所謂的仿函數(functor),是通過重載()運算符模擬函數形為的類。
因此,這里需要明確兩點:
1 仿函數不是函數,它是個類;
2 仿函數重載了()運算符,使得它的對你可以像函數那樣子調用(代碼的形式好像是在調用函數)。
for_each
這里的for循環語句有點冗余,想到了std::for_each ,為了使用for_each,我們需要定義一個函數,如下:
|
1
2
3
4
|
void print( state* pstate ){ pstate->print();} |
于是就可以簡化為下面代碼:
std::for_each( vect.begin(), vect.end(), &print );
stl大致分為六大模塊:容器(container),算法(algorithm),迭代器(iterator),仿函數(functor),配接器(adapter),配置器(allocator)。其中仿函數是體積最小,觀念最簡單,但是在stl算法的搭配中起到了非常重要的作用,這是與簡單的lambda或者指針函數所不同的。
在stl中提供了大量有用的仿函數,比如plus,minus,multiplies,divides,modulus,equal_to,not_equal_to,greater…很多很多,根據傳入的參數的個數我們可以分為只需要接受一個參數的仿函數(unary_function)和需要接收兩個參數的仿函數(binary_function)。
仿函數實現示例
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
//仿函數1,比較大小template<typename t> struct comp{ bool operator()(t in1, t in2) const { return (in1>in2); }};comp<int> m_comp_objext;cout << m_comp_objext(6, 3) << endl; //使用對象調用cout << comp<int>()(1, 2) << endl; //使用仿函數實現 |
在上面的代碼中,第一種調用方式是使用comp的定義的一個對象,然后通過這個對象來調用操作符(),來實現兩個數組的比較的;對于第二個調用comp()(1, 2)是產生一個臨時(無名的)對象。
2.2 仿函數詳細說明
在下面的使用場景(統計一個容器中的符合規定的元素),將說明之前提到的函數指針為什么不能在stl中替換掉仿函數
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
bool my_count(int num){ return (num < 5);}int a[] = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9};std::vector<int> v_a(a, a+10);cout << "count: " << std::count_if(v_a.begin(), v_a.end(), my_count); |
在上面我們傳遞進去了一個函數指針作為count_if的比較條件。但是現在根據新的需求,不再統計容器中小于5的變量個數,改為了8或者3。那么最直接的方法就是加一個參數threshold就可以了,就像下面這樣
|
1
2
3
4
|
bool my_count(int num, int threshold){ return (num < threshold));} |
但是這樣的寫法stl中是不能使用的,而且當容器中的元素類型發生變化的時候就不能使用了,更要命的是不能使用模板函數。
那么,既然多傳遞傳遞參數不能使用,那就把需要傳遞進來的那個參數設置為全局的變量,那樣確實能夠實現當前情況下對閾值條件的修改,但是修改起來存在隱患(要是沒有初始化就調用怎么辦)。因而解決這樣問題的方式就是
方式就很好的兼容了stl。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
template<typename t> struct my_count1{ my_count1(t a) { threshold = a; } t threshold; bool operator()(t num) { return (num < threshold); }};int a[] = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9};std::vector<int> v_a(a, a+10);cout << "count: " << std::count_if(v_a.begin(), v_a.end(), my_count1<int>(8)); |
1.仿函數當做排序準則
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
|
#include <iostream>#include <string>#include <set>#include <algorithm>using namespace std;class person{public: person(string a, string b) : strfirstname(a), strlastname(b) {}public: string firstname() const { return strfirstname; } string lastname() const { return strlastname; }private: const string strfirstname; const string strlastname;};//仿函數實現自定義排序class personsortcriterion{public: //仿函數 //排序規則為:按照lastname升序排列,lastname相同時按firstname升序排列 bool operator()(const person &p1, const person &p2) { return (p1.lastname() > p2.lastname() || ((p2.lastname() <= p1.lastname()) && p1.firstname() > p2.firstname())); }};int main(int argc, char *argv[]){ //類型重定義,并指定排序規則 typedef set<person, personsortcriterion> personset; personset col1; //創建元素,并添加到容器 person p1("jay", "chou"); person p2("robin", "chou"); person p3("robin", "lee"); person p4("bob", "smith"); //向容器中插入元素 col1.insert(p1); col1.insert(p2); col1.insert(p3); col1.insert(p4); personset::iterator pos; //輸出personset中的所有元素 for (pos = col1.begin(); pos != col1.end(); ++pos) { cout << pos->firstname() << " " << pos->lastname() << endl; } cout << endl; system("pause"); return 0;} |

有多種狀態的仿函數
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
|
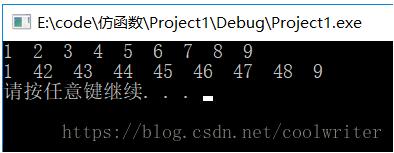
#include <iostream>#include <list>#include<algorithm>using namespace std;class intsequence{private: int value; //記錄內部狀態的成員變量public: intsequence(int initialvalue) : value(initialvalue) { } //仿函數 int operator()() { return value++; }};int main(){ list<int> col1; //產生長度為9的序列,依次插值到col1容器的尾部 generate_n(back_inserter(col1), 9, intsequence(1)); //1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 for (auto t : col1) { cout << t << " "; } cout << endl; //替換col1容器中第2個到倒數第2個,從42開始 generate(++col1.begin(), --col1.end(), intsequence(42)); //1 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 9 for (auto t : col1) { cout << t << " "; } cout << endl; system("pause"); return 0;} |
仿函數都是傳值,而不是傳址的。因此算法并不會改變隨參數而來的仿函數的狀態。
比如:
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
intsequence seq(1); //從1開始的序列//從1開始向容器col1中插入9個元素generate_n(back_inserter(col1), 9, seq);//仍然從1開始向容器col1中插入9個元素generate_n(back_inserter(col1), 9, seq); |
generate函數
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
#include <iostream>#include <algorithm>#include <array>#include <vector>#include <functional>using namespace std;int main(){ array<int,8> t1; //產生序列個100內的隨機數 generate(t1.begin(),t1.end(),[](){return rand()%100;}); //產生5個1000內的隨機數 generate_n(t1.begin(),5,[](){return rand()%1000;}); for_each(t1.begin(),t1.end(),[](int i){cout<<i<<endl;}); return 0;} |
當然,也有方法來解決上述使仿函數內部狀態改變的問題。
方法有兩種:
1、以引用的方式傳遞仿函數;
2、運用for_each()算法的返回值。
因為for_each()算法它返回其仿函數。也就是說,我們可以通過返回值可以取得仿函數的狀態。
以引用的方式傳遞仿函數
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
|
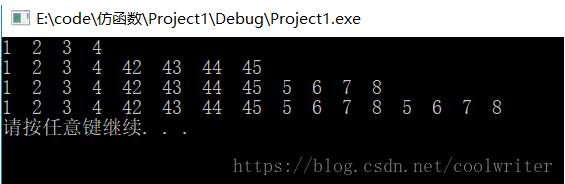
#include <iostream>#include <list>#include <algorithm>using namespace std;class intsequence{private: int value;public: intsequence(int initvalue) : value(initvalue) {} int operator()() { return value++; }};int main(){ list<int> col1; intsequence seq(1); //采用引用類型 generate_n<back_insert_iterator<list<int> >, int, intsequence&>(back_inserter(col1), 4, seq); //1 2 3 4; for (auto t : col1) { cout << t << " "; } cout << endl; //相當于重新構建一個對象從42開始插入4個元素 generate_n(back_inserter(col1), 4, intsequence(42)); //1 2 3 4; 42 43 44 45 for (auto t : col1) { cout << t << " "; } cout << endl; //前面使用的是引用類型,所以seq的內部狀態已經被改變了 //插值從上次完成后的5開始 //注意:這次調用仍然使用的是傳值類型 generate_n(back_inserter(col1), 4, seq); //1 2 3 4; 42 43 44 45; 5 6 7 8 for (auto t : col1) { cout << t << " "; } cout << endl; //上一次調用使用的是傳值類型,所以這次還是從5開始插值 generate_n(back_inserter(col1), 4, seq); //1 2 3 4; 42 43 44 45; 5 6 7 8; 5 6 7 8 for (auto t : col1) { cout << t << " "; } cout << endl; system("pause"); return 0;} |
運用for_each()算法的返回值
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
|
#include <iostream>#include <vector>#include <algorithm>using namespace std;class meanvalue{private: long num; long sum;public: meanvalue() : num(0), sum(0) {} void operator() (int elem) { num++; sum += elem; } double value() { return static_cast<double>(sum) / static_cast<double>(num); }};class meansum{private: //long num; long sum;public: meansum() : sum(0) {} void operator() (int elem) { sum += elem; } double value() { return sum; }};int main(){ vector<int> col1; for (int i = 1; i <= 8; ++i) { col1.push_back(i); } for (auto t : col1) { cout << t << " "; } cout << endl; meanvalue mv = for_each(col1.begin(), col1.end(), meanvalue()); meansum sum = for_each(col1.begin(), col1.end(), meansum()); cout << "mean value: " << mv.value() << endl; cout << "mean sum: " << sum.value() << endl; system("pause"); return 0;} |
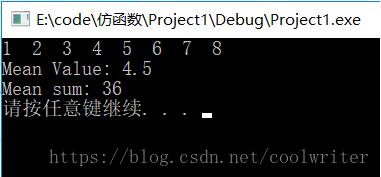
判斷式與仿函數
判斷式就是返回布爾型的函數或者仿函數。對于stl而言,并非所有返回布爾值的函數都是合法的判斷式。這可能會導致很多出人意料的行為,比如下例:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
|
#include <iostream>#include <list>#include <algorithm>using namespace std;class nth{private: int nth; int count;public: nth(int n) : nth(n), count(0) { } bool operator() (int) { return ++count == nth; }};int main(){ list<int> col1; for (int i = 1; i <= 9; ++i) { col1.push_back(i); } //1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 for (auto t : col1) { cout << t << " "; } cout << endl; list<int>::iterator pos; pos = remove_if(col1.begin(), col1.end(), nth(3)); col1.erase(pos, col1.end()); for (auto t : col1) { cout << t << " "; } cout << endl; system("pause");} |
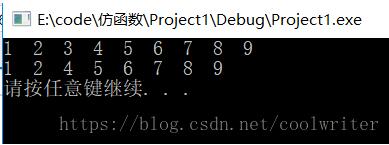
函數配接器(函數 適配器)
函數配接器:能夠將仿函數和另一個仿函數(或某個值,或某個一般函數)結合起來的仿函數。
函數配接器包含在頭文件<functional>中。預定義的函數配接器如下表所示:

先弄清幾個概念,什么叫一元函數,二元函數
1、一元函數一個參數
2、二元函數 兩個參數
3、一元謂詞 一個參數,返回類型為bool型
4、二元謂詞 兩個參數,返回類型為bool型
函數適配器是用來讓一個函數對象表現出另外一種類型的函數對象的特征。因為,許多情況下,我們所持有的函數對象或普通函數的參數個數或是返回值類型并不是我們想要的,這時候就需要函數適配器來為我們的函數進行適配
c++中有三類適配器,分別是容器適配器,迭代器適配器和函數適配器,這里主要介紹函數適配器。
函數適配器用于特化和擴展一元二元函數對象,函數適配器主要有以下兩類:
1 綁定器
該類適配器用于將二元函數適配成一元函數
將二元函數的一個參數綁定到一個特定的值上,將二元函數對象轉換成一元函數對象。
綁定器適配器有兩種:bind1st bind2nd。每個綁定器接受一個函數對象和一個值
bind1st將給定值綁定到二元函數對象的第一個實參
bind2nd將給定值綁定到二元函數對象的第二個實參
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
|
#include <iostream>#include <algorithm>#include <functional>#include <vector>using namespace std;bool is_odd(int n){ return n % 2 == 1;}int main(void){ int a[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 }; vector<int> v(a, a + 5); cout << count_if(v.begin(), v.end(), is_odd) << endl; //計算奇數元素的個數 // 這里的bind2nd將二元函數對象modulus轉換為一元函數對象。 //bind2nd(op, value) (param)相當于op(param, value) cout << count_if(v.begin(), v.end(),bind2nd(modulus<int>(), 2)) << endl; //bind1st(op, value)(param)相當于op(value, param); //把4綁定為第一個參數,即 4 < value //比4大的數字有幾個 cout << count_if(v.begin(), v.end(),bind1st(less<int>(), 4)) << endl; //把3綁定為第二個參數,即 value < 3 //比3小的數字有幾個 cout << count_if(v.begin(), v.end(), bind2nd (less<int>(), 3)) << endl; //把3綁定為第二個參數,即 value < 3 //not1 對第一個對象取反。 //對一元函數對象的結果取反 //比3小的數字有幾個的結果取反 cout << count_if(v.begin(), v.end(),not1( bind2nd (less<int>(), 3)) )<< endl; system("pause"); return 0; //輸出 3 3 1 2 3} |
以上為個人經驗,希望能給大家一個參考,也希望大家多多支持服務器之家。如有錯誤或未考慮完全的地方歡迎留言討論,望不吝賜教。
原文鏈接:https://blog.csdn.net/coolwriter/article/details/81533226