; if (numMoved > 0) System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index, numMoved); elementData[--size] = null; // Let gc do its work return oldValue; } |
remove(Object o)這個就需要先進性驗證然后找到這個元素的位置最后進行刪除
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
public boolean remove(Object o) { if (o == null) { for (int index = 0; index < size; index++) if (elementData[index] == null) { fastRemove(index); return true; } } else { for (int index = 0; index < size; index++) if (o.equals(elementData[index])) { fastRemove(index); return true; } } return false; } |
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
private void fastRemove(int index) { modCount++; int numMoved = size - index - 1; if (numMoved > 0) System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index, numMoved); elementData[--size] = null; // Let gc do its work } |
clear就是把所有的原素置空
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
public void clear() { modCount++; // Let gc do its work for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) elementData[i] = null; size = 0; } |
subList方法,我們知道ArrayList是有這個方法,在ArrayList源碼并不存在,因為是繼承AbstractList而來的
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
public List<E> subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {return (this instanceof RandomAccess ? new RandomAccessSubList<E>(this, fromIndex, toIndex) : new SubList<E>(this, fromIndex, toIndex));} |
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
class SubList<E> extends AbstractList<E> { private AbstractList<E> l; private int offset; private int size; private int expectedModCount; SubList(AbstractList<E> list, int fromIndex, int toIndex) { if (fromIndex < 0) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("fromIndex = " + fromIndex); if (toIndex > list.size()) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("toIndex = " + toIndex); if (fromIndex > toIndex) throw new IllegalArgumentException("fromIndex(" + fromIndex + ") > toIndex(" + toIndex + ")"); l = list; offset = fromIndex; size = toIndex - fromIndex; expectedModCount = l.modCount; } |
從代碼中我們可以看出這個一個基本內(nèi)部類的實現(xiàn),subList只是去List中的一段數(shù)據(jù)。但是關(guān)于subList我們要注意幾個事項。
第一:如果我們改變了List的數(shù)值,那么你獲取的subList中的值也隨之改變,原因如下
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
public E get(int index) {rangeCheck(index);checkForComodification();return l.get(index+offset);} |
因為獲取的還是以前List中的數(shù)據(jù)。同樣如果修改subList獲取的數(shù)值,List同樣改變,
第二:如果改變了List結(jié)構(gòu),可能導(dǎo)致subList的不可用,因為這些修改已然基于原來的list,他們共同用一個list數(shù)組。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
public void add(int index, E element) { if (index<0 || index>size) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(); checkForComodification(); l.add(index+offset, element); expectedModCount = l.modCount; size++; modCount++; } |
5:關(guān)于list刪除錯誤分析
list在采用循環(huán)刪除的時候會報ConcurrentModificationException異常,那么我們來看看具體原因,先看一段代碼
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>(); list.add("a"); list.add("b"); list.add("c"); list.add("d"); list.add("e"); for (String str:list){ list.remove(str); } |
由于foreach遍歷最終會for (Iterator it=iterator;iterators.hasNext();)模式那么所以獲取元素的時候必然會用到迭代器中的next方法,next方法我們前面說了會有if(modCount!= expectedModCount)throw new ConcurrentModificationException()驗證。因為調(diào)用remove(T x)方法時候modCount會+1,所以2次比較就會出現(xiàn)不一致。
正確寫法如下
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
Iterator iterator=list.iterator();while (iterator.hasNext()){ iterator.next(); iterator.remove();} |
為啥迭代器中remove就可以呢,是由于在remove代碼中有expectedModCount = modCount這句代碼。
6:ArrayList是線程安全嗎
線程不安全就是指多個線程同時操作造成臟讀,錯讀情況,很明顯ArrayList是非線程安全的,比如說ArrayList現(xiàn)在只有一個值后,如果A,B2個線程同時刪除這個值,A線程判斷得到size=1,而此時時間片段到,CPU調(diào)用B線程執(zhí)行發(fā)現(xiàn)size也是1,開始刪除操作,然后A繼續(xù)進行發(fā)現(xiàn)ArrayList已經(jīng)空了就會報異常。或者添加等等。但是Vector是線程安全的,因為里面所有方法都加入了synchronized,這樣造成的結(jié)果就是所有線程執(zhí)行ArrayList方法都必須等待,直到獲取同步鎖才可以繼續(xù)進行,這樣一來性能大大降低。
以上就是本文的全部內(nèi)容,希望本文的內(nèi)容對大家的學(xué)習(xí)或者工作能帶來一定的幫助,同時也希望多多支持服務(wù)器之家!
原文鏈接:http://www.cnblogs.com/LipeiNet/p/6523350.html















