選擇和冒泡
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
|
#include<stdio.h> void maopao(int a[],int len){ int i,j,temp; for(i = 0;i < len - 1 ; i ++){//從第一個到倒數第二個 for (j = 0 ; j < len - 1 - i ; j ++)//排在后的是已經排序的 { if (a[j] > a[j + 1])//大的數換到后面去 { temp = a[j]; a[j] = a[j + 1]; a [j + 1] = temp; } } } } void xuanze(int a[],int len){ int i , j , t , temp; for (i = 0 ; i < len - 1 ;i ++) { t = i; for (j = i + 1 ; j < len ; j ++)//前面的實排好的 { if (a[t] > a[j]) { t = j;//記下該趟最小數的序號 } } if (t != i)//如果序號不變就什么也不做 { temp = a[t];//否則元素交換 a[t] = a[i]; a[i] = temp; } } } void main(){ int i; int a[] = {5,4,6,7,2,5,4,6,8,9,1,2}; //maopao(a, 12); xuanze(a, 12); for (i = 0 ; i < 12 ; i ++) { printf("%d ",a[i]); } } |
快速排序與冒泡、選擇的比較:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
|
#include <stdio.h> #include <time.h> #include <windows.h> //快速排序,參數是數組,最低索引,最高索引(從0開始) void qSort(int a[], int low, int high){ int temp; int mid = low;//定義一個中索引,用于記錄一次排序后確定位置的一個元素索引 int right = high;//記錄最右元素索引 //默認中值是左值,現在要把凡是比中值大的元素放到中值左邊 while(right > mid){//因此從右開始向中值遍歷,到達中值時遍歷結束 if (a[right] < a[mid])//如果右值比中值還小,說明他不該在右邊,要把它放到左邊 { temp = a[mid];//所以先把中值的地盤騰出來 a[mid] = a[right];//把比中值小的那個數放在那兒 //中值沒地方放,必須右移移位,但是直接右移會覆蓋原來他右邊的那個值 a[right] = a[++mid];//不過right索引的空間已經騰出來了,就把中值原來右邊的值放到right a[mid] = temp;//然后就可以把mid右移一位 } else{ right--;//否則的話說明right已然大于等于mid,不用移動,繼續判斷right左邊那個數 } }//這樣right與mid重合之時,退出循環,此時mid的位置已經確定了就是排完序后他的位置 //因為他左邊的都比他小,右邊的都比他大 if (mid - low > 1)//如果low到mid之間還有兩個或以上元素,還要對他們排序 { qSort(a, low, mid - 1); } if (high - mid > 1)//右邊那半也是一樣 { qSort(a, mid + 1, high); } } void sSort(int a[], int len){//選擇排序,參數是數組名和元素個數 int i, j, m, temp; for (i = 0; i < len - 1; i++)//從開始到倒數第二個元素 { m = i;//先記錄最左邊的元素索引,假設他為最小 for (j = i + 1; j < len; j++)//從左往右遍歷一直到最后 { if (a[j] < a[m])//如果發現更小的元素 { m = j;//記下這個元素的索引 } } if (m != i)//如果最小的元素不是開始那個,就需要把最小的換到最左邊 { temp = a[i]; a[i] = a[m]; a[m] = temp; } } } void mSort(int a[], int len){//冒泡法排序,參數是數組名,元素個數 int i, j, temp; for (i = 0; i < len - 1; i ++)//從開始到倒數第二個元素 { for (j = 0; j < len - 1 - i; j++)//從頭遍歷到已序隊列往前第二個 { if (a[j] > a[j + 1])//如果元素比他的后一個大,則交換 { temp = a[j]; a[j] = a[j + 1]; a[j + 1] = temp; } }//一次遍歷后最大元素放到最后面 } } int checkSorted(int a[], int len){//檢查數組排序是否已經正確 int i; for (i = 0; i < len - 1; i++) { if (a[i] > a[i + 1])//如果一個元素比他的下一個還要大,說明發生錯誤 { return 0; } } return 1; } void main(){ int i, j; int a[99999]; clock_t begin, end; double cost; for (j = 0; j < 6; j++)//做6次測試 { srand((int)time(0));//用時間做種,是每次數字都不同 for (i = 0; i < 99999; i++) { a[i] = rand();//產生隨機數放入數組 } begin = clock(); //qSort(a, 0, 99998);//1秒左右 //sSort(a, 99999);//20秒左右 mSort(a, 99999);//40秒左右 end = clock(); for (i = 0; i < 12; i++)//輸出前面的幾個排好序的元素 { printf("%d ", a[i]); } cost = (double)(end - begin) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC;//計算排序時間 printf("...\t排序用時 %lf 秒 ", cost);//輸出排序所用時間 if (checkSorted(a, 99999))//檢查排序是否正確 { printf("正確!\n"); }else{ printf("有錯!\n"); } Sleep(1200);//暫停一下,使每次時間種子不同 } } |
1. 快速排序的結果:
99999個隨機數一般不超過0.05秒,很快
2.選擇法排序結果:
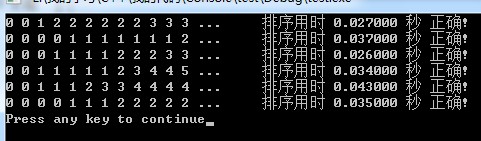
99999個隨機數一般不超過0.05秒,很快
2.選擇法排序結果:
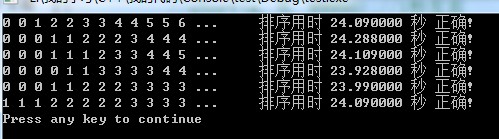
一般在20多秒;
3.冒泡法,一般情況下交換的次數會很多,結果:
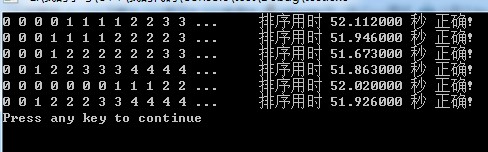
排序時間一般在50秒左右,最慢。
在C++中,還可以定義函數模板
因為快速排序通常很快,所以用它來對不同的數據類型排序
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
|
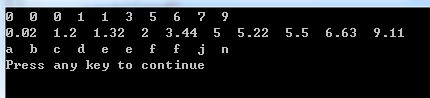
#include <iostream.h> template<class T> void qSort(T a[], int low, int high){//在C++中,可以定義函數模板 T temp; int mid = low; int right = high; while (right > mid) { if (a[right] < a[mid]) { temp = a[mid]; a[mid] = a[right]; a[right] = a[++mid]; a[mid] = temp; }else{ right--; } } if (mid - low > 1) { qSort(a, low, mid - 1); } if (high - mid > 1) { qSort(a, mid + 1, high); } } void main(){ int a[10] = {1, 9, 6, 3, 5, 7, 1};//有了一個函數模板,可以對整型排序 qSort(a, 0, 9); for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { cout<<a[i]<<" "; } cout<<endl; float b[10] = {2.0f, 1.2f, 5.5f, 6.63f, 9.11f, 1.32f, 3.44f, 5.0f, 5.22f, 0.02f}; qSort(b, 0, 9);//對浮點數排序 for (i = 0; i < 10; i++) { cout<<b[i]<<" "; } cout<<endl; char c[10] = {'d','e','f','n','j','c','e','b','f','a'};//對字符數組排序 qSort(c, 0, 9); for (i = 0; i < 10; i++) { cout<<c[i]<<" "; } cout<<endl; }//凡是可以用‘<'來比較大小的類型都可以排序了 |