本文實例講述了java堆排序原理與實現方法。分享給大家供大家參考,具體如下:
堆是一個數組,被看成一個近似完全二叉樹。
舉例說明:
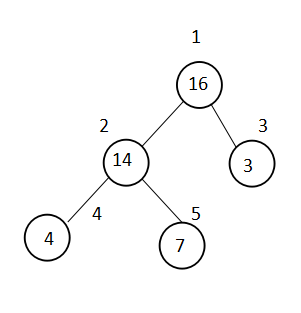
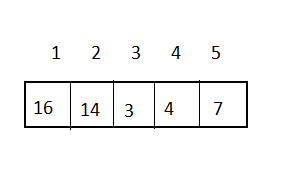
堆的性質:
1.已知元素在數組中的序號為i
其父節點的序號為 i/2的整數
其左孩子節點的序號為2*i
其右孩子節點的序號為2*i+1
2.堆分為最大堆和最小堆
在最大堆中,要保證父節點的值大于等于其孩子節點的值
在最小堆中,要保證父節點的值小于等于其孩子節點的值
java實現堆排序
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
|
public class myheapsort { public void heap_sort(int[] a) { /** * 這個函數完成堆排序 * 先構建一個最大堆 * 將數組中第一個元素和最后一個交換, * 堆的長度減一 * 在從第一個位置開始保證堆的性質調用max_heapify()函數。 * 這樣保證目前最大的元素在數組的最后位置。 * 以此類推,直到最后一個元素。 */ build_max_heap(a); for (int i = a.length - 1; i >= 1; i--) { int temp = a[0]; a[0] = a[i]; a[i] = temp; max_heapify(a, 0, i); } } public void build_max_heap(int[] a) { /** * 這個函數用來構建堆 * a:待排序的數組 * (for循環中i的值從數組長度的一般開始取,是因為完全二叉樹的性質, * 一半的節點葉根節點所以從葉節點開始向上遍歷來保證堆的性質) */ for (int i = a.length/2; i >= 0; i--) { max_heapify(a, i, a.length); } } public void max_heapify(int[] a, int i, int heap_size) { /**這個函數用來維護堆的性質, * 保證以序號為i的元素為根節點的子樹中,父節點的值大于其孩子節點的值。 * a:待排序數組 * i:在數組a中的序號 * heap_size:堆的大小 */ int largest = i; int l = i * 2 + 1; int r = i * 2 + 2; if (l < heap_size && a[l] > a[i]) largest = l; if (r < heap_size && a[r] > a[largest]) largest = r; if (largest != i) { int temp = a[i]; a[i] = a[largest]; a[largest] = temp; max_heapify(a, largest, heap_size); } } public static void main(string[] args) throws exception { system.out.println("服務器之家測試結果:"); int[] a = new int[]{1,3,2,5,34,23,44,15,67,45}; new myheapsort().heap_sort(a); for (int x : a) system.out.println(x); }} |
代碼中例子的運行結果:

希望本文所述對大家java程序設計有所幫助。
原文鏈接:https://blog.csdn.net/u014028027/article/details/78626416















